Abstract
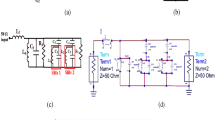
A passive deep brain stimulation (DBS) device can be equipped with a rectenna, consisting of an antenna and a rectifier, to harvest energy from electromagnetic fields for its operation. This paper presents optimization of radio frequency rectifier circuits for wireless energy harvesting in a passive head-mountable DBS device. The aim is to achieve a compact size, high conversion efficiency, and high output voltage rectifier. Four different rectifiers based on the Delon doubler, Greinacher voltage tripler, Delon voltage quadrupler, and 2-stage charge pumped architectures are designed, simulated, fabricated, and evaluated. The design and simulation are conducted using Agilent Genesys at operating frequency of 915 MHz. A dielectric substrate of FR-4 with thickness of 1.6 mm, and surface mount devices (SMD) components are used to fabricate the designed rectifiers. The performance of the fabricated rectifiers is evaluated using a 915 MHz radio frequency (RF) energy source. The maximum measured conversion efficiency of the Delon doubler, Greinacher tripler, Delon quadrupler, and 2-stage charge pumped rectifiers are 78, 75, 73, and 76 % at −5 dBm input power and for load resistances of 5–15 kΩ. The conversion efficiency of the rectifiers decreases significantly with the increase in the input power level. The Delon doubler rectifier provides the highest efficiency at both −5 and 5 dBm input power levels, whereas the Delon quadrupler rectifier gives the lowest efficiency for the same inputs. By considering both efficiency and DC output voltage, the charge pump rectifier outperforms the other three rectifiers. Accordingly, the optimised 2-stage charge pumped rectifier is used together with an antenna to harvest energy in our DBS device.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RJ, Frye MA, Abulseoud OA, Lee KH, McGillivray JA, Berk M, Tye SJ (2012) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: efficacy, safety and mechanisms of action. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1920–1933
Kouzani AZ, Abulseoud OA, Tye SJ, Hosain MK, Berk M (2013) A low power micro deep brain stimulation device for murine preclinical research. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 1:1–9
Hosain MK, Kouzani A, Tye S (2012) Multi-layer implantable antenna for closed loop deep brain stimulation system, in International symposium on communications and information technologies (ISCIT), Gold Coast, pp 643–648
Hosain MK, Kouzani AZ (2013) Assessment of functional and biological compatibility of antenna in a head-mountable DBS device using a rat model. Neurosci Biomed Eng 1:73–82
Hosain MK, Kouzani AZ (2013) Electromagnetic energy harvesting in a head-mountable DBS device using a circular PIFA, in ICME International conference on complex medical engineering (CME), Beijing, pp 541–546
Marian V, Allard B, Vollaire C, Verdier J (2012) Strategy for microwave energy harvesting from ambient field or a feeding source. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27:4481–4491
Hosain M, Kouzani AZ, Tye S, Walder K, Kong L (2012) Design of a miniature UHF PIFA for DBS implants, in ICME international conference on complex medical engineering (CME), Japan, pp 485–489
Jiang F, Guo D, Cheng L (2008) Analysis and design of power generator on passive RFID transponders, in Progress in electromagnetics research symposium, Hangzhou, pp 1357–1362
Umeda T, Yoshida H, Sekine S, Fujita Y, Suzuki T, Otaka S (2006) A 950-MHz rectifier circuit for sensor network tags with 10-m distance. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 41:35–41
Le T, Mayaram K, Fiez T (2008) Efficient far-field radio frequency energy harvesting for passively powered sensor networks. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 43:1287–1302
Yuan F (2010) CMOS circuits for passive wireless microsystems. Springer, New York
Kotani K, Ito T (2007) High efficiency CMOS rectifier circuit with self-Vth-cancellation and power regulation functions for UHF RFIDs, in IEEE Asian solid-state circuits conference, ASSCC ‘07, Jeju, pp 119–122
Shameli A, Safarian A, Rofougaran A, Rofougaran M, De Flaviis F (2007) Power harvester design for passive UHF RFID tag using a voltage boosting technique. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 55:1089–1097
Jabbar H, Song YS, Jeong TT (2010) RF energy harvesting system and circuits for charging of mobile devices. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 56:247–253
Zbitou J, Latrach M, Toutain S (2006) Hybrid rectenna and monolithic integrated zero-bias microwave rectifier. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 54:147–152
Nimo A, Grgić D, Reindl LM (2012) Impedance optimization of wireless electromagnetic energy harvesters for maximum output efficiency at µw input power, in Proceedings of SPIE, pp 83410W1–14
Rahimi A, Zorlu O, Muhtaroglu A, Kulah H (2012) Fully self-powered electromagnetic energy harvesting system with highly efficient dual rail output. IEEE Sens J 12:2287–2298
Monti G, Congedo F, De Donno D, Tarricone L (2012) Monopole-based rectenna for microwave energy harvesting of UHF RFID systems. Prog Electromagn Res C 31:109–121
Huang F-J, Lee C-M, Chang C-L, Chen L-K, Yo T-C, Luo C-H (2011) Rectenna application of miniaturized implantable antenna design for triple-band biotelemetry communication. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 59:2646–2653
Akkermans J, van Beurden M, Doodeman G, Visser H (2005) Analytical models for low-power rectenna design. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 4:187–190
Merabet B, Cirio L, Takhedmit H, Costa F, Vollaire C, Allard B, Picon O (2009) Low-cost converter for harvesting of microwave electromagnetic energy, in IEEE Energy conversion congress and exposition, ECCE, San Jose, pp 2592–2599
Jongshin S, In-Young C, Young-June P, Min HS (2000) A new charge pump without degradation in threshold voltage due to body effect [memory applications]. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 35:1227–1230
Zhou Y, Froppier B, Razban T (2011) Study of a matching circuit effect on a microwave rectifier, in 11th Mediterranean microwave symposium (MMS), Hammamet, pp 29–33
Wetenkamp S (1983) Comparison of single diode vs. dual diode detectors for microwave power detection, in IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest, Boston, pp 361–363
Cardoso AJ, de Carli LG, Galup-Montoro C, Schneider MC (2012) Analysis of the rectifier circuit valid down to its low-voltage limit. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 59:106–112
Ungan T, Le Polozec X, Walker W, Reindl L (2009) RF energy harvesting design using high Q resonators, in IEEE MTT-S international microwave workshop on wireless sensing, local positioning, and RFID, IMWS, Cavtat, pp 1–4
Bowick C, Ajluni C, Blyler J (2011) RF circuit design. Newnes, Burlington
Zhan A, Dang GT, Ren F, Cho H, Lee K-P, Pearton SJ, Chyi J-I, Nee T-Y, Chuo C-C (2001) Comparison of GaN pin and Schottky rectifier performance. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 48:407–411
Maas SA (2003) Nonlinear microwave and RF circuits. Artech House on Demand, Norwood
Hosain MK, Kouzani AZ (2013) Design and analysis of efficient rectifiers for wireless power harvesting in DBS devices, in 8th IEEE conference on industrial electronics and applications (ICIEA), Melbourne, pp 651–655
Selvakumaran R, Liu W, Boon-Hee S, Luo M, Sum YL (2009) Design of low power rectenna for wireless power transfer, in TENCON 2009–2009 IEEE Region 10 Conference, pp 1–5
Karthaus U, Fischer M (2003) Fully integrated passive UHF RFID transponder IC with 16.7-μW minimum RF input power. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 38:1602–1608
Dobkin DM (2012) The RF in RFID: passive UHF RFID in practice, Kindle edition edn. Newnes, Amsterdam
Olgun U, Chi-Chih C, Volakis JL (2010) Wireless power harvesting with planar rectennas for 2.45 GHz RFIDs, in URSI international symposium on electromagnetic theory (EMTS), Berlin 2010, pp 329–331
Nimo A, Grgić D, Reindl LM (2012) Optimization of passive low power wireless electromagnetic energy harvesters. Sensors 12:13636–13663
Pinuela M, Mitcheson PD, Lucyszyn S (2013) Ambient RF energy harvesting in urban and semi-urban environments. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 61:2715–2726
Taris T, Vigneras V, Fadel L (2012) A 900 MHz RF energy harvesting module, in 2012 IEEE 10th international new circuits and systems conference (NEWCAS), Montreal, pp 445–448
Hosain MK, Kouzani AZ, Tye SJ, Abulseoud OA, Amiet A, Galehdar A, Kaynak A, Berk M (2014) Development of a compact rectenna for wireless powering of a head-mountable deep brain stimulation device. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 2:1–13
Kouzani A, Tye S, Walder K, Kong L (2012) A head mountable deep brain stimulation device for laboratory Animals. In: Wu Y (ed) Advances in computer, communication, control & automation, vol 121. Springer, Berlin, pp 275–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosain, M.K., Kouzani, A.Z., Tye, S. et al. RF rectifiers for EM power harvesting in a Deep Brain Stimulating device. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 38, 157–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-015-0328-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-015-0328-7