Abstract
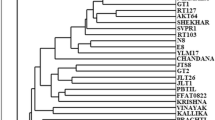
In order to increase the molecular tools and markers needed to detect genetic diversity of rice, Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD), Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) and Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) markers were used to reveal genetic diversity in 22 upland and lowland rice cultivars from Bangladesh. DNA from fresh leaves of young plants was extracted and subjected to the DNA polymorphism studies using the above mentioned markers. Among ten RAPD primers tested, four showed high polymorphism (90.90 %) with an average of 8.25 bands per primer with band size of approximately 220–1531 bp. Four ISSR primers out of ten produced high polymorphism (90.47 %) with an average of 10.5 bands per primer with band size of approximately 222–1750 bp. Among seven SSR primers tested, three amplified polymorphic bands with an average number of 4.0 bands per primer (ranging from approximately 233–950 bp) and 100 % polymorphism. Based on combined dataset generated by RAPD, ISSR and SSR markers, the highest similarity was showed between BRRI dhan 27 and BRRI dhan 29 (similarity coefficient value 0.89) and the lowest similarity was recorded between BR-3 and BRRI dhan 19 (similarity coefficient value 0.25). The UPGMA dendrogram based on genetic similarity grouped the cultivars into several clusters. Results obtained from PCA analysis were similar with UPGMA dendrogram. The evaluation of genetic similarity and cluster analysis provides useful guides for assisting plant breeders in selecting suitable genetically diverse parents for the future breeding programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Yokozeki Y, Inagaki A, Nakamura A, Fujimura T. A co-dominant DNA marker closely linked to the rice nuclear restorer gene, Rf-1, identified with inter-SSR fingerprinting. Genome. 1996;39:1205–9.
Bhuyan N, Borah BK, Sarma RN. Genetic diversity analysis in traditional lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) of Assam using RAPD and ISSR markers. Curr Sci. 2007;93:967–72.
Bornet B, Muller C, Paulus F, Branchard M. Highly informative nature of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) sequences amplified using tri- and tetra-nucleotide primers from DNA of cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. ‘botrytus’ L.). Genome. 2002;45:890–6.
Borsch T, Hilu KW, Quandt D, Wilde V, Neinhuis C, Barthlott W. Noncoding plastid trnT-trnF sequences reveal a well resolved phylogeny of basal angiosperms. J Evol Biol. 2003;16:558–76.
Bounphanousay C, Jaisil P, McNally KL, Sanitchon J, Hamilton NRS. Variation of microsatellite markers in a collection of Lao’s black glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J Plant Sci. 2008;7:140–8.
Brondani C, Caldeira KDS, Borba TCO, Rangel PN, de Morais OP, de Castro EM, Rangel PDN, Mendonça JA, Brondani RV. Genetic variability analysis of elite upland rice genotypes with SSR markers. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol. 2006;6:9–17.
Carvalho A, Matos M, Lima-Brito J, Guedes-Pinto H, Benito C. DNA fingerprint of F1 interspecific hybrids from the Triticeae tribe using ISSRs. Euphytica. 2005;143:93–9.
Davierwala AP, Chowdari KV, Kumar S, Reddy APK, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS. Use of three different marker systems to estimate genetic diversity of Indian elite rice varieties. Genetica. 2000;108:269–84.
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull. 1987;19:11–5.
Fernández E, Figueiras M, Benito C. The use of ISSR and RAPD markers for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and genetic diversity among barley cultivars with known origin. Theor Appl Genet. 2002;104:845–51.
Galván MZ, Bornet B, Balatti PA, Branchard M. Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers as a tool for the assessment of both genetic diversity and gene pool origin in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica. 2003;132:297–301.
Garris AJ, Tai TH, Coburn J, Kresovich S, McCouch S. Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L. Genetics. 2005;169:1631–8.
Godwin ID, Aitken EA, Smith LW. Application of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers to plant genetics. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:1524–8.
Hamada H, Petrino MG, Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:6465–9.
Jaccard P Nouvelles rescherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaudoise Sci Nat. 1908;44:223–70.
Jain S, Jain RK, McCouch SR. Genetic analysis of Indian aromatic and quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using panels of fluorescently-labeled microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet. 2004;109:965–77.
Jayamani P, Negrão S, Martins M, Oliveira MM. Genetic relatedness of Portuguese rice accessions from diverse origins as assessed by microsatellite markers. Crop Sci. 2007;47:879–84.
Joshi SP, Gupta VS, Aggarwal RK, Ranjekar PK, Brar DS. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism in the genus Oryza. Theor Appl Genet. 2000;100:1311–20.
Kanawapee N, Sanitchon J, Srihaban P, Theerakulpisut P. Genetic diversity analysis of rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) differing in salinity tolerance based on RAPD and SSR markers. Electronic J Biotechnol. 2011;14(6):2–2.
Kantety RV, Zeng X, Bennetzen JL, Zehr BE. Assessment of genetic diversity in dent and popcorn (Zea mays L.) inbred lines using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification. Mol Breed. 1995;1:365–73.
Kaushik A, Saini N, Jain S, Rana P, Singh RK, Jain RK. Genetic analysis of a CSR10 (indica) × Taraori Basmati F3 population segregating for salt tolerance using ISSR markers. Euphytica. 2003;134:231–8.
Kojima T, Nagaoka T, Noda K, Ogihara Y. Genetic linkage map of ISSR and RAPD markers in Einkorn wheat in relation to that of RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet. 1998;96:37–45.
Lima-Brito J, Carvalho A, Martin A, Heslop-Harrison JS, Guedes-Pinto H. Morphological, yield, cytological and molecular characterization of a breed wheat × tritordeum F1 hybrid. J Genet. 2006;85:123–31.
Nagaoka T, Ogihara Y. Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet. 1997;94:597–602.
Nazari L, Pakniyat H. Genetic diversity of wild and cultivated barley genotypes under drought stress using RAPD markers. Biotechnol. 2008;7:745–50.
Pakniyat H, Tavakol E. RAPD markers associated with drought tolerance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak J Biol Sci. 2007;10:3237–9.
Rabbani MA, Pervaiz ZH, Masood MS. Genetic diversity analysis of traditional and improved cultivars of Pakistani rice (Oryza sativa L.) using RAPD markers. Electron J Biotechnol. 2008;11:3.
Rahman SN, Islam MS, Alam MS, Nasiruddin KM. Genetic polymorphism in rice (Oryza sativa L) through RAPD analysis. Indian J Biotechnol. 2007;6:224–9.
Ren F, Lu B-R, Li S, Huang J, Zhu Y. A comparative study of genetic relationships among the AA-genome Oryza species using RAPD and SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet. 2003;108:113–20.
Rohlf FJ. NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy and multivariate analysis System. New York: Ver. 2.1. Exeter Publishing Ltd. Setauket; 2000.
Saker MM, Youssef SS, Abdallah NA, Bashandy HS, El El Sharkawy AM. Genetic analysis of some Egyptian rice genotypes using RAPD, SSR and AFLP. Afr J Biotechnol. 2005;4:882–90.
Shishido R, Kikuchi M, Nomura K, Ikehashi H. Evaluation of genetic diversity of wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) in Myanmar using simple sequence repeats (SSRs). Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2006;53:179–86.
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR. Numerical taxonomy. San Francisco, USA: W.H. Freeman and Company; 1973.
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:6531–5.
Youssef MA, Mansour A, Solliman SS. Molecular markers for new promising drought tolerant lines of rice under drought stress via RAPD-PCR and ISSR markers. J Amer Sci. 2010;6:355–63.
Yu SB, Xu WJ, Vijaykumar CHM, Ali J, Fu BY, Xu JL, Jiang YZ, Marghirang R, Domingo J, Aquino C, Virmani SS, Li ZK. Molecular diversity and multilocus organization of the parental lines used in the International Rice Molecular Breeding Program. Theor Appl Genet. 2003;108:131–40.
Zeng L, Kwon T-R, Liu X, Wilson C, Grieve CM, Gregorio GB. Genetic diversity analyzed by microsatellite markers among rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes with different adaptations to saline soils. Plant Sci. 2004;166:1275–85.
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D. Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics. 1994;20:176–83.
Acknowledgments
The authors are gratefully acknowledged to Professor Joarder DNA and Chromosome Laboratory, Department of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, University of Rajshahi and USDA (Grant No. 09.111.014.10.01.002.2009-13) and Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST), Bangladesh (Grant No. BS 58 (2010-2011)), for financial support. The authors also acknowledge the support and encouragement of the Principal, Vivekananda College, Thakurpukur, West Bengal, India.
Authors’ contribution
Shah Md. Mahbub Alam, Sadia siddika, Md. Enamul Haque, Md. Asadul Islam and Biswanath Sikdar designed the workplan, performed the experiments and wrote the paper. Ashutosh Mukherjee performed statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, S.M.M., Siddika, S., Haque, M.E. et al. Genetic diversity of some upland and lowland rice cultivars in Bangladesh using RAPD, ISSR and SSR markers. Nucleus 59, 15–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-015-0148-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-015-0148-x