Abstract
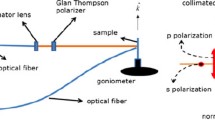
We have investigated the optical properties of laterally aligned Si nanowire (SiNW) arrays in order to explore their potential applicability in transparent electronics. The SiNW array exhibited good optical transparency in the visible spectral range with a transmittance of ∼90% for a NW density of ∼20–25 per 10 μm. In addition, polarization-dependent measurements revealed a variation in transmittance in the range of 80%–95% depending on the angle between the polarization of incident light and the NW axis. Using the SiNWs, we demonstrated that transparent transistors exhibit good optical transparency (greater than 80%) and showed typical p-type SiNW transistor characteristics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Ueda, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Thin-film transistor fabricated in single-crystalline transparent oxide semiconductor. Science 2003, 300, 1269–1272.
Someya, T. Optics: Electronic eyeballs. Nature 2008, 454, 703–704.
Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Takagi, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 2004, 432, 488–492.
Cao, Q.; Hur, S. H.; Zhu, Z. T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Meitl, M. A.; Shim, M.; Rogers, J. A. Highly bendable, transparent thin-film transistors that use carbon-nanotube-based conductors and semiconductors with elastomeric dielectrics. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 304–309.
Gorrn, P.; Sander, M.; Meyer, J.; Kroger, M.; Becker, E.; Johannes, H. H.; Kowalsky, W.; Riedl, T. Towards seethrough displays: Fully transparent thin-film transistors driving transparent organic light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 738–741.
Kim, H.; Horwiz, J. S.; Kushto, G. P.; Kafafi, Z. H.; Chrisey, D. B. Indium tin oxide thin films grown on flexible plastic substrates by pulsed-laser deposition for organic light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 284–286.
Izaki, M.; Omi, T. Transparent zinc oxide films prepared by electrochemical reaction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2439–2440.
Ju, S.; Facchetti, A.; Xuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Ishikawa, F.; Ye, P.; Zhou, C.; Marks, T. J.; Janes, D. B. Fabrication of fully transparent nanowire transistors for transparent and flexible electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 378–384.
Dattoli, E. N.; Wan, Q.; Guo, W.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X.; Lu, W. Fully transparent thin-film transistor devices based on SnO2 nanowires. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2463–2469.
Artukovic, E.; Kaempgen, M.; Hecht, D. S.; Roth, S.; Gruner, G. Transparent and flexible carbon nanotube transistors. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 757–760.
Ishikawa, F. N.; Chang, H. K.; Ryu, K.; Chen, P.; Badmaev, A.; De Arco Gomez, L.; Shen, G.; Zhou, C. Transparent electronics based on transfer printed aligned carbon nanotubes on rigid and flexible substrates. ACS Nano 2008, 3, 73–79.
Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C. M. Fabrication of silicon nanowire devices for ultrasensitive, label-free, real-time detection of biological and chemical species. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1711–1724.
Duan, X.; Niu, C.; Sahi, V.; Chen, J.; Parce, J. W.; Empedocles, S.; Goldman, J. L. High-performance thin-film transistors using semiconductor nanowires and nanoribbons. Nature 2003, 425, 274–278.
Oubre, C.; Nordlander P. Optical properties of metallodielectric nanostructures calculated using the finite difference time domain method. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17740–17747.
Javey, A.; Nam, S. W.; Friedman, R. S.; Yan, H.; Lieber, C. M. Layer-by-layer assembly of nanowires for three-dimensional, multifunctional electronics. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 773–777.
Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E. M.; Pitaevskii, L. P. Electrodynamics of Continuous Media; Pergamon: Oxford, England, 1984.
Wang, J.; Gudiksen, M. S.; Duan, X.; Cui, Y.; Lieber, C. M. Highly polarized photoluminescence and photo detection from single indium phosphide nanowires. Science 2001, 293, 1455–1457.
Pangal, K.; Sturm, J. C.; Wagner, S. Integration of amorphous and polycrystalline silicon thin-film transistors through selective crystallization of amorphous silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 2091–2093.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Yi, J., Lee, W.W. et al. Optical properties of laterally aligned Si nanowires for transparent electronics applications. Nano Res. 4, 817–823 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0138-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0138-5