Abstract
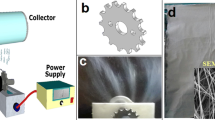
Needleless electrospinning is expected to produce nanofibers with a large productivity. In this study, a sprocket wheel disk was used as spinneret to electrospin nanofibers. The sprocket disk shows reliable electrospinning process. In comparison with the conventional disk spinneret, which has no sprocket on the edge, the sprocket wheel produced more uniform nanofibers with smaller fiber diameter. The electric field analysis results indicated that the sprocket wheel generates higher intensity of electric field.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahay R, Parveen H, Baji A, Ganesh VA, Ranganath AS (2017) Fabrication of PVDF hierarchical fibrillar structures using electrospinning for dry-adhesive applications. J Mater Sci 52:2435–2441. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0537-9
Cai Y, Gevelber M (2017) Analysis of bending region physics in determining electrospun fiber diameter: effect of relative humidity on evaporation and force balance. J Mater Sci 52:2605–2627. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0553-9
Sanfelice RC, Mercante LA, Pavinatto A, Tomazio NB, Mendonça CR, Ribeiro SJL et al (2017) Hybrid composite material based on polythiophene derivative nanofibers modified with gold nanoparticles for optoelectronics applications. J Mater Sci 52:1919–1929. doi:10.1007/s10853-016-0481-8
Panthi G, Park S-J, Kim T-W, Chung H-J, Hong S-T, Park M et al (2015) Electrospun composite nanofibers of polyacrylonitrile and Ag2CO3 nanoparticles for visible light photocatalysis and antibacterial applications. J Mater Sci 50:4477–4485. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-8995-z
Chiscan O, Dumitru I, Tura V, Stancu A (2012) PVC/Fe electrospun nanofibers for high frequency applications. J Mater Sci 47:2322–2327. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-6047-x
Zhang L, Aboagye A, Kelkar A, Lai C, Fong H (2014) A review: carbon nanofibers from electrospun polyacrylonitrile and their applications. J Mater Sci 49:463–480. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7705-y
Van Hong Thien D, Hsiao SW, Ho MH, Li CH, Shih JL (2013) Electrospun chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci 48:1640–1645. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6921-1
Jing X, Jin E, Mi H-Y, Li W-J, Peng X-F, Turng L-S (2015) Hierarchically decorated electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/nanohydroxyapatite composite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Sci 50:4174–4186. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-8933-0
Zahedi P, Rezaeian I, Jafari SH (2013) In vitro and in vivo evaluations of phenytoin sodium-loaded electrospun PVA, PCL, and their hybrid nanofibrous mats for use as active wound dressings. J Mater Sci 48:3147–3159. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-7092-9
Ramakrishna S, Jose R, Archana PS, Nair AS, Balamurugan R, Venugopal J et al (2010) Science and engineering of electrospun nanofibers for advances in clean energy, water filtration, and regenerative medicine. J Mater Sci 45:6283–6312. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4509-1
Goh Y-F, Shakir I, Hussain R (2013) Electrospun fibers for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound dressing. J Mater Sci 48:3027–3054. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7145-8
Fang J, Niu H, Wang H, Wang X, Lin T (2013) Enhanced mechanical energy harvesting using needleless electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibre webs. Energy Environ Sci 6:2196–2202
Peng S, Li L, Lee JKY, Tian L, Srinivasan M, Adams S et al (2016) Electrospun carbon nanofibers and their hybrid composites as advanced materials for energy conversion and storage. Nano Energy 22:361–395
Zhang B, Kang F, Tarascon J-M, Kim J-K (2016) Recent advances in electrospun carbon nanofibers and their application in electrochemical energy storage. Progress Mater Sci 76:319–380
Wang J, Yang G, Wang L, Yan W (2016) Fabrication of one-dimensional CdFe2O4 yolk/shell flat nanotubes as a high-performance anode for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Sci, pp 1–13, doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0672-3
Qin X, Subianto S (2017) 17 - Electrospun nanofibers for filtration applications A2 - Afshari, Mehdi. In: Electrospun nanofibers, ed, Woodhead Publishing, p 449–466
Ortenzi MA, Basilissi L, Farina H, Di Silvestro G, Piergiovanni L, Mascheroni E (2015) Evaluation of crystallinity and gas barrier properties of films obtained from PLA nanocomposites synthesized via “in situ” polymerization of l-lactide with silane-modified nanosilica and montmorillonite. Eur Polym J 66:478–491
Neppalli R, Causin V, Benetti EM, Ray SS, Esposito A, Wanjale S et al (2014) Polystyrene/TiO2 composite electrospun fibers as fillers for poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate): structure, morphology and properties. Eur Polym J 50:78–86
Wang L, Ryan AJ (2011) Introduction to electrospinning. In: Bosworth LA, Downes S (eds) Electrospinning for tissue regeneration. Woodhead Publishing, Oxford, pp 3–33
Wang S, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Fei X, Zhou C, Zhang Y et al (2014) Fabrication of large-scale superhydrophobic composite films with enhanced tensile properties by multi-nozzle conveyor belt electrospinning. J Appl Polym Sci 131:39735. doi:10.1002/app.39735
Angammana CJ, Jayaram SH (2011) The effects of electric field on the multijet electrospinning process and fiber morphology. Ind Appl IEEE Trans 47:1028–1035
Kumar A, Wei M, Barry C, Chen J, Mead J (2010) Controlling fiber repulsion in multijet electrospinning for higher throughput. Macromol Mater Eng 295:701–708
Liu Y, He JH (2007) Bubble electrospinning for mass production of nanofibers. In: International journal of nonlinear sciences and numerical simulation 8, ed, p 393
Niu H, Lin T (2012) Fiber generators in needleless electrospinning. J Nanomater 2012:1–13
Yalcinkaya F, Yalcinkaya B, Jirsak O (2016) Analysis of the effects of rotating roller speed on a roller electrospinning system. Text Res J. doi:10.1177/0040517516641362
Yalcinkaya B, Callioglu FC, Yener F (2014) Measurement and analysis of jet current and jet life in roller electrospinning of polyurethane. Text Res J 84:1720–1728
Wei L, Yu H, Jia L, X (2016) Qin High-throughput nanofiber produced by needleless electrospinning using a metal dish as the spinneret. Text Res J. doi:10.1177/0040517516677232
Lu B, Wang Y, Liu Y, Duan H, Zhou J, Zhang Z et al (2010) Superhigh-throughput needleless electrospinning using a rotary cone as spinneret. Small 6:1612–1616
Bhattacharyya I, Molaro MC, Braatz RD, Rutledge GC (2016) Free surface electrospinning of aqueous polymer solutions from a wire electrode. Chem Eng J 289:203–211
Niu H, Lin T, Wang X (2009) Needleless electrospinning. I. A comparison of cylinder and disk nozzles. J Appl Polym Sci 114:3524–3530
Jiang G, Zhang S, Qin X (2014) Effect of processing parameters on free surface electrospinning from a stepped pyramid stage. J Ind Text 45(4):483–494
Jiang G, Qin X (2014) An improved free surface electrospinning for high throughput manufacturing of core–shell nanofibers. Mater Lett 128:259–262
Wang X, Niu H, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Needleless electrospinning of uniform nanofibers using spiral coil spinnerets. J Nanomater 2012:1–9
Wang X, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Electric field analysis of spinneret design for needleless electrospinning of nanofibers. J Mater Res 27:3013–3019
Thoppey NM, Bochinski JR, Clarke LI, Gorga RE (2010) Unconfined fluid electrospun into high quality nanofibers from a plate edge. Polymer 51:4928–4936
Lu W, Ma M, Xu H, Zhang B, Cao X, Guo Y (2015) Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater Lett 140:1–4
Liu Z, Chen R, He J (2016) Active generation of multiple jets for producing nanofibres with high quality and high throughput. Mater Des 94:496–501
Jani H, Toni P, Eero S, Mikko R (2015) Needleless electrospinning with twisted wire spinneret. Nanotechnology 26:025301
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the Bahauddin Zakariya University through the College of Textile Engineering, Multan, Pakistan, under research support grant (No. DR & EL/D-883) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, U., Niu, H., Aslam, S. et al. Needleless electrospinning using sprocket wheel disk spinneret. J Mater Sci 52, 7567–7577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0989-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0989-6