Abstract
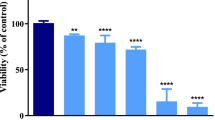
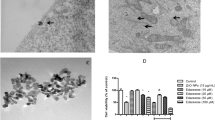
This study was to determine the possible neurotoxicity and mechanisms underlying the effects of nano-ZnO with sizes of 20–80 nm on central nervous system (CNS). The cytotoxicity of nano-ZnO was investigated in PC12 cells. The viability of cells was observed by a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) for cells was evaluated by a fluorometry assay. The apoptosis of cells was detected and analyzed by flow cytometry. In addition, effects of nano-ZnO on the properties of high-voltage-activated (HVA) calcium currents were studied in acutely isolated rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons using the whole-cell patch clamp technique. The results of MTT assay showed that nano-ZnO (10−4 g/mL) caused a significant decrease in cell viability (P < 0.05). Nano-ZnO induced intracellular accumulation of ROS and the apoptosis of PC12 cells with the increasing concentration of nano-ZnO in flow cytometric assay (P < 0.05). Further results of electrophysiological recording indicated that 10−4 g/mL nano-ZnO first altered the current–voltage curve and the peak amplitudes of HVA calcium currents at 10 min of the recording, and the peak current amplitudes were increased significantly at the end of 30 min (P < 0.05). All these results suggested that the increase of intracellular ROS was one of potential mechanisms of cellular apoptosis induced by nano-ZnO. Nano-ZnO could cause the elevation of cytosolic calcium levels by enhancement of HVA calcium currents, which would increase the generation of intracellular ROS, and consequently promote the neuronal apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arundine M, Tymianski M (2003) Molecular mechanisms of calcium-dependent neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 34:325–337. doi:10.1016/S0143-4160(03)00141-6
Beckman KB, Ames BN (1998) The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev 78:547–581
Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Peppiatt CM, Prothero LS, MacKenzie L, De Smet P, Travers M, Tovey SC, Seo JT, Berridge MJ, Ciccolini F, Lipp P (2001) Calcium signaling: an overview. Semin Cell Dev Biol 12:3–10. doi:10.1006/scdb.2000.0211
Bouron A, Boisseau S, De Waard M, Peris L (2006) Differential down-regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel currents by glutamate and BDNF in embryonic cortical neurons. Eur J Neurosci 24:699–708. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04946.x
Brayner R, Ferrari-Iliou R, Brivois N, Djediat S, Benedetti MF, Fievet F (2006) Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett 6:866–870. doi:10.1021/nl052326h
Brunner TJ, Wick P, Manser P, Spohn P, Grass RN, Limbach LK, Bruinink A, Stark WJ (2006) In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 40:4374–4381. doi:10.1021/es052069i
Campbell LW, Hao SY, Thibault O, Blalock EM, Landfield PW (1996) Aging changes in voltage-gated calcium currents in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurosci 16:6286–6295
Catterall WA (2000) Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:521–555
Doering CJ, Zamponi GW (2003) Molecular pharmacology of high voltage-activated calcium channels. J Bioenerg Biomembr 35:491–505. doi:10.1023/B:JOBB.0000008022.50702.1a
Elder A, Gelein R, Silva V, Feikert T, Opanashuk L, Carter J, Potter R, Maynard A, Ito Y, Finkelstein J, Oberdörster G (2006) Translocation of inhaled ultrafine manganese oxide particles to the central nervous system. Environ Health Perspect 114:1172–1178. doi:10.1289/ehp.9030
Elhamdani A, Bossu JL, Feltz A (1995) ADP exerts a protective effect against rundown of the Ca2+ current in bovine chromaffin cells. Pflug Arch Eur J Phy 430:401–409. doi:10.1007/BF00373916
Feissner RF, Skalska J, Gaum WE, Sheu SS (2009) Crosstalk signaling between mitochondrial Ca2+ and ROS. Front Biosci 14:1197–1218
Franklin NM, Rogers NJ, Apte SC, Batley GE, Gadd GE, Casey PS (2007) Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, Bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 41:8484–8490. doi:10.1021/es071445r
Furukawa K, Wang Y, Yao PJ, Fu W, Mattson MP, Itoyama Y, Onodera H, D’Souza I, Poorkaj PH, Bird TD, Schellenberg GD (2003) Alteration in calcium channel properties is responsible for the neurotoxic action of a familial frontotemporal dementia tau mutation. J Neurochem 87:427–436. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02020.x
Ghule K, Ghule A, Chen BJ, Ling YC (2006) Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles coated paper and its antibacterial activity study. Green Chem 8:1034–1041. doi:10.1039/B605623G
Green KN, Peers C (2002) Divergent pathways account for two distinct effects of amyloid β peptides on exocytosis and Ca2+ currents involvement of ROS and NF-κB. J Neurochem 81:1043–1051. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.00907.x
Green KN, Boyle JP, Peers C (2002) Hypoxia potentiates exocytosis and Ca2+ channels in PC12 cells via increased amyloid beta peptide formation and reactive oxygen species generation. J Physiol 541:1013–1023. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.017582
Han D, Tian Y, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2011) Nano-zinc oxide damages spatial cognition capability via over-enhanced long-term potentiation in hippocampus of Wistar rats. Int J Nanomed 6:1453–1461. doi:10.2147/IJN.S18507
Heinlaan M, Ivask A, Blinova I, Dubourguier HC, Kahru A (2008) Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere 71:1308–1316. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.047
Jen J (1999) Calcium channelopathies in the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9:274–280. doi:10.1016/S0959-4388(99)80040-3
Jeng HA, Swanson J (2006) Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J Environ Sci Health A 41:2699–2711. doi:10.1080/10934520600966177
Jiang W, Mashayekhi H, Xing B (2009) Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano- and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ Pollut 157:1619–1625. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.12.025
Kourie JI (1998) Interaction of reactive oxygen species with ion transport mechanisms. Am J Physiol 275:C1–C24
Lin WS, Xu Y, Huang CC, Ma Y, Shannon KB, Chen DR, Huang YW (2009) Toxicity of nano- and micro-sized ZnO particles in human lung epithelial cells. J Nanopart Res 11:25–39. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9419-7
Lockman PR, Koziara JM, Mumper RJ, Allen DD (2004) Nanoparticle surface charges alter blood–brain barrier integrity and permeability. J Drug Target 12:635–641. doi:10.1080/10611860400015936
Long TC, Tajuba J, Sama P, Saleh N, Swartz C, Parker J, Hester S, Lowry GV, Veronesi B (2007) Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ Health Perspect 115:1631–1637. doi:10.1289/ehp.10216
Ma H, Bertsch PM, Glenn TC, Kabengi NJ, Williams PL (2009) Toxicity of manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1324–1330. doi:10.1897/08-262.1
Mattson MP (1996) Calcium and free radicals: mediators of neurotrophic factor and excitatory transmitter-regulated developmental plasticity and cell death. Perspect Dev Neurobiol 3:79–91
Mattson MP (2007) Calcium and neurodegeneration. Aging Cell 6:337–350. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00275.x
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627. doi:10.1126/science.1114397
Oberdorster G, Sharp Z, Atudorei V, Elder A, Gelein R, Kreyling W, Cox C (2004) Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal Toxicol 16:437–445. doi:10.1080/08958370490439597
Ohkuma S, Katsura M, Higo A, Shirotani K, Hara A, Tarumi C, Ohgi T (2001) Peroxynitrite affects Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent calcium channels. J Neurochem 76:341–350. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00045.x
Peers C, Scragg JL, Boyle JP, Fearon IM, Taylor SC, Green KN, Webster NJ, Ramsden M, Pearson HA (2005) A central role for ROS in the functional remodelling of L-type Ca2+ channels by hypoxia. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:2247–2254. doi:10.1098/rstb.2005.1761
Reddy KM, Feris K, Bell J, Wingett DG, Hanley C, Punnoose A (2007) Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Appl Phys Lett 90:2139021–2139023. doi:10.1063/1.2742324
Sayes CM, Reed KL, Warheit DB (2007) Assessing toxicity of fine and nanoparticles: comparing in vitro measurements to in vivo pulmonary toxicity profiles. Toxicol Sci 97:163–180. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfm018
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 5:415–418. doi:10.1023/A:1009616228304
Tam KH, Djurišić AB, Chan CMN, Xi YY, Tse CW, Leung YH, Chan WK, Leung FCC, Au DWT (2008) Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanorods prepared by a hydrothermal method. Thin Solid Films 516:6167–6174. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.11.081
Turski L, Bressler K, Rettig KJ, Loschmann PA, Wachtel H (1991) Protection of substantia nigra from MPP+ neurotoxicity by N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists. Nature 349:414–418
Tymianski M, Wallace MC, Spigelman I, Uno M, Carlen PL, Tator CH, Charlton MP (1993) Cell-permeant Ca2+ chelators reduce early excitotoxic and ischemic neuronal injury in vitro and in vivo. Neuron 11:221–235. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(93)90180-Y
Wagner JJ, Alger BE (1994) GTP modulates run-up of whole-cell Ca2+ channel current in a Ca2+-dependent manner. J Neurophysiol 71:814–816
Wang ZL (2008) Splendid one-dimensional nanostructures of zinc oxide: a new nanomaterial family for nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2:1987–1992. doi:10.1021/nn800631r
Wang B, Feng WY, Wang M, Shi JW, Zhang F, Ouyang H, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Huang YY, Xie YN, Wang HF, Wang J (2007) Transport of intranasally instilled fine Fe2O3 particles into the brain: micro-distribution, chemical states, and histopathological observation. Biol Trace Elem Res 118:233–243. doi:10.1007/s12011-007-0028-6
Wang B, Feng WY, Wang M, Wang TC, Gu YQ, Zhu MT, Ouyang H, Shi JW, Zhang F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Wang HF, Wang J (2008a) Acute toxicological impact of nano- and submicro-scaled zinc oxide powder on healthy adult mice. J Nanopart Res 10:263–276. doi:10.1007/s11051-007-9245-3
Wang JX, Chen CY, Liu Y, Jiao F, Li W, Lao F, Li YF, Li B, Ge CC, Zhou GQ, Gao Y, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2008b) Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO2 nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicol Lett 183:72–80. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.10.001
Wang JX, Liu Y, Jiao F, Lao F, Li W, Gu YQ, Li YF, Ge CC, Zhou GQ, Li B, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Chen CY (2008c) Time-dependent translocation and potential impairment on central nervous system by intranasally instilled TiO2 nanoparticles. Toxicology 254:82–90. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.09.014
Wang B, Feng WY, Zhu MT, Wang Y, Wang M, Gu YQ, Ouyang H, Wang HJ, Li M, Zhao YL, Chai ZF, Wang HF (2009) Neurotoxicity of low-dose repeatedly intranasal instillation of nano- and submicron-sized ferric oxide particles in mice. J Nanopart Res 11:41–53. doi:10.1007/s11051-008-9452-6
Weiss JH, Hartley DM, Koh J, Choi DW (1990) The calcium channel blocker nifedipine attenuates slow excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity. Science 247:1474–1477
Wiench K, Wohlleben W, Hisgen V, Radke K, Salinas E, Zok S, Landsiedel R (2009) Acute and chronic effects of nano- and non-nano-scale TiO2 and ZnO particles on mobility and reproduction of the freshwater invertebrate Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 76:1356–1365. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.025
Yamamoto O, Komatsu M, Sawai J, Nakagawa ZE (2004) Effect of lattice constant of zinc oxide on antibacterial characteristics. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:847–851. doi:10.1023/B:JMSM.0000036271.35440.36
Yang Z, Liu ZW, Allaker R, Reip P, Oxford J, Ahmad Z, Ren G (2010) A review of nanoparticle functionality and toxicity on the central nervous system. J R Soc Interface 7:S411–S422. doi:10.1098/rsif.2010.0158.focus
Zhang L, Jiang Y, Ding Y, Povey M, York D (2007) Investigation into the antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids). J Nanopart Res 9:479–489. doi:10.1007/s11051-006-9150-1
Zhao J, Xu L, Zhang T, Ren G, Yang Z (2009) Influences of nanoparticle zinc oxide on acutely isolated rat hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. Neurotoxicology 30:220–230. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2008.12.005
Zhu X, Zhu L, Duan Z, Qi R, Li Y, Lang Y (2008) Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. J Environ Sci Health A 43:278–284. doi:10.1080/10934520701792779
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070890) and the Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (10JCZDJC19100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhao Jingxia and Yao Yang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Yao, Y., Liu, S. et al. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and high-voltage-activated calcium currents in nanoparticle zinc oxide-induced cytotoxicity in vitro. J Nanopart Res 14, 1238 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1238-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1238-1