Abstract
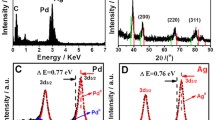
Hexagram shaped gold particles and their analogues enclosed by high index facets with kinks have been successfully synthesized by reducing HAuCl4 with ascorbic acid (AA) in the presence of poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) at room temperature. By using electron microscopy, the surfaces of the hexagram shaped Au particle were found to be {541} planes, which contain high-density steps and kinks. In addition, it was found that hexagonal shield-like and other kind of particles present in the product were analogues of the hexagram shaped Au particles structure, in that they had the same surface structure. In order to confirm the surface structure of all the prepared particles, surface structure sensitive underpotential deposition of Pb was carried out, and the cyclic voltammetric profile was in accordance with the proposed {541} surface. Finally, structure-property relationships of the Au hexagrams were experimentally analyzed by employing the electrocatalytic oxidation of AA as a probe reaction. The electrocatalytic reactions of gold cubes with low-index {100} facets and gold trioctahedra with {221} facets were studied as references. The experimental results showed that the hexagram shaped Au particles and their analogues with exposed {541} facets have the highest catalytic activity among the three kinds of gold particles, owing to the high density of kink atoms. This study should motivate us to further explore methods for the preparation of other well-defined polyhedral metal nanocrystals enclosed by high index surfaces.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Somorjai, G. A.; Blakely, D. W. Mechanism of catalysis of hydrocarbon reactions by platinum surfaces. Nature 1975, 258, 580–583.
Somorjai, G. A. Modern surface science and surface technologies: An introduction. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 1223–1236.
Baldauf, M.; Kolb, D. M. Formic acid oxidation on ultrathin Pd films on Au(hkl) and Pt(hkl) electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 11375–11381.
Hoshi, N.; Kida, K.; Nakamura, M.; Nakada, M.; Osada, K. Structural effects of electrochemical oxidation of formic acid on single crystal electrodes of palladium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 12480–12484.
Mahmoud, M. A.; Tabor, C. E.; El-Sayed, M. A.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. L. A new catalytically active colloidal platinum nanocatalyst: The multiarmed nanostar single crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4590–4591.
Lee, H.; Habas, S. E.; Kweskin S.; Butcher D.; Somorjai, G. A.; Yang, P. D. Morphological control of catalytically active platinum nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7824–7828.
Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M. A. Catalysis with transition metal nanoparticles in colloidal solution: Nanoparticle shape dependence and stability. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12663–12676.
Zijlstra, P.; Chon, J. W. M.; Gu, M. Five-dimensional optical recording mediated by surface plasmons in gold nanorods. Nature 2009, 459, 410–413.
Tao, A. R.; Habas, S.; Yang, P. D. Shape control of colloidal metal nanocrystals. Small 2008, 4, 310–325.
Tian, Z. Q.; Ren, B.; Wu, D. Y. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: From noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9463–9383.
Choi, J. S.; Choi, H. J.; Jung, D. C.; Lee, J. H.; Cheon, J. Nanoparticle assisted magnetic resonance imaging of the early reversible stages of amyloid β self-assembly. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2197–2199.
Meulenberg, R. W.; Lee, J. R. I.; McCall, S. K.; Hanif, K. M.; Haskel, D.; Lang, J. C.; Terminello, L. J.; Buuren, T. V. Evidence for ligand-induced paramagnetism in CdSe quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6888–6889.
Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782.
Yang, H. G.; Sun, C. H.; Qiao, S. Z.; Zou, J.; Liu, G.; Smith, S. C.; Cheng, H. M.; Lu, G. Q. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature 2008, 453, 638–641.
Hang, X. G.; Kuang, Q.; Jin, M. S.; Xie, Z. X.; Zheng, L. S. Synthesis of titania nanosheets with a high percentage of exposed (001) facets and related photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3152–3153.
Yang, H. G.; Liu, G.; Qiao, S. Z.; Sun, C. H.; Jin, Y. G.; Smith, S. C.; Zou, J.; Cheng, H. M.; Lu, G. Q. Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant {001} facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4078–4083.
Xie, X. W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Q.; Haruta, M.; Shen, W. J. Low- temperature oxidation of CO catalysed by Co3O4 nanorods. Nature 2009, 458, 746–749.
Lebedeva, N. P.; Koper, M. T. M.; Feliu, J. M.; van Santen, R. A. Role of crystalline defects in electrocatalysis: Mechanism and kinetics of CO adlayer oxidation on stepped platinum electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 12938–12947.
Sun, S. G.; Chen, A. C.; Huang, T. S.; Li, J. B.; Tian, Z. W. Electrocatalytic properties of Pt(111), Pt(332), Pt(331) and Pt(110) single crystal electrodes towards ethylene glycol oxidation in sulphuric acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1992, 340, 213–216.
Sau, T. K.; Murphy, C. J. Room temperature, high-yield synthesis of multiple shapes of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8648–8649.
Li, C. C.; Shuford, K. L.; Park, Q. -H.; Cai, W. P.; Li, Y.; Lee, E. J.; Cho, S. O. High-yield synthesis of single-crystalline gold nano-octahedra. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3264–3268.
Niu, W. X.; Zheng, S. L.; Wang, D. W.; Liu, X. Q.; Li, H. J.; Han, S.; Chen, J. A.; Tang, Z. Y.; Xu, G. B. Selective synthesis of single-crystalline rhombic dodecahedral, octahedral, and cubic gold nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 697–703.
Tian, N.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Sun, S. G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 2007, 316, 732–735.
Tian, N.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Sun, S. G. Platinum metal catalysts of high-index surfaces: From single-crystal planes to electrochemically shape-controlled nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19801–19817.
Ma, Y. Y.; Kuang, Q.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Xie, Z. X.; Huang, R. B.; Zheng, L. S. Synthesis of trisoctahedral gold nanocrystals with exposed high-index facets by a facile chemical method. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8901–8904.
Ming, T.; Feng, W.; Tang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, L. D.; Wang, J. F.; Yan, C. H. Growth of tetrahexahedral gold nanocrystals with high-index facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16350–16351.
Liao, H. G.; Jiang, Y. X.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Chen, S. P.; Sun, S. G. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles in deep eutectic solvents for studies of structure-functionality relationships in electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9100–9103.
Zhang, J.; Langille, M. R.; Personick, M. L.; Zhang, K.; Li, S. Y.; Mirkin, C. A. Concave cubic gold nanocrystals with high-index facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14012–14014.
Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q. B.; Lu, X. M.; Lee, J. Y. Seed-mediated synthesis of monodisperse concave trisoctahedral gold nanocrystals with controllable sizes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 11119–11126.
Li, J.; Wang, L. H.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Han, X. D.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral Au nanocrystals with exposed high-index surfaces. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5109–5111.
Kim, D. Y.; Im, S. H.; Park, O. O. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral gold nanocrystals with high-index facets. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 3321–3323.
Murphy, C. J.; Sau, T. K.; Gole, A. M.; Orendorff, C. J.; Gao, J. X.; Gou, L. F.; Hunyadi, S. E.; Li, T. Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: Synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13857–13870.
Liang, H. Y.; Yang, H. X.; Wang, W. Z.; Li, J. Q.; Xu, H. X. High-yield uniform synthesis and microstructure-determination of rice-shaped silver nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6068–6069.
Germain, V.; Li, J.; Ingert, D.; Wang, Z. L.; Pileni, M. P. Stacking faults in formation of silver nanodisks. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8717–8720.
Zhang, S. H.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Xie, Z. X.; Xu, X.; Huang, R. B.; Zheng L. S. Growth of silver nanowires from solutions: A cyclic penta-twinned-crystal growth mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 9416–9421.
Aherne, D.; Ledwith, D. M.; Gara, M.; Kelly, J. M. Optical properties and growth aspects of silver nanoprisms produced by a highly reproducible and rapid synthesis at room temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2005–2016.
Hamelin, A. Cyclic voltammetry at gold single-crystal surfaces. Part 1. Behaviour at low-index faces. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 407, 1–11.
Hernández, J.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Herrero, E. Gold nanoparticles synthesized in a water-in-oil microemulsion: Electrochemical characterization and effect of the surface structure on the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 574, 185–196.
Hernández, J.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Herrero, E.; Aldaz, A.; Feliu, J. M. Electrochemistry of shape-controlled catalysts: Oxygen reduction reaction on cubic gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14078–14083.
Wang, Z. J.; Yuan, J. H.; Zhou, M.; Niu, L.; Ivaska, A. Synthesis, characterization and mechanism of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide bilayer-encapsulated gold nanosheets and nanocrystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 6289–6293.
Kou, X. S.; Zhang, S. Z.; Tsung, C. K.; Yang, Z.; Yeung, M. H.; Stucky, G. D.; Sun, L. D.; Wang, J. F.; Yan, C. H. One-step synthesis of large-aspect-ratio single-crystalline gold nanorods by using CTPAB and CTBAB surfactants. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 2929–2936.
Gole, A.; Murphy, C. J. Seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanorods: Role of the size and nature of the seed. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 3633–3640.
Yamamoto, M.; Kashiwagi, Y.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H.; Nakamoto, M. Synthesis and morphology of star-shaped gold nanoplates protected by poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone). Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5391–5393.
Li, C. C.; Shuford, K. L.; Chen, M. H.; Lee, E. J.; Cho, S. O. A facile polyol route to uniform gold octahedra with tailorable size and their optical properties. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1760–1769.
Chen, H. J.; Wang, Y. L.; Dong, S. J. An effective hydrothermal route for the synthesis of multiple PDDA-protected noble-metal nanostructures. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 10587–10593.
Trasatti, S.; Petrii, O. A. Real surface area measurements in electrochemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 711–734.
Woods, R. Chemisorption at electrodes: Hydrogen and oxygen on nobel metals and their alloys. In Electroanalytical Chemistry—A Series of Advances; Bard, A. J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York and Basel, 1976; pp. 119–125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., Jiang, Z., Zhang, L. et al. Synthesis and high electrocatalytic performance of hexagram shaped gold particles having an open surface structure with kinks. Nano Res. 4, 612–622 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0117-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-011-0117-x