Abstract
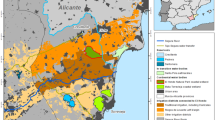
The Mediterranean wetlands are unique in biological diversity and provide multiple benefits, constituting a great water reserve for the planet and producing biomass and nutrients for the trophic chain. However, the increasing human impact and socio-economic development in recent decades have caused important losses in these ecosystems. This work was carried out in the Natural Park of L’Albufera (Valencia, Spain), which includes a coastal lagoon, marshlands, dunes and pinewoods, surrounded by rice fields and orchard in its non-urbanized part. Despite this great ecological value, it suffers impacts derived from the high human and industrial occupation and the hydrological contributions of the connected irrigation systems. The study focused on the development of a combined methodology, based on environmental forensics principles, with the aim of identifying the presence, flow paths and spatial distribution of illicit drugs entering the Natural Park. It is organized around two major procedures: analysis of 16 water samples and application of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) integrating different sources and data formats, as analysis of 14 drugs of abuse by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry techniques, and social and environmental data in either GIS layers or tabular digital formats. Results show that, at present, most analyzed drugs have been identified in all sample points. Besides the population distribution pattern, the traditional irrigation system connected to sewage treatment plant (STP) locations is the way by which illicit substances are introduced into the Natural Park waters.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Bartelt-Hunt SL, Snow DD, Damon T, Shockley J, Hoagland K (2009) The occurrence of illicit and therapeutic pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluent and surface waters in Nebraska. Environ Pollut 157:786–791. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.11.025
Boleda MR, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2007) Trace determination of cannabinoids and opiates in wastewater and surface waters by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1275:38–48. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.029
Boleda MR, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2009) Monitoring of opiates, cannabinoids and their metabolites in wastewater, surface water and finished water in Catalonia, Spain. Water Res 43:1126–1136. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.056
Boles TH, Wells MJM (2010) Analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine as emerging pollutants in wastewater and wastewater-impacted streams. J Chromatogr A 1217:2561–2568. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.014
Bossard M, Feranec J, Otahel J (2000) CORINE land cover technical guide—Addendum 2000. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
Gheorghe A, Van Nuijs A, Pecceu B, Bervoets L, Jorens PG, Blust R, Neels H, Covaci A (2008) Analysis of cocaine and its principal metabolites in waste and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1309–1319. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1754-5
González-Mariño I, Benito Quintana J, Rodríguez I, Cela R (2010) Determination of drugs of abuse in water by solid-phase extraction, derivatisation and gas chromatography–ion trap-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217:1748–1760. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.01.046
Hermosilla Pla J (2006) Las Riberas del Xúquer: Paisaje y Patrimonio Valencianos. Generalitat Valenciana, Valencia
Hermosilla Pla J (2007) El patrimonio hidráulico del Bajo Turia: L’Horta de València. Generalitat Valenciana, Valencia
Huerta-Fontela M, Galceran MC, Ventura F (2007) Ultraperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of stimulatory drugs of abuse in wastewater and surface waters. Anal Chem 79:3821–3829. doi:10.1021/ac062370x
Karolak S, Nefau T, Bailly E, Solgadi A, Levi Y (2010) Estimation of illicit drugs consumption by wastewater analysis in Paris area (France). Forensic Sci Int 200:153–160. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.04.007
Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Dinsdale RM, Guwy AJ J (2009) Illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment—forensic applications of environmental data. Part 1: estimation of the usage of drugs in local communities. Environ Pollut 157:1773–1777. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.03.017
Li Y, Zhua X, Suna X, Wang F (2010) Landscape effects of environmental impact on bay-area wetlands under rapid urban expansion and development policy: a case study of Lianyungang, China. Landsc Urban Plan 94:218–227
Lotze HK, Lenihan HS, Bourque BJ, Bradbury RH, Cooke RG, Kay MC, Kidwell SM, Kirby MX, Peterson CH, Jackson JBC (2006) Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 312:1806–1809. doi:10.1126/science.1128035
Mari F, Politi L, Biggeri A, Gabriele A, Trignano C, Di Padua M, Bertol E (2009) Cocaine and heroin in waste water plants: a 1-year study in the city of Florence, Italy. Forensic Sci Int 189:88–92. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.04.018
Metcalfe C, Tindale K, Li H, Rodayan A, Yargeau V (2010) Illicit drugs in Canadian municipal wastewater and estimates of community drug use. Environ Pollut 158:3179–3185. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.07.002
Postigo C, López de Alga MJ, Barceló D (2010) Drugs of abuse and their metabolites in the Ebro River basin: occurrence in sewage and surface water, sewage treatment plants removal efficiency, and collective drug usage estimation. Environ Int 36:75–84. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2009.10.004
Readman JW, Albanis TA, Barcelo D, Galassi S, Tronczynski J, Gabrielides GP (1993) Herbicide contamination of Mediterranean estuarine waters: results from a MED POL pilot survey. Mar Pollut Bull 26:613–619
Richardson SD (2008) Environmental mass spectrometry: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 80:4373–4402. doi:10.1021/ac800660d
Richardson SD (2009) Water Analysis: emerging Contaminants and Current Issues. Anal Chem 81:4645–4677. doi:10.1021/ac9008012
Richardson SD (2010) Environmental mass spectrometry: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 82:4742–4774. doi:10.1021/ac101102d
Sadler Simões S, Castañera Ajenjo A, Franco JM, Nuno Vieira D, Dias MJ (2009) Liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of illicit drugs and medicines in preserved oral fluid. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:1451–1460. doi:10.1002/rcm.4020
Soria JM, Vicente E (2000) Estudio de los aportes hídricos al pParquet natural Natural de la Albufera de Valencia. Limnetica 21:105–115
Soria JM, Miracle MR, Vicente E (2002) Relations between physic-chemical and biological variables in aquatic ecosystems of the Albufera Natural Park (Valencia, Spain). Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 28:564–568
Taylor DA (2004) Environmental forensic files. Environ Health Perspect 112:a88–a88. doi:10.1289/ehp.112-a88
Van Nuijs ALN, Tarcomnicu I, Bervoets L, Blust R, Jorens PG, Neels H, Covaci A (2009) Analysis of drugs of abuse in wastewater by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:819–828. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-3017-0
Vazquez-Roig P, Andreu V, Blasco C, Picó Y (2010) SPE and LC-MS/MS determination of 14 illicit drugs in surface waters from the Natural Park of L’Albufera (València, Spain). Anal Bioanal Chem 39:2851–2864. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-3720-x
Zuccato E, Castiglioni S (2009) Illicit drugs in the environment. Philos Trans R Soc A 367:3965–3978. doi:10.1098/rsta.2009.0107
Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Chiabrando C, Grassi P, Fanelli R (2007) Illicit drugs, a novel group of environmental contaminants. Water Res 42:961–968. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.09.010
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out in the scope of project HUCOMED CGL2008-01693/BTE, CTQ2010-16448 and project GCL2007-66687-C02-01/BOS, all financed by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascual Aguilar, J.A., Andreu, V., Vázquez, P. et al. Presence and spatial distribution of emerging contaminants (drugs of abuse) in protected agroecological systems (L’Albufera de Valencia Coastal Wetland, Spain). Environ Earth Sci 71, 31–37 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2688-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2688-1