Abstract
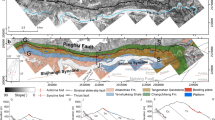
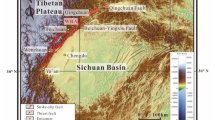
The Kashmir earthquake 2005 (magnitude M W 7.6) triggered thousands of mass movements in northern Pakistan. These mass movements were mainly rock falls, debris falls, rockslides and rock avalanches. The mass movements vary in size from a few hundred cubic meters up to about 100 million cubic meters estimated for the Hattian Bala rock avalanche, the biggest one associated with this earthquake. This mass movement, which moved in southeastern direction, created two natural dams on the valley bottom and blocked the water ways of the Karli and Tung tributaries of the Jhelum River. Topographic, lithologic and structural information were used to investigate the Hattian Bala rock avalanche. Geotechnical and structural maps were prepared to understand relationship between geology and structure of Hattian Bala rock avalanche. The geometry and failure mode of this rock avalanche are controlled by southeast plunging synclinal structures, lithology, a bedding parallel slip surface and a pre-existing old rockslide. The structural map shows that the mass movement failure was due to Danna and Dandbeh synclinal structures plunging southeast on the hanging wall block of the reactivated Muzaffarabad fault. The slip surface of the mass movement followed the bedding planes along mudstone, claystone and sandstone surfaces. The mass movement perfectly followed the pre-existing synclinal morphology of the Danna and Dandbeh synclines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Armbruster, J., Seeber, L., Jacob, K. B., 1978. The Northwestern Termination of the Himalayan Mountain Front: Active Tectonics from Microearthquakes. J. Geophys. Res., 83(B1): 269–282
Asian Development Bank and World Bank, 2005. Preliminary Damage and Needs Assessment (Pakistan Earthquake 2005), 1–124
Avouac, J. P., Ayoub, F., Leprince, S., et al., 2006. The 2005, M w 7.6 Kashmir Earthquake: Sub-Pixel Correlation of ASTER Images and Seismic Waveforms Analysis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 249: 514–528
Baig, M. S., Lawrence, R. D., 1987. Precambrian to Early Paleozoic Orogenesis in the Himalaya. Kashmir Journal of Geology, 5: 1–22
Baig, M. S., 2006. Active Faulting and Earthquake Deformation in Hazara-Kashmir Syntaxis, Azad Kashmir, Northwest Himalaya, Pakistan. In: Kausar, A. B., Karim, T., Khna, T., et al., eds., Extended Abstracts, International Conference on 8 October 2005 Earthquake in Pakistan: Its Implications and Hazard Mitigation. Geological Survey of Pakistan, Islamabad. 27–28
Bossart, P., Dietrich, D., Greco, A., et al., 1988. The Tectonic Structure of Hazara Kashmir Syntaxis, Southern Himalayas, Pakistan. Tectonics, 7(2): 273–297, doi:10.1029/TC007i002p00273
Calkins, J. A., Offield, T. W., Abdulla, S. K. M., et al., 1975. Geology of the Southern Himalaya in Hazara, Pakistan, and Adjacent Areas. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 716-c: 29
Dunning, S. A., Mitchell, W. A., Rosser, N. J., et al., 2007. The Hattian Bala Rock Avalanche and Associated Landslides Triggered by the Kashmir Earthquake of 8 October 2005. Engineering Geology, 93(3–4): 130–144, doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.07.003
EERI (Earthquake Engineering Research Institute), 2005. First Special Earthquake Report on the Kashmir Earthquake of October 8, 2005. 1–8
Greco, A., 1991. Stratigraphy, Metamorphism and Tectonics of the Hazara-Kashmir Syntaxis Area. Kashmir Journal of Geology, 8–9: 39–66
Harp, E. L., Crone, A. J., 2006. Landslides Triggered by the October 8, 2005, Pakistan Earthquake and Associated Landslide-Dammed Reservoirs. U. S. Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1–13
Hussain, A., Iqbal, S., Nasir, S., 2004. Geological Maps of the Garhi Habibullah and Nauseri Area, District Muzaffarabad, AJK: Geol. Survey of Pakistan, Preliminary Map Series, VI (14), Sheet No. 43 F/7, 11, 1: 50 000
Jibson, R. W., Harp, E. L., Schulz, W., et al., 2006. Large Rock Avalanches Triggered by the M 7.9 Denali Fault, Alaska, Earthquake of 3 November 2002. Eng. Geo., 83(1–3): 144–160, doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.06.029
JSCE (Japan Society of Civil Engineers), 2006. Quick Report of the JSCE Mission for Geotechnical Survey along Jehlem and Kunhar Valleys (Ver. 1.1). 1–11
Kamp, U., Growley, B. J., Khattak, G. A., et al., 2008. GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping for the 2005 Kashmir Earthquake Region. Geomorphology, 101(4): 631–642
Kaneda, H., Nakata, T., Tsutsumi, H., et al., 2008. Surface Rupture of the 2005 Kashmir, Pakistan Earthquake and Its Active Tectonic Implications. Bull. of the Seismol. Soc. America, 98(2): 521–557, doi:10.1785/0120070073
Keefer, D. K., 1984. Landslides Caused by Earthquakes. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 95(4): 406–421
Land Use Planning and Development Department Muzaffarabad, 2007. Location Map of Muzaffarabad District AJ & K, Muzaffarabad, Pakistan. Scale 1: 50 000. Government of AJ & K, Muzaffarabad
Munir, H. M., Baig, M. S., Mirza, K., 2006. Upper Cretaceous of Hazara and Paleogene Biostratigraphy of Azad Kashmir, North-West Himalayas, Pakistan. Geol. Bull. of Punjab. Univ., 40–41: 69–87
Nakata, T., Tsutsumi, H., Khan, S. H., et al., 1991. Active Faults of Pakistan: Map Sheets and Inventories. Special Publication 21, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima.141
Owen, L. A., Kamp, U., Khattak, G. A., et al., 2008. Landslides Triggered by the 8 October 2005 Kashmir Earthquake. Geomorphology, 94(1–2): 1–9, doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2007.04.007
Parsons, T., Yeats, R. S., Yagi, Y., et al., 2006. Static Stress Change from the 8 October, 2005 M=7.6 Kashmir Earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33: L06304, doi:10.1029/2005GL025429
Peiris, N., Rossetto, T., Burton, P., 2006. EEFIT Mission: October 8, 2005 Kashmir Earthquake. The Institution of Structural Engineers, London. 31
Petley, D., Dunning, S., Rosser, N., et al., 2006. Incipient Landslides in the Jhelum Valley, Pakistan Following the 8th October 2005 Earthquake. Disaster Mitigation of Rock Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides. In: Marui, H., ed., Disaster Mitigation of Debris Flows, Slope Failures and Landslides. Frontiers of Science Series, Universal Academy Press, Tokyo. 47: 47–56
Rao, N. P., Kumar, P., Kalpana, T., et al., 2006. The Devastating Muzaffarabad Earthquake of 8 October 2005: New Insight into Himalayan Seismicity and Tectonics. Gondwana Research, 9(4): 365–378
Schneider, J. F., 2008. Seismically Reactivated Hattian Slide in Kashmir, Northern Pakistan. Journal of Seismology, 13(3): 387–398, doi:10.1007/s10950-008-9103-5
Survey of Pakistan, 2005. Location Map of Pakistan. Govt. of Pakistan, Islamabad
Thakur, V. C., 2006. Reassessment of Earthquake Hazard in the Himalaya and Implications from the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake. Current Science, 90(8): 1070–1072
USGS (United States Geological Survey), 2006. Magnitude M w 7.6 Pakistan Earthquake 2005 Summary. www.earthquake.usgs.gov.
Wadia, D. N., 1931. The Syntaxis of the North-West Himalaya-Its Rocks, Tectonics, and Orogeny. Rec. Geol. Surv. India., 65: 189–220
Yeats, R. S., Parsons, T., Hussain, A., et al., 2006. Stress Changes with the 8 October 2005 Kashmir Earthquake, Lessons for the Future. In: Kausar, A. B., Karim, T., Khna, T., et al., eds., Extended Abstracts, International Conference on 8 October 2005 Earthquake in Pakistan: Its Implications and Hazard Mitigation. Geological Survey of Pakistan, Islamabad. 16–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the University of Azad Jammu and Kashmir Muzaffarabad, Pakistan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basharat, M., Rohn, J., Ehret, D. et al. Lithological and structural control of Hattian Bala rock avalanche triggered by the Kashmir earthquake 2005, sub-Himalayas, northern Pakistan. J. Earth Sci. 23, 213–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0248-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0248-3