Abstract
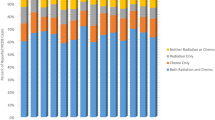
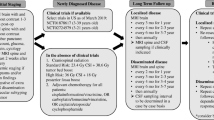
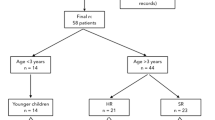
The literature on medulloblastoma in adults is generally limited to case reports and retrospective series, and there is no accepted standard of care. The Cooperative Trials Group for Neuro-Oncology (COGNO) sought to determine the range and consistency of clinicians’ approaches to management as a basis for future trials. We aimed to identify current treatment strategies for adult medulloblastoma through an online survey launched at the 2012 Society of Neuro-Oncology meeting and by email invitation. Clinicians who had treated at least one adult patient with medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), or pineoblastoma in the preceding year were asked about their most recent patient and invited to discuss their approach to a typical clinical scenario. Between November 2012 and January 2013, 45 clinicians (11 medical oncologists, 8 radiation oncologists, 5 pediatric oncologists, and 21 others) from Australia (24), United States (3), Europe (4) and other countries (14) completed the survey. Responding clinicians had treated 54 cases in the past 12 months. The most common histological type was medulloblastoma (64 %), then PNET (20 %). Most patients were male (68 %), and had high-risk disease (65 %). Complete surgical resection in 56 and 32 % had molecular testing. Radiotherapy was predominantly cranio-spinal (92 %) and given mostly post-resection (80 %). Combination chemotherapy was more common than single-agent chemotherapy. The choice of chemotherapy varied considerably. There is substantial variation in the treatment of adult medulloblastoma, most pronounced in the choice of chemotherapeutic agents, highlighting the need for further collaborative research to guide evidence-based treatment strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114(2):97–109
Gandhi R, Babu R, Cummings TJ, Adamson C (2013) Adult primitive neuroectodermal tumors: the prognostic value of supratentorial location. J Neuro-Oncol 114(1):141–148
Polkinghorn WR, Tarbell NJ (2007) Medulloblastoma: tumorigenesis, current clinical paradigm, and efforts to improve risk stratification. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4(5):295–304
Korshunov A, Remke M, Werft W et al (2010) Adult and pediatric medulloblastomas are genetically distinct and require different algorithms for molecular risk stratification. J Clin Oncol 28(18):3054–3060
Parkin D, Whelan S, Ferlay J, Teppo L, Thomas D (2002) Cancer incidence in five continents. Vol. VIII. IARC Scient. Publ Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, p 155
Wong SF, Mak G, Rosenthal MA, Cher L, Gan HK (2013) Local perspective on a rare brain tumour: adult medulloblastoma. Intern Med J 43(5):567–572
Lai R (2008) Survival of patients with adult medulloblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer 112(7):1568–1574
Ang C, Hauerstock D, Guiot MÄ et al (2008) Characteristics and outcomes of medulloblastoma in adults. Ped Blood Cancer 51(5):603–607
Remke M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA et al (2011) Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29(19):2717–2723
Pfister S, Remke M, Benner A et al (2009) Outcome prediction in pediatric medulloblastoma based on DNA copy-number aberrations of chromosomes 6q and 17q and the MYC and MYCN loci. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1627–1636
Chan AW, Tarbell NJ, Black PM et al (2000) Adult medulloblastoma: prognostic factors and patterns of relapse. Neurosurgery 47(3):623–631
Silvani A, Gaviani P, Lamperti E et al (2012) Adult medulloblastoma: multiagent chemotherapy with cisplatinum and etoposide: a single institutional experience. J Neuro-Oncol 106(3):595–600
Brandes A, Franceschi E, Tosoni A et al (2009) Adult neuroectodermal tumors of posterior fossa (medulloblastoma) and of supratentorial sites (stPNET). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 71(2):165–179
Brandes A, Franceschi E, Tosoni A et al (2007) Long-term results of a prospective study on the treatment of medulloblastoma in adults. Cancer 110(9):2035–2041
Call JA, Naik M, Rodriguez FJ et al (2014) Long-term outcomes and role of chemotherapy in adults with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol 37(1):1–7
Friedrich C, von Bueren AO, von Hoff K et al (2013) Treatment of adult nonmetastatic medulloblastoma patients according to the paediatric HIT 2000 protocol: a prospective observational multicentre study. Eur J Cancer 49(4):893–903
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted under the auspices of the Cooperative Trials Group for Neuro-Oncology (COGNO), coordinated at the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Clinical Trials Centre, University of Sydney. Special thanks to COGNO staff for coordinating the survey. This study was partly funded by the ‘Support for Cancer Clinical Trials 2013-2016’ Cancer Australia grant to the Cooperative Trials Group for Neuro-oncology (COGNO).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cosman, R., Brown, C.S.B., DeBraganca, K.C. et al. Patterns of care in adult medulloblastoma: results of an international online survey. J Neurooncol 120, 125–129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1525-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1525-z