Abstract
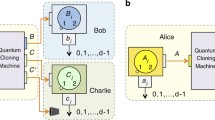
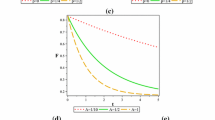
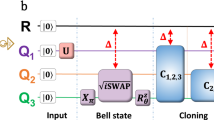
We demonstrate the possibility of controlling the success probability of a secret sharing protocol using a quantum cloning circuit. The cloning circuit is used to clone the qubits containing the encoded information and en route to the intended recipients. The success probability of the protocol depends on the cloning parameters used to clone the qubits. We also establish a relation between the concurrence of initially prepared state, entanglement of the mixed state received by the receivers after cloning scheme and the cloning parameters of cloning machine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., Rosen, N.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys. Rev. 47, 777 (1935)
Bennett, C.H., Divincenzo, D.: Quantum information and computation. Nature 404, 247 (2000)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Bouwmeester, D., Pan, J.W., Mattle, K., Eibl, M., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575 (1997)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145 (2002)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829 (1999)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59, 162 (1999)
Bandyopadhyay, S.: Teleportation and secret sharing with pure entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012308 (2000)
Bagherinezhad, S., Karimipour, V.: Quantum secret sharing based on reusable Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states as secure carriers. Phys. Rev. A 67, 044302 (2003)
Lance, A.M., Symul, T., Bowen, W.P., Sanders, B.C., Lam, P.K.: Tripartite quantum state sharing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 177903 (2004)
Gordon, G., Rigolin, G.: Generalized quantum-state sharing. Phys. Rev. A 73, 062316 (2006)
Zheng, S.B.: Splitting quantum information via W states. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054303 (2006)
Li, Q., Chan, W.H., Long, D.-Y.: Semiquantum secret sharing using entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 82, 022303 (2010)
Tittel, W., Zbinden, H., Gisin, N.: Experimental demonstration of quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 63, 042301 (2001)
Schmidt, C., Trojek, P., Bourennane, M., Kurtsiefer, C., Zukowski, M., Weinfurter, H.: Experimental single qubit quantum secret sharing. Rev. Lett. 95, 230505 (2005)
Schmidt, C., Trojek, P., Gaertner, S., Bourennane, M., Kurtsiefer, C., Zukowski, M., Weinfurter, H.: Experimental quantum secret sharing. Fortschritte der Physik 54, 831 (2006)
Bogdanski, J., Rafiei, N., Bourennane, M.: Experimental quantum secret sharing using telecommunication fiber. Phys. Rev. A 78, 062307 (2008)
Buzek, V., Hillery, M.: Universal optimal cloning of arbitrary quantum states: from qubits to quantum registers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5003 (1998)
Hill, S., Wootters, W.K.: Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 5022 (1997)
Wootters, W.K.: Entanglement of a pair of quantum bits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2245 (1998)
Bertlmann, R.A., Durstberger, K., Hiesmayr, B.C., Krammer, P.: Optimal entanglement witnesses for qubits and qutrits. Phys. Rev. A 72, 052331 (2005)
Sanpera, A., Bruss, D., Lewenstein, M.: Schmidt-number witnesses and bound entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 63, 050301(R) (2001)
Werner, R.F.: Quantum states with Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model. Phys. Rev. A 40, 4277 (1989)
Wootters, W.K., Zurek, W.H.: A single quantum cannot be cloned. Nature 299, 802 (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adhikari, S., Roy, S., Chakraborty, S. et al. Controlled secret sharing protocol using a quantum cloning circuit. Quantum Inf Process 13, 2071–2080 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0791-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0791-1