Abstract
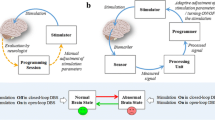
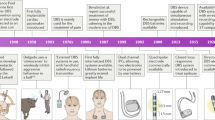
Deep brain stimulation is an effective and safe medical treatment for a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders including Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and treatment resistant obsessive compulsive disorder. A closed loop deep brain stimulation (CLDBS) system automatically adjusts stimulation parameters by the brain response in real time. The CLDBS continues to evolve due to the advancement in the brain stimulation technologies. This paper provides a study on the existing systems developed for CLDBS. It highlights the issues associated with CLDBS systems including feedback signal recording and processing, stimulation parameters setting, control algorithm, wireless telemetry, size, and power consumption. The benefits and limitations of the existing CLDBS systems are also presented. Whilst robust clinical proof of the benefits of the technology remains to be achieved, it has the potential to offer several advantages over open loop DBS. The CLDBS can improve efficiency and efficacy of therapy, eliminate lengthy start-up period for programming and adjustment, provide a personalized treatment, and make parameters setting automatic and adaptive.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flora ED, Perera CL, Cameron AL, Maddern GJ (2010) Deep brain stimulation for essential tremor: a systematic review. Mov Disord 25:1550–1559
Liker MA, Won DS, Rao VY, Hua SE (2008) Deep brain stimulation: an evolving technology. Proc IEEE 96:1129–1141
Hamani C, Nobrega JN, Lozano AM (2010) Deep brain stimulation in clinical practice and in animal models. Clin Pharmacol Ther 88:559–562
Covalin A, Feshali A, Judy J (2005) Deep brain stimulation for obesity control: analyzing stimulation parameters to modulate energy expenditure. In: Conference proceedings. 2nd international IEEE EMBS conference on neural engineering, 2005, pp 482–485
Schiff ND, Giacino J, Kalmar K, Victor J, Baker K, Gerber M, Fritz B, Eisenberg B, O’Connor J, Kobylarz E (2007) Behavioural improvements with thalamic stimulation after severe traumatic brain injury. Nature 448:600–603
Sillay KA, Sani S, Starr PA (2010) Deep brain stimulation for medically intractable cluster headache. Neurobiol Dis 38:361–368
Lu L, Wang X, Kosten TR (2009) Stereotactic neurosurgical treatment of drug addiction. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 35:391–393
Castrioto A, Moro E (2013) New targets for deep brain stimulation treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 13:1319–1328
Stanslaski S, Cong P, Carlson D, Santa W, Jensen R, Molnar G, Marks WJ, Shafquat A, Denison T (2009) An implantable bi-directional brain-machine interface system for chronic neuroprosthesis research. In: Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine biology society, 2009, pp 5494–5497
Carron R, Chaillet A, Filipchuk A, Pasillas-Lépine W, Hammond C (2013) Closing the loop of deep brain stimulation. Front Syst Neurosci 7: 112
Leondopulos SS, Micheli-Tzanakou E. (2010) Advances toward closed-loop deep brain stimulation. In: Computational neuroscience, Springer, New York, pp 227–253
Hirata M, Matsushita K, Suzuki T, Yoshida T, Sato F, Morris S, Yanagisawa T, Goto T, Kawato M, Yoshimine T (2011) A fully-implantable wireless system for human brain-machine interfaces using brain surface electrodes: W-HERBS. IEICE Trans Commun E94b:2448–2453
Pham J, Cabrera SM, Sanchis-Segura C, Wood MA (2009) Automated scoring of fear-related behavior using EthoVision software. J Neurosci Methods 178:323–326
Patel S, Hester T, Hughes R, Huggins N, Standaert D, Flaherty A, Bonato P (2006) Using wearable sensors to enhance DBS parameter adjustment for Parkinson’s disease patients through measures of motor response. In: 3rd IEEE/EMBS international summer school on medical devices biosensors, 2006, pp 141–144
Montgomery EB (2010) Deep brain stimulation programming: principles and practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Feng X-J, Shea-Brown E, Greenwald B, Kosut R, Rabitz H (2007) Optimal deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus—a computational study. J Comput Neurosci 23:265–282
Priori A, Foffani G, Rossi L, Marceglia S (2012) Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) controlled by local field potential oscillations. Exp Neurol 245:77–86
Santaniello S, Fiengo G, Glielmo L, Grill WM (2011) Closed-loop control of deep brain stimulation: a simulation study. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 19:15–24
Rosin B, Slovik M, Mitelman R, Rivlin-Etzion M, Haber SN, Israel Z, Vaadia E, Bergman H (2011) Closed-loop deep brain stimulation is superior in ameliorating parkinsonism. Neuron 72:370–384
Santos FJ, Costa RM, Tecuapetla F (2011) Stimulation on demand: closing the loop on deep brain stimulation. Neuron 72:197–198
Bazavan R, Strungaru R (2010) Option to provide the necessary feedback for closed-loop neurostimulation. In: 10th international conference development application systems, Suceava
Băzăvan R (2005) The brain closed-loop stimulation method with the biopotential mediation of the subthalamic nucleus for the parkinson’s disease therapy. U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series C, 75: 157–168
Little S, Pogosyan A, Neal S, Zavala B, Zrinzo L, Hariz M, Foltynie T, Limousin P, Ashkan K, FitzGerald J (2013) Adaptive deep brain stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 74:449–457
Lee J, Rhew H-G, Kipke DR, Flynn MP (2010) A 64 channel programmable closed-loop neurostimulator with 8 channel neural amplifier and logarithmic ADC. Solid-State Circuits IEEE J 45:1935–1945
Osorio I, Frei MG, Sunderam S, Giftakis J, Bhavaraju NC, Schaffner SF, Wilkinson SB (2005) Automated seizure abatement in humans using electrical stimulation. Ann Neurol 57:258–268
Kossoff EH, Ritzl EK, Politsky JM, Murro AM, Smith JR, Duckrow RB, Spencer DD, Bergey GK (2004) Effect of an external responsive neurostimulator on seizures and electrographic discharges during subdural electrode monitoring. Epilepsia 45:1560–1567
Good LB, Sabesan S, Marsh ST, Tsakalis K, Treiman D, Iasemidis L (2009) Control of synchronization of brain dynamics leads to control of epileptic seizures in rodents. Int J Neural Syst 19:173–196
Graupe D, Basu I, Tuninetti D, Vannemreddy P, Slavin KV (2010) Adaptively controlling deep brain stimulation in essential tremor patient via surface electromyography. Neurol Res 32:899–904
Makous J, Schleicher B, Carbunaru R, Jaax K, DiGiore A (2010) Methods and apparatus for using sensors with a deep brain stimulation system. Google Patents, 2010
Lee J, Rhew H-G, Kipke DR, Flynn MP (2010) A 64 channel programmable closed-loop neurostimulator with 8 channel neural amplifier and logarithmic ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 45:1935–1945
Avestruz AT, Santa W, Carlson D, Jensen R, Stanslaski S, Helfenstine A, Denison T (2008) A 5 uW/channel spectral analysis IC for chronic bidirectional brain-machine interfaces. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 43:3006–3024
Giannicola G, Rosa M, Servello D, Menghetti C, Carrabba G, Pacchetti C, Zangaglia R, Cogiamanian F, Scelzo E, Marceglia S (2012) Subthalamic local field potentials after seven-year deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 237:312–317
Kent AR, Grill WM (2011) Instrumentation to record evoked potentials for closed-loop control of deep brain stimulation. In: Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine biology society, EMBC, 2011, pp 6777–6780
Little S, Brown P (2012) What brain signals are suitable for feedback control of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1265:9–24
McCreery D, Lossinsky A, Pikov V, Xindong L (2006) Microelectrode array for chronic deep-brain microstimulation and recording. IEEE Trans Bio-med Eng 53:726–737
Mohseni P, Najafi K, Eliades SJ, Xiaoqin W (2014) Wireless multichannel biopotential recording using an integrated FM telemetry circuit. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 8:1–11
Rossi L, Foffani G, Marceglia S, Bracchi F, Barbieri S, Priori A (2007) An electronic device for artefact suppression in human local field potential recordings during deep brain stimulation. J Neural Eng 4:96–106
Kent A, Grill W (2011) Instrumentation to record evoked potentials for closed-loop control of deep brain stimulation. In: 33rd annual international conference on IEEE EMBS, Boston, pp 6777–6780
Yoon-Kyu S, Patterson WR, Bull CW, Borton DA, Yanqiu L, Nurmikko AV, Simeral JD (2007) A brain implantable microsystem with Hybrid RF/IR telemetry for advanced neuroengineering applications. In: Engineering in medicine and biology Society, 2007. EMBS 2007. 29th annual international conference of the IEEE, pp 445–448
Harrison RR, Watkins PT, Kier RJ, Lovejoy RO, Black DJ, Greger B, Solzbacher F (2007) A low-power integrated circuit for a wireless 100-electrode neural recording system. IEEE J solid-state Circuits 42:123–133
Moo Sung C, Zhi Y, Yuce MR, Linh H, Liu W (2009) A 128-channel 6 mW wireless neural recording IC with spike feature extraction and UWB transmitter. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 17:312–321
Kimble CJ, Johnson DM, Winter BA, Whitlock SV, Kressin KR, Horne AE, Robinson JC, Bledsoe JM, Tye SJ, Chang S-Y (2009) Wireless instantaneous neurotransmitter concentration sensing system (WINCS) for intraoperative neurochemical monitoring. In: Engineering in medicine and biology society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Annual international conference of the IEEE, pp 4856–4859
Shon Y-M, Chang S-Y, Tye SJ, Kimble CJ, Bennet KE, Blaha CD, Lee KH (2010) Comonitoring of adenosine and dopamine using the wireless instantaneous neurotransmitter concentration system: proof of principle. J Neurosurg 112:539
Griessenauer CJ, Chang S-Y, Tye SJ, Kimble CJ, Bennet KE, Garris PA, Lee KH (2010) wireless instantaneous neurotransmitter concentration system: electrochemical monitoring of serotonin using fast-scan cyclic voltammetry-a proof-of-principle study: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg 113:656–665
Agnesi F, Tye SJ, Bledsoe JM, Griessenauer CJ, Kimble CJ, Sieck GC, Bennet KE, Garris PA, Blaha CD, Lee KH (2009) Wireless instantaneous neurotransmitter concentration system–based amperometric detection of dopamine, adenosine, and glutamate for intraoperative neurochemical monitoring. J Neurosurg 111:701
Amaru F, Arena P, Latteri A, Lombardo D, Mazzone P, Vagliasindi G (2009)Towards a wearable device for deep brain signals monitoring. In: Human system interactions, 2009. HSI ‘09. 2nd conference on, Catania, pp 128–131
Niazmand K, Tonn K, Kalaras A, Fietzek UM, Mehrkens JH, Lueth TC (2011) Quantitative evaluation of Parkinson’s disease using sensor based smart glove. In: 24th international symposium on computer-based medical systems (CBMS), Bristol
Patel S, Mancinelli C, Hughes R, Dalton A, Shih L, Bonato P (2009) Optimizing deep brain stimulation settings using wearable sensing technology. In: 4th international IEEE/EMBS conference on neural engineering, 2009. NER ‘09, pp 6–9
Grimaldi G, Manto M (2010) Neurological tremor: sensors, signal processing and emerging applications. Sensors 10:1399–1422
Warwick K (1996) Introduction to control systems, vol 8. World Scientific, Singapore
Rhew H-G, Jeong J, Fredenburg JA, Dodani S, Patil P, Flynn MP (2012) A wirelessly powered log-based closed-loop deep brain stimulation SoC with two-way wireless telemetry for treatment of neurological disorders. In: Symposium on VLSI circuits (VLSIC), Honolulu, HI
Popovych OV, Hauptmann C, Tass PA (2005) Effective desynchronization by nonlinear delayed feedback. Phys Rev Lett 94:164102
Lee J (2008) A Closed-loop deep brain stimulation device with a logarithmic pipeline ADC. Doctor of Philosophy, Electrical Engineering, University of Michigan
Gorzelic P, Schiff S, Sinha A (2013) Model-based rational feedback controller design for closed-loop deep brain stimulation of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Eng 10:026016
Tarsy D (2008) Deep brain stimulation in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Humana Press, Totowa
O’Suilleabhain PE, Frawley W, Giller C, Dewey RB (2003) Tremor response to polarity, voltage, pulsewidth and frequency of thalamic stimulation. Neurology 60:786–790
Moro E, Esselink R, Xie J, Hommel M, Benabid A, Pollak P (2002) The impact on Parkinson’s disease of electrical parameter settings in STN stimulation. Neurology 59:706–713
Kringelbach ML, Jenkinson N, Owen SL, Aziz TZ (2007) Translational principles of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:623–635
Feng XJ, Greenwald B, Rabitz H, Shea-Brown E, Kosut R (2007) Toward closed-loop optimization of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: concepts and lessons from a computational model. J Neural Eng 4:L14–L21
Arfin SK, Long MA, Fee MS, Sarpeshkar R (2009) Wireless neural stimulation in freely behaving small animals. J Neurophysiol 102:598–605
Song YK, Borton DA, Park S, Patterson WR, Bull CW, Laiwalla F, Mislow J, Simeral JD, Donoghue JP, Nurmikko AV (2009) Active microelectronic neurosensor arrays for implantable brain communication interfaces. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 17:339–345
Aubert H (2011) RFID technology for human implant devices. CR Phys 12:675–683
Finkenzeller K (2003) RFID handbook : fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester
Radiom S, Baghaei-Nejad M, Vandenbosch G, Li-Rong Z, Gielen G (2010) Far-field RF powering system for RFID and implantable devices with monolithically integrated on-chip antenna. In: 2010 IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits symposium (RFIC), Anaheim, CA, 2010, pp 113–116
Lehpamer H (2008) RFID design principles. Artech House, London
Ghovanloo M, Najafi K (2004) A Modular 32-site wireless neural stimulation microsystem. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 39:2457–2466
Yao N, Lee HN, Chang CC, Sclabassi RJ, Sun M (2007) A power-efficient communication system between brain-implantable devices and external computers. In: 29th annual international conference of the IEEE EMBS. France, Lyon, pp 6588–6591
Bronstein JM, Tagliati M, Alterman RL, Lozano AM, Volkmann J, Stefani A, Horak FB, Okun MS, Foote KD, Krack P (2011) Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: an expert consensus and review of key issues. Arch Neurol 68:165
Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schäfer H, Bötzel K, Daniels C, Deutschländer A, Dillmann U, Eisner W (2006) A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 355:896–908
Eberle W, Penders J, Yazicioglu RF (2011) Closing the loop for deep brain stimulation implants enables personalized healthcare for Parkinson’s disease patients. In: Engineering in medicine and biology society, EMBC. Annual international conference of the IEEE 2011:1556–1558
Adhikari MH, Heeroma JH, di Bernardo M, Krauskopf B, Richardson MP, Walker MC, Terry JR (2009) Characterisation of cortical activity in response to deep brain stimulation of ventral–lateral nucleus: modelling and experiment. J Neurosci Methods 183:77–85
Stanslaski S, Afshar P, Cong P, Giftakis J, Stypulkowski P, Carlson D, Linde D, Ullestad D, Avestruz A, Denison T (2012) Design and validation of a fully implantable, chronic, closed-loop neuromodulation device with concurrent sensing and stimulation. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 20:410–421
Fountas KN, Smith JR, Murro AM, Politsky J, Park YD, Jenkins PD (2005) Implantation of a closed-loop stimulation in the management of medically refractory focal epilepsy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 83:153–158
de Solages C, Hill BC, Koop MM, Henderson JM, Bronte-Stewart H (2010) Bilateral symmetry and coherence of subthalamic nuclei beta band activity in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 221:260–266
Frankemolle AM, Wu J, Noecker AM, Voelcker-Rehage C, Ho JC, Vitek JL, McIntyre CC, Alberts JL (2010) Reversing cognitive–motor impairments in Parkinson’s disease patients using a computational modelling approach to deep brain stimulation programming. Brain 133:746–761
Shen H (2014) Neuroscience: tuning the brain. Nature 507:290–292
Grahn PJ, Khurram O, Berry BM, Hachmann JT, Mallory GW, Bieber AJ, Bennet KE, Lee KH, Lujan JL (2014) A neurochemical closed-loop controller for deep brain stimulation: toward individualized smart neuromodulation therapies. Front Neurosci, p 0
Sakatani K, Katayama Y, Yamamoto T, Suzuki S (1999) Changes in cerebral blood oxygenation of the frontal lobe induced by direct electrical stimulation of thalamus and globus pallidus: a near infrared spectroscopy study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:769–773
Jech R, Urgošík D, Tintěra J, Nebuželský A, Krásenský J, Liščák R, Roth J, Růžička E (2001) Functional magnetic resonance imaging during deep brain stimulation: a pilot study in four patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16:1126–1132
Niazmand K, Tonn K, Kalaras A, Fietzek UM, Mehrkens JH, Lueth TC (2011) Quantitative evaluation of Parkinson’s disease using sensor based smart glove. In: 24th international symposium on computer-based medical systems (CBMS), Bristol
Afshar P, Khambhati A, Stanslaski S, Carlson D, Jensen R, Linde D, Dani S, Lazarewicz M, Cong P, Giftakis J (2012) A translational platform for prototyping closed-loop neuromodulation systems. Front Neural Circuits 6:117
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosain, M.K., Kouzani, A. & Tye, S. Closed loop deep brain stimulation: an evolving technology. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 37, 619–634 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-014-0297-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-014-0297-2