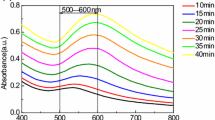
Abstract
A new protocol for the synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold nanoparticles with controllable size is described. The pathway is based on the reduction of AuCl −4 by ammonium bicarbonate in the presence of sodium stearate under hydrothermal conditions. The particle sizes could be easily tuned by regulating the reaction conditions including precursor concentration, reaction temperature and growth time. A tentative explanation for the reduction and growth mechanism of uniform gold nanoparticles has been proposed. The as-prepared gold particles showed good catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol by excess NaBH4, and a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) study suggested that the gold nanoparticles exhibited a high SERS effect on the probe molecule Rhodamine 6G.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daniel, M. C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346.
Jana, N. R.; Peng, X. G. Single-phase and gram-scale routes toward nearly monodisperse Au and other noble metal nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14280–14281.
Haruta, M. When Gold is not noble: Catalysis by nanoparticles. Chem. Rec. 2003, 3, 75–87.
Park, J.; Joo, J.; Kwon, S. G.; Jang, Y.; Hyeon, T. Synthetic procedure for monodisperse nanoparticles using hot injection method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4630–4660.
Yang, X.; Skrabalak, S. E.; Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L. V. Photoacoustic tomography of a rat cerebral cortex in vivo with Au nanocages as an optical contrast agent. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3798–3802.
Chen, M.; Kumar, D.; Yi, C.; Goodman, D. W. The promotional effect of gold in catalysis by palladium-gold. Science 2005, 310, 291–293.
Alvarez-Puebla, R. A.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzán, L. M. Au@pNIPAM colloids as molecular traps for surface-enhanced, spectroscopic, ultrasensitive analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 138–143.
Brust, M.; Schiffrin, D. J.; Bethell, D.; Kiely, C. J. Novel gold-dithiol nano-networks with non-metallic electronic properties. Adv. Mater. 1995, 7, 795–797.
Hussain, I.; Graham, S.; Wang, Z.; Tan, B.; Sherrington, D. C.; Rannard, S. P.; Cooper, A. I.; Brust, M. Size-controlled synthesis of near-monodisperse gold nanoparticles in the 1–4 nm range using polymeric stabilizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16398–16399.
Pretzer, L. A.; Nguyen, Q. X.; Wong, M. S. Controlled growth of sub-10 nm gold nanoparticles using carbon monoxide reductant. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21226–21233.
Wang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Peng, Q.; Li, Y. A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature 2005, 437, 121–124.
Hiramatsu, H.; Osterloh, F. E. A simple large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse gold and silver nanoparticles with adjustable sizes and with exchangeable surfactants. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2509–2511.
Hoppe, C. E.; Lazzari, M.; Pardiňas-Blanco, I.; López-Quintela, M. A. One-step synthesis of gold and silver hydrosols using poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) as a reducing agent. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7027–7034.
Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179.
Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D. J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a twophase liquid-liquid system. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1994, 801–802.
Brust, M.; Fink, J.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D. J.; Kiely, C. Synthesis and reactions of functionalised gold nanoparticles. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1995, 1655–1656.
Toshima, N.; Yonezawa, T. Bimetallic nanoparticles-novel materials for chemical and physical applications. New J. Chem. 1998, 22, 1179–1201.
Zheng, N.; Fan, J.; Stucky, G. D. One-step one-phase synthesis of monodisperse noble-metallic nanoparticles and their colloidal crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6550–6551.
Shen, C.; Hui, C.; Yang, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, J.; Bao, L.; Chen, S.; Ding, H.; Gao, H. Monodisperse noble-metal nanoparticles and their surface enhanced Raman scattering properties. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6939–6944.
Faraday, M. Experimental relations of gold (and other metals) to light. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London 1857, 147, 145–181.
Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P. C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75.
Ji, X.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, X. Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: The third role of citrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 13939–13948.
Turkevich, J.; Kim, G. Palladium: Preparation and catalytic properties of particles of uniform size. Science 1970, 169, 873–879.
Chang, C. C.; Wu, H. L.; Kuo, C. H.; Huang, M. H. Hydrothermal synthesis of monodispersed octahedral gold nanocrystals with five different size ranges and their self-assembled structures. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 7570–7574.
Peng, X. G.; Wickham, J.; Alivisatos, A. P. Kinetics of II–VI and III–V colloidal semiconductor nanocrystal growth: “Focusing” of size distributions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5343–5344.
Kumar, S. S.; Kumar, C. S.; Mathiyarasu, J.; Phani, K. L. Stabilized gold nanoparticles by reduction using 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene-polystyrenesulfonate in aqueous solutions: Nanocomposite formation, stability, and application in catalysis. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3401–3408.
Bailie, J. E.; Hutchings, G. J. Promotion by sulfur of gold catalysts for crotyl alcohol formation from crotonaldehyde hydrogenation. Chem. Commun.1999, 2151–2152.
Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R. Facile synthesis of highly stable gold nanoparticles and their unexpected excellent catalytic activity for Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2060–2061.
Su, F. Z.; He, L.; Ni, J.; Cao, Y.; He, H. Y.; Fan, K. N. Efficient and chemoselective reduction of carbonyl compounds with supported gold catalysts under transfer hydrogenation conditions. Chem. Commun. 2008, 3531–3533.
Hayakawa, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Esumi, K. Preparation of gold dendrimer nanocomposites by laser irradiation and their catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol, Langmuir 2003, 19, 5517–5521.
Zeng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xia. Y. A comparison study of the catalytic properties of Au-based nanocages nanoboxes, and nanoparticles. Nano. Lett. 2010, 10, 30–35.
Kneipp, K.; Kneipp, H.; Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R. R.; Feld, M. S. Ultrasensitive chemical analysis by Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2957–2975.
Creighton, J. A.; Blatchford, C. G.; Albretch, M. G. Plasma resonance enhancement of Raman scattering by pyridine adsorbed on silver or gold sol particles of size comparable to the excitation wavelength. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2 1979, 75, 790–798.
Ghosh, S. K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: From theory to applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4797–4862.
Hildebrandt, P.; Stockburger, M. Surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy of Rhodamine 6G adsorbed on colloidal silver. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5935–5944.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Yang, Q. Ammonium bicarbonate reduction route to uniform gold nanoparticles and their applications in catalysis and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nano Res. 4, 861–869 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0142-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0142-9