Abstract
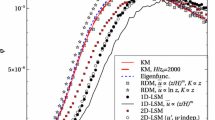
Flux footprint functions estimate the location and relative importance of passive scalar sources influencing flux measurements at a given receptor height. These footprint estimates strongly vary in size, depending on receptor height, atmospheric stability, and surface roughness. Reliable footprint calculations from, e.g., Lagrangian stochastic models or large-eddy simulations are computationally expensive and cannot readily be computed for long-term observational programs. To facilitate more accessible footprint estimates, a scaling procedure is introduced for flux footprint functions over a range of stratifications from convective to stable, and receptor heights ranging from near the surface to the middle of the boundary layer. It is shown that, when applying this scaling procedure, footprint estimates collapse to an ensemble of similar curves. A simple parameterisation for the scaled footprint estimates is presented. This parameterisation accounts for the influence of the roughness length on the footprint and allows for a quick but precise algebraic footprint estimation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Haan, P. and Rotach, M. W.: 1998, ‘A Novel Approach to Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling: The Puff-Particle Model (PPM)’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 124, 2771–2792.
Hanna, S. R., Chang, J. C., and Strimaitis, D. G.: 1993, ‘Hazardous Gas Model Evaluation with Field Observations’, Atmos. Environ. 27A, 2265–2281.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1992, ‘Footprint Estimation for Scalar Flux Measurements in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 59, 279–296.
Horst, T. W. and Weil, J. C.: 1994, ‘How Far is Far Enough?: The Fetch Requirements for Micrometeorological Measurement of Surface Fluxes’, J. Atmos. Ocean. Tech. 11, 1018–1025.
Hsieh, C. I., Katul, G., and Chi, T.: 2000, ‘An Approximate Analytical Model for Footprint Estimation of Scalar Fluxes in Thermally Stratified Atmospheric Flows’, Adv. Water Resour. 23, 765–772.
Kljun, N., Kormann, R., Rotach, M. W., and Meixner, F. X.: 2003, ‘Comparison of the Lagrangian Footprint Model LPDM-B with an Analytical Footprint Model'. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 106, 349–355.
Kljun, N., Rotach, M. W., and Schmid, H. P.: 2002, ‘A 3D Backward Lagrangian Footprint Model for a Wide Range of Boundary Layer Stratifications’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 103, 205–226.
Kormann, R. and Meixner, F. X.: 2001, ‘An Analytical Footprint Model for Non-Neutral Stratification’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 99, 207–224.
Miyake, M.: 1965, Transformation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Inhomogeneous Surfaces, Sci. Rep. 5R-6, University of Washington, Seattle, U.S.A.
Raupach, M. R., Antonia, R. A., and Rajagopalan, S.: 1991, ‘Rough-Wall Turbulent Boundary Layers’, Appl. Mech. Rev. 44, 1–25.
Rotach, M. W.: 2001a, ‘Simulation of Urban-Scale Dispersion Using a Lagrangian Stochastic Dispersion Model’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 99, 379–410.
Rotach, M. W.: 2001b, ‘Urban-Scale Dispersion Modeling Taking into Account the Turbulence and Flow Characteristics of the Roughness Sublayer’, in 3rd International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulics, Tempe, AZ.
Rotach, M. W., Gryning. S.-E., and Tassone, C.: 1996, ‘A Two-Dimensional Lagrangian Stochastic Dispersion Model for Daytime Conditions’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 122, 367–389.
Schmid, H. P.: 1994, ‘Source Areas for Scalars and Scalar Fluxes’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 293–318.
Schmid, H. P.: 2002, ‘Footprint Modeling for Vegetation Atmosphere Exchange Studies: A Review and Perspective’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 113, 159–184.
Stull, R. B.: 1988, An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 666 pp.
Van Ulden, A. P.: 1978, ‘Simple Estimates for Vertical Diffusion from Sources near the Ground’, Atmos. Environ. 12, 2125–2129.
Weil, J. C. and Horst, T. W.: 1992, ‘Footprint Estimates for Atmospheric Flux Measurements in the Convective Boundary Layer’, in S. Schartz and W. Slinn (eds.), Precipitation Scavening and Atmosphere-Surface Exchange, Vol. 2, pp. 717–728.
Wilson, J. D. and Swaters, G. E.: 1991, ‘The Source Area Influencing aMeasurement in the Planetary Boundary Layer: The “Footprint” and the “Distribution of Contact Distance” ’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 55, 25–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kljun, N., Calanca, P., Rotach, M.W. et al. A Simple Parameterisation for Flux Footprint Predictions. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 112, 503–523 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000030653.71031.96
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000030653.71031.96