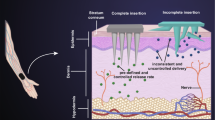
Abstract
Microemulsion has the potentials to enhance dissolution as well as facilitate absorption and permeation of poorly water-soluble drugs through biological membranes. However, its application to govern a controlled release buccal delivery for local treatment has not been discovered. The aim of this study is to develop microemulsion-based mucoadhesive wafers for buccal delivery based on an incorporation of the microemulsion with mucoadhesive agents and mannitol. Ratio of oil to surfactant to water in the microemulsion significantly impacted quality of the wafers. Furthermore, the combination of carbopol and mannitol played a key role in forming the desired buccal wafers. The addition of an extra 50% of water to the formulation was suitable for wafer formation by freeze-drying, which affected the appearance and distribution of carbopol in the wafers. The amount of carbopol was critical for the enhancement of mucoadhesive properties and the sustained drug release patterns. Release study presented a significant improvement of the drug release profile following sustained release for 6 h. Ex vivo mucoadhesive studies provided decisive evidence to the increased retention time of wafers along with the increased carbopol content. The success of this study indicates an encouraging strategy to formulate a controlled drug delivery system by incorporating microemulsions into mucoadhesive wafers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Talegaonkar S, Azeem A, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK, Pathan SA, Khan ZI. Microemulsions: a novel approach to enhanced drug delivery. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008;2(3):238–57.
Tran TT-D, Tran KA, Tran PH. Modulation of particle size and molecular interactions by sonoprecipitation method for enhancing dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drug. Ultrason Sonochem. 2015;24:256–63. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.11.020.
Tran TT-D, Tran PH-L, Nguyen MNU, Tran KTM, Pham MN, Tran PC, et al. Amorphous isradipine nanosuspension by the sonoprecipitation method. Int J Pharm. 2014;474(1–2):146–50. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.08.017.
Van Ngo H, Nguyen PK, Van Vo T, Duan W, Tran V-T, Tran PH-L, et al. Hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer blend for modulation of crystalline changes and molecular interactions in solid dispersion. Int J Pharm. 2016;513(1–2):148–52. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.09.017.
Nguyen TN-G, Tran PH-L, Van Vo T, Duan W, Tran TT-D. Development of a sustained release solid dispersion using swellable polymer by melting method. Pharm Res. 2016;33(1):102–9.
Williams AC, Timmins P, Lu M, Forbes RT. Disorder and dissolution enhancement: deposition of ibuprofen on to insoluble polymers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26(3–4):288–94. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2005.06.006.
Nguyen TN-G, Tran PH-L, Tran TV, Vo TV, Tran TT-D. Development of a modified—solid dispersion in an uncommon approach of melting method facilitating properties of a swellable polymer to enhance drug dissolution. Int J Pharm. 2015;484:228–34. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.02.064.
Saito M, Ugajin T, Nozawa Y, Sadzuka Y, Miyagishima A, Sonobe T. Preparation and dissolution characteristics of griseofulvin solid dispersions with saccharides. Int J Pharm. 2002;249(1–2):71–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00455-6.
Tran TT-D, Tran PH-L, Khanh TN, Van TV, Lee B-J. Solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs using solid dispersions. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2013;7(2):122–33.
Wong JW, Yuen KH. Improved oral bioavailability of artemisinin through inclusion complexation with β- and γ-cyclodextrins. Int J Pharm. 2001;227(1–2):177–85. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00796-7.
Tran TT-D, Tran PH-L, Lee B-J. Dissolution-modulating mechanism of alkalizers and polymers in a nanoemulsifying solid dispersion containing ionizable and poorly water-soluble drug. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72(1):83–90. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.12.009.
Tran TT-D, Tran PH-L, Choi H-G, Han H-K, Lee B-J. The roles of acidifiers in solid dispersions and physical mixtures. Int J Pharm. 2010;384(1-2):60–6. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.09.039.
Tran TT-D, PHL T, Lim J, Park JB, Choi SK, Lee BJ. Physicochemical principles of controlled release solid dispersion containing a poorly water-soluble drug. Ther Deliv. 2010;1(1):51–62. doi:10.4155/tde.10.3.
Tran PHL, Tran HTT, Lee B-J. Modulation of microenvironmental pH and crystallinity of ionizable telmisartan using alkalizers in solid dispersions for controlled release. J Control Release. 2008;129(1):59–65. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.04.001.
Tran PHL, Tran TTD, Lee SA, Nho VH, Chi SC, Lee BJ. Roles of MgO release from polyethylene glycol 6000-based solid dispersions on microenvironmental pH, enhanced dissolution and reduced gastrointestinal damage of telmisartan. Arch Pharm Res. 2011;34(5):747–55. doi:10.1007/s12272-011-0508-2.
Tran PHL, Tran TTD, Park JB, Min DH, Choi HG, Han HK, et al. Investigation of physicochemical factors affecting the stability of a pH-modulated solid dispersion and a tablet during storage. Int J Pharm. 2011;414(1-2):48–55. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.04.065.
Tran TTD, Tran PHL, Park J-B, Lee B-J. Effects of solvents and crystallization conditions on the polymorphic behaviors and dissolution rates of valsartan. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(7):1223–30. doi:10.1007/s12272-012-0713-7.
Tran PH-L, Tran TT-D, Lee B-J. Enhanced solubility and modified release of poorly water-soluble drugs via self-assembled gelatin–oleic acid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2013;455(1–2):235–40. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.07.025.
Tran PH-L, Tran TT-D, Piao ZZ, Van Vo T, Park JB, Lim J, et al. Physical properties and in vivo bioavailability in human volunteers of isradipine using controlled release matrix tablet containing self-emulsifying solid dispersion. Int J Pharm. 2013;450(1–2):79–86. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.04.022.
Feeney OM, Crum MF, McEvoy CL, Trevaskis NL, Williams HD, Pouton CW, et al. 50 years of oral lipid-based formulations: Provenance, progress and future perspectives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;101:167–94. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.007.
Borkar N, Holm R, Yang M, Müllertz A, Mu H. In vivo evaluation of lipid-based formulations for oral delivery of apomorphine and its diester prodrugs. Int J Pharm. 2016;513(1–2):211–7. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.09.024.
Carrière F. Impact of gastrointestinal lipolysis on oral lipid-based formulations and bioavailability of lipophilic drugs. Biochimie. 2016;125:297–305. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2015.11.016.
Patel A, Patel J. Mucoadhesive microemulsion based prolonged release vaginal gel for anti-fungal drug. Am J PharmTech Res. 2012;2(4):649–61.
Patel R, Patel Z, Patel K, Patel M. Micro emulsion based gel: recent expansions for topical drug delivery system. J Med Pharm Allied Sci. 2014;1:1–15.
Jha SK. Microemulsions-potential carrier for improved drug delivery. Asian J Biomed Pharm Sci. 2012;1(1):5–9.
Gundogdu E, Baspinar Y, Koksal C, Ince I, Karasulu E. A microemulsion for the oral drug delivery of pitavastatin. Pharmaceutica Analytica Acta. 2013;4(1):1–5.
Kumria R, Nair AB, Goomber G, Gupta S. Buccal films of prednisolone with enhanced bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(2):471–8.
Zakeri-Milani P, Nezhadi SH, Barzegar-Jalali M, Mohammadi L, Nokhodchi A, Valizadeh H. Studies on dissolution enhancement of prednisolone, a poorly water-soluble drug by solid dispersion technique. Adv Pharm Bull. 2011;1(1):48.
Kumria R, Nair AB, Goomber G, Gupta S. Buccal films of prednisolone with enhanced bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2014;23(1):1-8.
Chauhan CS, Naruka PS, Rathore RS, Badadwal V. Formulation and evaluation of prednisolone tablet for colon targeted drug delivery system. J Chem Pharm Res. 2010;2(4):993–8.
Ghabanchi J, Bahri Najafi R, Haghnegahdar S. Treatment of oral inflammatory diseases with a new mucoadhesive prednisolone tablet versus triamcinolone acetonide paste. IRCMJ. 2009;11(2):155–9.
Iram Shahzadi, Muhammad Irfan Masood, Farzana Chowdhary, Aftab Ahmad Anjum, Muhammad Awais Nawaz, Iram Maqsoo, Muhammad Quaid Zaman. Microemulsion formulation for topical delivery of miconazole nitrate. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2014:24(2):31.
Rasal A, Mahajan H, Shaikh H, Surana S. Development and characterization of nasal mucoadhesive microemulsion of sumatriptan succinate. Indian J Novel Drug Deliv. 2010;2:103–8.
Ho HO, Hsiao CC, Sheu MT. Preparation of microemulsions using polyglycerol fatty acid esters as surfactant for the delivery of protein drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85(2):138–43.
Nirmala m, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N. Enhanced solubilization of aqueous insoluble anti-hypertensive drug. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012;4(5):366–8.
Sabale V, Vora S. Formulation and evaluation of microemulsion-based hydrogel for topical delivery. Int J Pharm Investig. 2012;2(3):140.
Shafiq S, Shakeel F, Talegaonkar S, Ahmad FJ, Khar RK, Ali M. Development and bioavailability assessment of ramipril nanoemulsion formulation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;66(2):227–43.
Yadav S, Khatri J, Bhalerao S. Development and evaluation of an ocular anti-inflammatory microemulsion. Int J Pharm Technol. 2012;4(2):4218–30.
Nguyen MN-U, Vo TV, Tran PH-L, Tran T-D, editors. Development of a zein-based system for colon specific delivery. Sixth International Conference on the Development of Biomedical Engineering in Vietnam; 2016; Vietnam.
Patel VM, Prajapati BG, Patel HV, Patel KM. Mucoadhesive bilayer tablets of propranolol hydrochloride. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2007;8(3):E203–E8.
SYED HK, PEH K. Identification of phases of various oil, surfactant/co-surfactants and water system by ternary phase diagram. Acta Pol Pharm. 2014;71(2):301.
Agrawal OP, Agrawal S. An overview of new drug delivery system: microemulsion. Asian J Pharm Sci Tech. 2012; 2: 1: 5. 2012; 12:5-12.
Wang Z, Mu H-J, Zhang X-M, Ma P-K, Lian S-N, Zhang F-P, et al. Lower irritation microemulsion-based rotigotine gel: formulation optimization and in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:633.
Harris RA, Shumbula PM, van der Walt H. Analysis of the interaction of surfactants oleic acid and oleylamine with iron oxide nanoparticles through molecular mechanics modeling. Langmuir. 2015;31(13):3934–43.
Verma S, Kaul M, Rawat A, Saini S. An overview on buccal drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2011;2(6):1303–132.
Bobade NN, Atram SC, Wankhade VP, Pande DS, Tapar DK, Bobade MNN. A review on buccal drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2013;3:35–40.
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 106-YS.05-2015.02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 617 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, M.N., Van Vo, T., Tran, VT. et al. Microemulsion-Based Mucoadhesive Buccal Wafers: Wafer Formation, In Vitro Release, and Ex Vivo Evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 18, 2727–2736 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-017-0754-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-017-0754-9