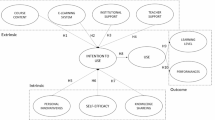
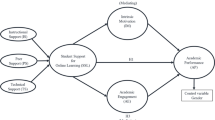
Abstract
Educating our future engineers so that they can gain high proficiency in computational thinking is essential for their career prospects. As educators, acquiring a good understanding of the various learning motivation factors/tools as well as their inter-relationships is a significant step forward in achieving this goal. In this article, we describe an exploratory, data-analytic investigation into the influences of the various learning motivation factors on one another as well as on effecting e-learning of a group of science and engineering students taking computer programming courses. Based on the algorithmic results, we highlight concrete ideas that may have direct impact on improving an existing e-learning system. Further, we describe how the graphical visualization of the algorithmic results can guide us to set priority for focusing on which learning motivation factors first, and which factors next, in achieving a given education goal. These are among some of the new insights not easily obtainable from confirmatory-based analyses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrachan, O.L. (2004). Non-competitive programming contest problems as the basis for just-in-time teaching. In Proceedings of 34th ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (pp. T3H-20–24).
Bandura, A. (1991). Self-regulation of motivation through anticipatory and self-regulatory mechanisms. In R. A. Dienstbier (Ed.), Perspectives on motivation: Nebraska symposium on motivation (Vol. 38, pp. 69–164). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Bandura, A. (1993). Perceived self-efficacy in cognitive development and functioning. Educational Psychologist, 28(2), 117–148.
Bhuasiri, W., Xaymoungkhoun, O., Zo, H., Rho, J. J., & Ciganek, A. P. (2012). Critical success factors for e-learning in developing countries: A comparative analysis between ICT experts and faculty. Computers & Education, 58, 843–855.
Black, A. E., & Deci, E. L. (2000). The effects of instructors’ autonomy support and students’ autonomous motivation on learning organic chemistry: A self-determination theory perspective. Science Education, 84(6), 740–756.
Bong, M. (2004). Academic motivation in self-efficacy, task value, achievement goal orientations, and attributional beliefs. The Journal of Educational Research, 97(6), 287–298.
Bonk, C.J. (2002). Online training in an online world. Education at a Distance, 16(3), Article 2.
Bühlmann, P., Kalisch, M., & Maathuis, M. H. (2010). Variable selection in high-dimensional linear models: Partially faithful distributions and the PC-simple algorithm. Biometrika, 97, 261–278.
Cameron, J., Banko, K. M., & Pierce, W. D. (2001). Pervasive negative effects of rewards on intrinsic motivation: The myth continues. The Behavior Analyst, 24(1), 1–44.
Cameron, J., Pierce, W. D., Banko, K. M., & Gear, A. (2005). Achievement-based rewards and intrinsic motivation: A test of cognitive mediators. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97(4), 641–655.
Cavaluzzo, L. (1996). Enhancing team performance. The Healthcare Forum Journal, 39(5), 57–59.
Chan, C. C. A., Pearson, C., & Entrekin, L. (2003). Examining the effects of internal and external team learning on team performance. Team Performance Management: An International Journal, 9, 174–181.
Chong, S.L., & Choy, M. (2004). Towards a progressive learning environment for programming courses. In New horizon in web-based learning: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference web-based learning (pp. 200–205).
Choy, M., Lam, S., Poon, C. K., Wang, F. L., Yu, Y. T., Yuen, L. (2008). Design and implementation of an automated system for assessment of computer programming assignments. In H. Leung, Q. Li, F. Li & R. Lau (Eds.), Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Web Based Learning (ICWL′07) (pp. 584–596). Berlin: Springer.
Churchill, G. A. (1979). A paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 16, 64–73.
deCharms, R. (1968). Personal causation. New York: Academic Press.
Deci, E. L. (1980). The psychology of self-determination. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., & Ryan, R. M. (1999). A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 125, 627–668.
Durham, C. C., Knight, D., & Locke, E. A. (1997). Effects of leader role, team-set goal difficulty, efficacy, and tactics on team effectiveness. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Process, 72(2), 203–231.
Edwards, S. H., & Pérez-Quiñones, M. A. (2007). Experiences using test-driven development with an automated grader. Journal of Computing Sciences in Colleges, 22(3), 44–50.
Fagan, M. H., Neill, S., & Wooldridge, B. R. (2008). Exploring the intention to use computers: An empirical investigation of the role of intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, and perceived ease of use. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 48(3), 31–37.
Harackiewicz, J. M., Barron, K. E., Carter, S. M., Lehto, A. T., & Elliott, A. J. (1997). Predictors and consequences of achievement goals in the college classroom: Maintaining interest and making the grade. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73(6), 1284–1295.
Harackiewicz, J. M., Barron, K. E., & Elliott, A. J. (1998). Rethinking achievement goals: When are they adaptive for college students and why? Educational Psychologist, 33(1), 1–21.
Hendry, G. D., Lyon, P. M., Prosser, M., & Sze, D. (2006). Conceptions of problem-based learning: The perspectives of students entering a problem-based medical program. Medical Teacher, 28(6), 573–575.
Hodges, C. B. (2004). Designing to motivate: Motivational techniques to incorporate in e-learning experiences. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 2(3), 1–7.
Johns, G. (1996). Organizational behaviour: Understanding and managing life at work (4th ed.). New York: HarperCollins.
Katzenbach, J. R., & Smith, D. K. (1993). The discipline of teams. Harvard Business Review, 71(2), 111–120.
Kelleher, C., & Pausch, R. (2007). Using storytelling to motivate programming. Communications of the ACM, 50(7), 58–64.
Kotnour, T. (2000). Organizational learning practices in the project management environment. The International Journal of Quality and Reliability Management, 17, 393–406.
Kusurkar, R. A., Croiset, G., Kruitwagen, C., & Cate, O. (2011). Validity evidence for the measurement of the strength of motivation for medical school. Advances in Health Science Education, 16, 183–195.
Lam, M. S., Chan, E. Y., Lee, V. C., Yu, Y. T. (2008). Designing an automatic debugging assistant for improving the learning of computer programming. In F. Joseph., K. Reggie & W. Fu Lee (Eds.), Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Hybrid Learning and Education (ICHL′08) (pp. 359–370). Berlin: Springer.
Lau, W. W. F., & Yuen, A. H. K. (2009). Exploring the effects of gender and learning styles on computer programming performance: Implications for programming pedagogy. British Journal of Educational Technology, 40(4), 696–712.
Law, K. M. Y., Lee, V. C. S., & Yu, Y. T. (2010). Learning motivation in e-learning facilitated computer programming courses. Computers & Education, 55, 218–228.
Law, K. M. Y., Sandnes, F. E., Jian, H., & Huang, Y. (2009). A comparative study of learning motivation among engineering students in South East Asia and beyond. International Journal of Engineering Education, 25(1), 144–151.
Lee, M. K. O., Cheung, C. M. K., & Chen, Z. (2005). Acceptance of internet-based learning medium: The role of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. Information & Management, 42(8), 1095–1104.
Lee, Y., & Ertmer, P. A. (2006). Examining the effect of small group discussions and question prompts on vicarious learning outcomes. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 39(1), 66–80.
Levesque, C. S., Zuehlke, N., Stanek, L., & Ryan, R. M. (2004). Autonomy and competence in German and U.S. university students: A comparative study based on self-determination theory. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96, 68–84.
Liaw, S. S. (2008). Investigating students’ perceived satisfaction, behavioral intention, and effectiveness of e-learning: A case study of the Blackboard system. Computers & Education, 51(2), 864–873.
Linnenbrink, E. A., & Pintrich, P. R. (2002). Motivation as an enabler for academic success. School Psychology Review, 31(3), 313–327.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal setting and task performance. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Lynch, D. J. (2010). Motivational beliefs and learning strategies as predictors of academic performance in college physics. College Student Journal, 44(4), 920–927.
Lynch, D. J., & Trujillo, H. (2011). Motivational beliefs and learning strategies in organic chemistry. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 9, 1351–1365.
Margolis, H., & McCabe, P. P. (2004). Self-efficacy, a key to improving the motivation of struggling learners. The Clearing House, 77(6), 241–249.
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50(4), 370–396.
Meyer, M. A. (1994). The dynamics of learning with team production implications for task assignment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 109(4), 1157–1184.
Ngan, S. C., & Tsang, A. S. L. (2012). Elucidating the conceptual structure of a business domain via exploratory network analysis of business survey data. Expert Systems with Applications, 39, 6359–6369.
Pierce, W. D., Cameron, J., Banko, K. M., & So, S. (2003). Positive effects of rewards and performance standards on intrinsic motivation. The Psychological Record, 53, 561–579.
Pintrich, P. R., & DeGroot, E. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 33–40.
Pintrich, P. R., & Garcia, T. (1991). Student goal orientation and self-regulation in the college classroom. In M. M. P. R. Pintrich (Ed.), Advances in motivation and achievement: Goals and self-regulatory processes (Vol. 7). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Poell, R. F., & Van der Krogt, F. J. (2003). Project-based learning in organizations: Towards a methodology for learning in groups. Journal of Workplace Learning, 15(5), 217–228.
Prussia, G. E., & Kinicki, A. J. (1996). A motivational investigation of group effectiveness using social-cognitive theory. Journal of Applied Psychology, 81(2), 187–198.
Ramsden, P. (2003). Learning to teach in higher education (2nd ed.). London: RoutledgeFalmer.
Rassuli, A., & Manzer, J. P. (2005). Teach to learn: Multivariate analysis of perception of success in team learning. Journal of Education for Business, 81(1), 21–27.
Roberts, E. (1997). Team training: When is enough…enough? The Journal for Quality and Participation, 39(5), 16–20.
Ryan, R. M., & Connell, J. P. (1989). Perceived locus of causality and internalization. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57, 749–761.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: Classic definitions and new directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25, 54–67.
Senge, P. (1990). The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization. New York: Doubleday.
Shmueli, G., & Koppius, O. R. (2011). Predictive analytics in information systems research. MIS Quarterly, 35(3), 553–572.
Stipek, D. J. (1996). Motivation and instruction. In D. C. B. R. C. Calfee (Ed.), Handbook of educational psychology. New York: Macmillan.
Teo, T. S. H., Lim, V. K. G., & Lai, R. Y. C. (1999). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in internet usage. Omega The International Journal Management Science, 27(1), 25–37.
Vroom, V. (1964). Work and motivation. New York: Wiley.
Wellins, R. S., Byham, W. C., & Wilson, J. M. (1991). Empowered teams: Creating self-directed work groups that improve quality, productivity, and participation. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Wofford, J. C., Goodwin, V. L., & Premack, S. (1992). Meta-analysis of the antecedents of personal goal level. Journal of Management, 18(3), 595–615.
Wong, T. C., Law, K. M. Y., Yau, H. K., & Ngan, S. C. (2011). Analyzing supply chain operation models with the PC-algorithm and the neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 7526–7534.
Wong, T. C., Ngan, S. C., Chan, F. T. S., & Chong, A. Y. L. (2012). A two-stage analysis of the influences of employee alignment on effecting business-IT alignment. Decision Support Systems, 53, 490–498.
Wood, R., & Bandura, A. (1989). Impact of conceptions of ability on self-regulatory mechanisms and complex decision making. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56, 407–415.
Yoo, S. J., Han, S. H., & Huang, W. (2012). The roles of intrinsic motivators and extrinsic motivators in promoting e-learning in the workplace: A case from South Korea. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(3), 942–950.
Yu, Y.T., Poon, C.K., & Choy, M. (2006). Experiences with PASS: Developing and using a Programming Assignment assessment System. In Proceedings of QSIC 2006: The 6th international conference on quality software (pp. 360–365).
Zimmerman, B. J., Bandura, A., & Martinez-Pons, M. (1992). Self-motivation for academic attainment: The role of self-efficacy beliefs and personal goal setting. American Educational Research Journal, 29, 663–676.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Kitsantas, A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs. Contemporary Education Psychology, 30, 397–417.
Acknowledgments
The authors very much appreciate the constructive comments and suggestions raised by the anonymous reviewers, the Associate Editor, and the Editor, which helped in improving the content and the presentation of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngan, SC., Law, K.M.Y. Exploratory Network Analysis of Learning Motivation Factors in e-Learning Facilitated Computer Programming Courses. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 24, 705–717 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-014-0223-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-014-0223-0