Abstract
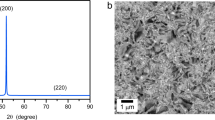
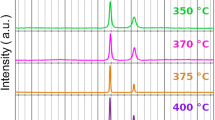
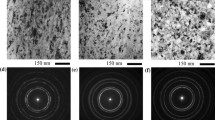
The microstructure and texture characteristics of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel have been investigated in the present work. The material has been studied both in an as-received state and after in-situ and ex-situ annealing. The ASTAR automated crystal orientation mapping in a transmission electron microscope complemented by electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) has been used in the investigation. The as-deposited material consisted of nanograins interspersed with coarser (sub)grain clusters, arranged in large mesoscale colonies and characterized by a dominant 〈001〉 fiber texture aligned with the deposition direction (DD). A large fraction of nanograin/cluster boundaries displayed a low-coincidence site lattice (low Σ) or twin character. The EBSD study confirmed the previously suggested presence of the “cobblestone”-type mesotexture, characterized by a local 〈001〉 fiber axis approximately perpendicular to the hemispherical growth surface of a mesoscale colony. The (sub)grain clusters contained low-angle boundaries and displayed large misorientation gradients; nevertheless, their orientations did not statistically differ from the surrounding nanograins. They did not serve as nuclei for the abnormal grain growth observed during annealing. The 〈001〉//DD to 〈111〉//DD fiber texture transition occurring during annealing did not result from the growth of pre-existing suitably oriented nuclei. Instead, copious twinning occurring along the migration front of the abnormally growing grains appeared to be primarily responsible for the above transition.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Dalla Torre, H. Van Swygenhoven, and M. Victoria: Acta Mater., 2002, vol. 50, pp. 3957-3970.
2. K.S. Kumar, S. Suresh, M.F. Chisholm, J.A. Horton, and P. Wang: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 387-405.
3. K.S. Kumar, H. Van Swygenhoven, and S. Suresh: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp. 5743-5774.
4. M.A. Meyers, A. Mishra, and D.J. Benson: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2006, vol. 51, pp. 427-556.
5. M. Dao, L. Lu, R.J. Asaro, J.T.M. De Hosson, and E. Ma: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 4041-4065.
6. U. Erb: Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, vol. 6, pp. 533-538.
7. A.M. El-Sherik and U. Erb: J. Mater. Sci., 1995, vol. 30, pp. 5743-5749.
8. B.Y.C. Wu, P.J. Ferreira, and C.A. Shuh: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 1927-1936.
9. K. Schüler, B. Philippi, M. Weinmann, V.M. Marx, and H. Vehoff: Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 3945-3955.
10. S. Ruan and C.A. Schuh, Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 1218-1221.
11. M.R. Barnett, P. Cizek, M. Nave, A. Sullivan, and R. Balasubramaniam: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 603-606.
12. P. Cizek, M.R. Barnett, M.D. Nave, E.F. Rauch, and R. Balasubramaniam: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 2048-2060.
13. U. Klement, U. Erb, and K.T. Aust: Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, vol. 6., pp. 581-584.
14. U. Klement, U. Erb, A.M. El-Sherik, and K.T. Aust: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, vol. A203, pp. 177-186.
15. N. Wang, Z. Wang, K.T. Aust, and U. Erb: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 1655-1669.
U. Klement and M. da Silva: J. Alloys Compd., 434-435, pp. 714-717.
17. U. Klement, M. da Silva, and W. Skrotzki: J. Microsc., 2008, vol. 230, pp. 455-463.
18. G.D. Hibbard, V. Radmilovic, K.T. Aust, and U. Erb: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2008, vol. A494, pp. 232-238.
19. F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Elsevier, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2004.
20. P. Cizek, A. Sankaran, E.F. Rauch, and M.R. Barnett: Scripta Mater., 2012, vol. 67, pp. 685-688.
21. F. Czerwinski, H. Li, M. Megret, J.A. Szpunar, D.G. Clark, and U. Erb: Scripta Mater., 1997, vol. 37, pp. 1967-1972.
22. E.F. Rauch and L. Dupuy: Archives Metall. Mater., 2005, vol. 50, pp. 87-99.
23. E.F. Rauch, J. Portillo, S. Nicolopoulos, D. Bultreys, S. Rouvimov, and P. Moeck: Z. Kristallogr., 2010, vol. 225, pp. 103-109.
24. E.F. Rauch and M. Véron: Mater. Charact., 2014, vol. 98, pp. 1-9.
25. G. Gottstein and L.S. Shvindlerman: Grain Boundary Migration in Metals, 2nd ed., CRC Press, London, United Kingdom, 2010.
26. C. Cayron: Acta Cryst., 2007, vol. A63, pp. 11-29.
27. H.J. Bunge: Texture Analysis in Materials Science – Mathematical Methods, Butterworth, London, United Kingdom, 1982.
28. O. Engler and V. Randle: Introduction to Texture Analysis – Macrotexture, Microtexture and Orientation Mapping, 2nd ed., CRC Press, Abingdon, United Kingdom, 2010.
Acknowledgments
The present work was carried out with the support of the Deakin Advanced Characterization Facility. Financial support provided by the Australian Research Council is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 10, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cizek, P., Sankaran, A., Rauch, E.F. et al. Microstructure and Texture of Electrodeposited Nanocrystalline Nickel in the As-Deposited State and After In-Situ and Ex-Situ Annealing. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 6655–6670 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3810-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3810-2