Abstract
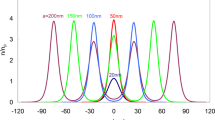
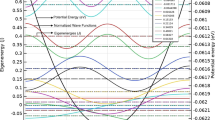
The effect of mass-asymmetry on the ground-state of coupled electron-hole quantum wire system is investigated within the quantum version of the self-consistent mean-field approximation of Singwi, Tosi, Land, and Sjölander. The pair-correlation functions, static density susceptibility, and correlation energy are calculated over a range of wire parameters. We find that the mass-asymmetry affects appreciably both the intra- and inter-wire correlations, which in turn bring in a marked change in the e-h ground-state. Below a critical density, the e-h correlations now favor the liquid-Wigner crystal phase transition at a sufficiently large wire spacing. This result is in striking difference with the corresponding study on the mass-symmetric e-h wire model since here transition to the Wigner crystal phase occurs in the adequately close proximity of two wires at a much lower density, and there also occurs a crossover from Wigner to a charge-density-wave phase at relatively higher densities. We find that for a GaAs based e-h wire the critical density for Wigner crystallization is enhanced by a factor of about 2.6. As an important result, our theory captures nicely the recent experimental observation of Wigner crystallization in an un-equal density GaAs based e-h wire by Steinberg et al. [Phys. Rev. B 73, 113307 (2006)].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei-ming Que, G. Kirczenow, Phys. Rev. B 39, 5998 (1989)
A. Gold, Philos. Mag. Lett. 66, 163 (1992)
R. Wang, P.P. Ruden, Phys. Rev. B 52, 7826 (1995)
S. Das Sarma, E.H. Hwang, Phys. Rev. B 59, 10730 (1999)
R.K. Moudgil, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 1781 (2000)
W. Hansen, M. Horst, J.P. Kotthaus, U. Merkt, Ch. Sikorski, K. Ploog, Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2586 (1987)
T. Demel, D. Heitmann, P. Grambow, K. Ploog, Phys. Rev. B 38, 12732 (1988)
P. Debray, V. Zverev, O Raichev, R. Klesse, P. Vasilopoulos, R.S. Newrock, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 3389 (2001)
P. Debray, V.N. Zverev, V. Gurevich, R. Klesse, R.S. Newrock, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 17, R21 (2002)
H. Steinberg, O.M. Auslaender, A. Yacoby, J. Qian, G.A. Fiete, Y. Tserkovnyak, B.I. Halperin, K.W. Baldwin, L.N. Pfeiffer, K.W. West, Phys. Rev. B 73, 113307 (2006)
Tadaaki Nagao, Shin Yaginuma, Takeshi Inaoka, Toshio Sakurai, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 116802 (2006)
B. Tanatar, C. Bulutay, Phys. Rev. B 59, 15019 (1999)
V. Garg, R.K. Moudgil, K. Kumar, P.K. Ahluwalia, Phys. Rev. B 78, 045406 (2008)
J.S. Thakur, D. Neilson, Phys. Rev. B 56, 4671 (1997)
L.K. Saini, K. Tankeshwar, R.K. Moudgil, Phys. Rev. B 70, 075302 (2004), and the references given therein
N. Mutluay, B. Tanatar, Phys. Rev. B 55, 6697 (1997)
N. Mutluay, B. Tanatar, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 3033 (1997)
N. Mutluay, B. Tanatar, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 9819 (1997)
K.S. Singwi, M.P. Tosi, R.H. Land, A. Sjölander, Phys. Rev. 176, 589 (1968)
T. Hasegawa, M. Shimizu, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 38, 965 (1975)
T.K. Ng, K.S. Singwi, Phys. Rev. B 35, 6683 (1987)
D. Pines, P. Noziers, The Theory of Quantum Liquids (Benjamin, New York, 1966), Vol. 1
See, for example, L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz, Statistical Physics, 3rd edn. (Pergamon Press, 1980), Part 1
L. Swierkowski, D. Neilson, J. Szymanski, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 240 (1991)
R.K. Moudgil, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18, 1285 (2006)
See, for example, G.D. Mahan, Many-Particle Physics, 2nd edn. (Plenum, New York, 1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moudgil, R., Garg, V. & Ahluwalia, P. Mass-asymmetry effects in coupled electron-hole quantum wire system. Eur. Phys. J. B 74, 517–525 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2010-00103-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2010-00103-9