Abstract
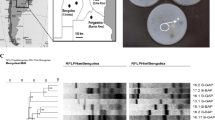
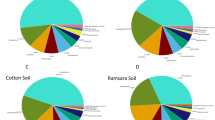
This study focused on the isolation, identification (sequencing of 16S rDNA gene) and determination of the phosphorus (P)-solubilizing efficiency of native populations of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) in 13 Kenyan soils with differing chemical characteristics. Air-dried soil samples were serially diluted and plated on NBRIP media and enumerated. Their phosphate-solubilizing efficiency was assessed on Frioni’s agar. Pearson correlation coefficients were determined between PSB populations and soil properties. The PSB populations varied among the sites tested and had a positive and significant correlation (p ≤ 0.05) with organic carbon (r = 0.76), exchangeable calcium (r = 0.93) and exchangeable magnesium (r = 0.92). A total of 150 isolates were identified to the genus and species level. Among the isolates, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus sp. and Arthrobacter sp. were the most abundant and well-distributed strains. However, only 5% of the total isolates were efficient in terms of phosphate-solubilizing efficiency. The results indicate that although there were many PSB strains in the soils tested, only a few (5%) were effective in terms of their phosphate-solubilizing ability. It is therefore unlikely that native PSB contribute significantly to solubilizing phosphate in the soils tested, which would ultimately benefit plant growth. Therefore, inoculation with effective strains with a high P solubilization potential is necessary.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Ingram JS (1993) Tropical soil biology and fertility: a handbook of methods. CAB International, Wallingford
Bationo A, Ayuke ED, Ballo D, Kone M (1997) Agronomic evaluation of Tilemsi phosphate rocks in different agro-ecological zones of Mali. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 48:179–189
Carney KM, Matson PA (2006) The influence of tropical plant diversity and composition on soil microbial communities. Microbial Ecol 52:226–238
Fankem H, Nwaga D, Deubel A, Dieng L, Merbach W, Etoa FX (2006) Occurrence and functioning of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms from oil palm tree (Elaeis guineensis) rhizosphere in Cameroon. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2450–2460
Fernandez LA, Zabla P, Gómez MA, Sargardoy MA (2007) Phosphate solubilization activity of bacterial strains in soil and their effect on soybean growth under greenhouse conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 43:805–809
Frioni L (1999) Procesos microbianos. Tomus I y II. Fundación de UNRC. Rio Cuarto Córdoba, 282 y 286p
Goldstein AH (1986) Bacterial mineral phosphate solubilization: Historical perspective and future prospects. Am J Altern Agric 1:57–65
Gyaneshwar P, Naresh KG, Parekh LJ, Poole PS (2002) Role of soil microorganisms in improving P nutrition of plants. Plant Soil 245:83–93
Jha DK, Sharma GD, Mishra RR (1992) Ecology of soil micro-flora and mycorrhizal symbionts. Biol Fert Soils 12:272–278
John L, Herms D, Stinner B, Hostink H (2001) Mulch effect on soil microbial activity, nutrient cycling, and plant growth in ornamental landscape. Ornamental Plant Annual Report and Research Reviews 2001. The Ohio State University, Columbus
Kämpfer P (2007) Taxonomy of phosphate solubilizing bacteria. In: Velazquez E, Rodriguez-Barrueco C (eds) First Int Meet microbial phosphate solubilization. Springer SBM, Dordrecht, pp 101–106
Kucey RMN (1983) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and fungi in various cultivated and virgin Alberta soils. Can J Soil Sci 63:671–678
Mehta S, Nautiyal SC (2001) An efficient method for qualitative screening of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Current Microbiol 43:51–56
Nahas E (2007) Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms: effects of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. In: Velazquez E, Rodriguez-Barrueco C (eds) First Int Meet microbial phosphate solubilization. Springer SBM, Dordrecht, pp 111–115
Ndung’u KW, Okalebo JR, Othieno CO, Kifuko MN, Kipkoech AK, Kimenye LN (2006) Residual effectiveness of Minjingu phosphate rock and improved fallows on crop yield and financial returns in western Kenya. Exp Agric 42:323–336
Okalebo JR, Schiner F, Lekasi, JK (1994) Maize response to fertilizer and rock phosphate in a high phosphate fixing soil of Malava, Kakamega. In: Kapkiyai JJ, Okalebo JR, Maritim HK. Proc PrePREP Workshop held in Moi University. Moi University, Eldoret, pp 77–82
Okalebo JR, Gathua KW,Woomer PL (2002) Laboratory methods of soil and plant analysis. A working manual. Marvel EPZ, Nairobi
Panhwar QI, Radziah O, Sariah M, Ismail MR (2009) Solubilization of different phosphate forms by phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from aerobic rice. Int J Agric Biol 11:667–673
Richardson AE (2007) Making microorganisms mobilize soil phosphorus. In: Velazquez E, Rodriguez-Barrueco C (eds) First International Meeting on microbial phosphate solubilization. First Int Meet microbial phosphate solubilization. Springer SBM, Dordrecht, pp 85–90
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339
SAS Institute (2006) SAS Users’ guide statistics. SAS Institute, Cary
Setiadi Y (1989) Pemanfaatan Mikroorganisme dalam Kehutanan. Institut Pertanian Bogor, Bogor
Stamford NP, Santos PR, Santos CE, Freitas AD, Dias SHL, Lira MA (2007) Agronomic effectiveness of biofertilizers with phosphate rock, sulphur and Acidithiobacillus for yam bean grown on a Brazilian tableland acidic soil. Bioresour Technol 98:1311–1318
Suliasih WS (2005) Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing and nitrogen fixing bacteria from soil in Wamena biological garden, Jayawijaya, Papua. Biodiversitas 6(3):175–177
Taha SM, Mahmoud SAZ, Halim A, Damaty E, El Hafez AMA (1969) Activity of phosphate dissolving bacteria in Egyptian soils. Plant Soil 31:149–160
Taurian T, Anzuay SM, Angelini JG, Tonelli ML, Ludueña L, Pena D, Ibáñez F, Fabra A (2010) Phosphate-solubilizing peanut associated bacteria: screening for plant growth-promoting activities. Plant Soil 329:421–431
Vikram A, Alagawadi AR, Hamzehzarghani H, Krishnaraj PU (2007) Factors related to the occurrence of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their isolation in Vertisols. Int J Agric Res 2(7):571–580
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Whitelaw MA (2000) Growth promotion of plants inoculated with phosphate-solubilizing fungi. Adv Agron 69:99–151
Wilson KJ (1987) Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular biology. Wiley Interscience, New York, pp 241–245
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation for their financial support of this study through the commercial products project “COMPRO” coordinated by the Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility Institute of CIAT (TSBF–CIAT). We are also indebted to TSBF–CIAT for providing the laboratory facilities and chemicals for studies and to Leticia A. Fernández for provision of the reference strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ndung’u-Magiroi, K.W., Herrmann, L., Okalebo, J.R. et al. Occurrence and genetic diversity of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in soils of differing chemical characteristics in Kenya. Ann Microbiol 62, 897–904 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0326-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0326-2