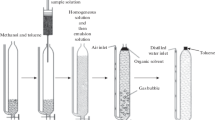
Abstract
Anthropogenic oil spills such as the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill present a number of unique challenges in environmental remediation, detection, and monitoring of a wide range of toxicants in complex environments. We have previously reported the use of cyclodextrin derivatives to accomplish the selective extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and facilitate their detection via proximity-induced energy transfer. Reported herein is the ability of these cyclodextrins to operate in a real-world scenario: extracting PAHs from oil collected from an oil spill site and from tar ball extracts into crude seawater from the Narragansett Bay in Rhode Island. The ability of this system to operate in this complex environment highlights the practical significance of cyclodextrin-based systems, and a direct comparison of the results obtained in seawater with those obtained using a variety of aqueous solvent systems provides significant insights into the factors responsible for efficient performance.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
McNutt, M.K., Chu, S., Lubchenco, J., Hunter, T., Dreyfus, G., Murawski, S.A., Kennedy, D.M.: Applications of science and engineering to quantify and control the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 20222–20228 (2012)
Ruddy, B.M., Huettel, M., Kostka, J.E., Lobodin, V.V., Bythell, B.J., McKenna, A.M., Aeppli, C., Reddy, C.M., Nelson, R.K., Marshall, A.G., Rodgers, R.P.: Targeted petroleomics: analytical investigation of Macondo well oil oxidation products from Pensacola beach. Energy Fuels 28, 4043–4050 (2014)
Hall, G.J., Frysinger, G.S., Aeppli, C., Carmichael, C.A., Gros, J., Lemkau, K.L., Nelson, R.K., Reddy, C.M.: Oxygenated weathering products of Deepwater Horizon oil come from surprising precursors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 75, 140–149 (2013)
Krahn, M.M., Ylitalo, G.M., Buzitis, J., Bolton, J.L., Wigren, C.A., Chan, S.-L., Varanasi, U.: Analyses for petroleum-related contaminants in marine fish and sediments following the Gulf oil spill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 27, 285–292 (1993)
John, G.F., Yin, F., Mulabagal, V., Hayworth, J.S., Clement, T.P.: Development and application of an analytical method using gas chromatography/triple quadrupole mass spectrometry for characterizing alkylated chrysenes in crude oil samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28, 948–956 (2014)
Aeppli, C., Carmichael, C.A., Nelson, R.K., Lemkau, K.L., Graham, W.M., Redmond, M.C., Valentine, D.L., Reddy, C.M.: Oil weathering after the Deepwater Horizon disaster led to the formation of oxygenated residues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 8799–8807 (2012)
Parker, A.M., Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Rosario-Ortiz, F.L., Linden, K.G.: Determination of COREXIT components used in the Deepwater Horizon cleanup by liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 6, 5498–5502 (2014)
Serio, N., Chanthalyma, C., Prignano, L., Levine, M.: Cyclodextrin-enhanced extraction and energy transfer of carcinogens in complex oil environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 11951–11957 (2013)
Serio, N., Levine, M.: Efficient extraction and detection of aromatic toxicants from crude oil and tar balls using multiple cyclodextrin derivatives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 95, 242–247 (2015)
Hamai, S.: Complex formation of tetrakis(4-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin with γ-cyclodextrin, phenylalanine, and tryptophan in aqueous solution. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 67, 471–481 (2010)
Hamai, S.: Ternary inclusion complexes of γ-cyclodextrin with resorufin and organic cations in aqueous solution. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 80, 1527–1533 (2007)
Serio, N., Prignano, L., Peters, S., Levine, M.: Detection of medium-sized polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via fluorescence energy transfer. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 34, 561–572 (2014)
Mako, T., Marks, P., Cook, N., Levine, M.: Fluorescent detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ternary cyclodextrin complexes. Supramol. Chem. 24, 743–747 (2012)
Serio, N., Chanthalyma, C., Peters, S., Levine, D., Levine, M.: 2-Hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin for the enhanced performance of dual function extraction and detection systems in complex oil environments. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 81, 341–346 (2015)
http://www.medicago.se/sites/default/files/pdf/productsheets/PBS_Buffer_v._01.pdf
Robert-Baldo, G.L., Morris, M.J., Byrne, R.H.: Spectrophotometric determination of seawater pH using phenol red. Anal. Chem. 57, 2564–2567 (1985)
Pytkowicz, R.M., Atlas, E., Culberson, C.H.: Chemical equilibrium in sea water. ACS Symp. Ser. 18, 1–24 (1975)
Breslow, R.: Hydrophobic effects on simple organic reactions in water. Acc. Chem. Res. 24, 159–164 (1991)
Breslow, R.: The hydrophobic effect in reaction mechanism studies and in catalysis by artificial enzymes. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 19, 813–822 (2006)
Riley, K.E., Hobza, P.: On the importance and origin of aromatic interactions in chemistry and biodisciplines. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 927–936 (2013)
Schneider, H.-J., Yatsimirsky, A.K.: Selectivity in supramolecular host-guest complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 37, 263–277 (2008)
Li, S., Xu, Y., Shen, Q., Liu, X., Lu, J., Chen, Y., Lu, T., Luo, C., Luo, X., Zheng, M., Jiang, H.: Non-covalent interactions with aromatic rings: current understanding and implications for rational drug design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 19, 6522–6533 (2013)
Shepherd, J.L., Kell, A., Chung, E., Sinclar, C.W., Workentin, M.S., Bizzotto, D.: Selective reductive desorption of a SAM-coated gold electrode revealed using fluorescence microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 8329–8355 (2004)
Yin, F., Hayworth, J.S., Clement, T.P.: A tale of two recent spills-comparison of 2014 Galveston Bay and 2010 deepwater horizon oil spill residues. PLoS One 10, e0118098/1–e0118098/17 (2015)
Mendoza, W.G., Riemer, D.D., Zika, R.G.: Application of fluorescence and PARAFAC to assess vertical distribution of subsurface hydrocarbons and dispersant during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 15, 1017–1030 (2013)
Aeppli, C., Reddy, C.M., Nelson, R.K., Kellermann, M.Y., Valentine, D.L.: Recurrent oil sheens at the Deepwater Horizon disaster site fingerprinted with synthetic hydrocarbon drilling fluids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 8211–8219 (2013)
McKenna, A.M., Nelson, R.K., Reddy, C.M., Savory, J.J., Kaiser, N.K., Fitzsimmons, J.E., Marshall, A.G., Rodgers, R.P.: Expansion of the analytical window for oil spill characterization by ultrahigh resolution mass spectrometry: beyond gas chromatography. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 7530–7539 (2013)
Warnock, A.M., Hagen, S.C., Passeri, D.L.: Marine tar residues: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 226, 1–24 (2015)
Chen, Z., Chang, K., Capraro, B.R., Zhu, C., Hsu, C.-J., Baumgart, T.: Intradimer/intermolecular interactions suggest autoinhibition mechanism in Endophilin A1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4557–4564 (2014)
Fisher, D.L., Harper, J., Sailor, M.J.: Energy transfer quenching of porous Si photoluminescence by aromatic molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 7846–7847 (1995)
Arakawa, T., Kita, Y., Ejima, D., Gagnon, P.: Solvent modulation of column chromatography. Protein Pept. Lett. 15, 544–555 (2008)
Patonay, G., Fowler, K., Shapira, A., Nelson, G., Warner, I.M.: Cyclodextrin complexes of polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the presence of aliphatic alcohols. J. Incl. Phenom. 5, 717–723 (1987)
Schneider, H.-J.: Binding mechanisms in supramolecular complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 3924–3977 (2009)
Connors, K.: The stability of cyclodextrin complexes in solution. Chem. Rev. 97, 1325–1357 (1997)
Müller, B.W., Albers, E.: Effect of hydrotropic substances on the complexation of sparingly soluble drugs with cyclodextrin derivatives and the influence of cyclodextrin complexation on the pharmacokinetics of the drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 80, 599–604 (1991)
Biedermann, F., Nau, W.M., Schneider, H.-J.: The hydrophobic effect revisited—studies with supramolecular complexes imply high-energy water as a noncovalent driving force. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 11158–11171 (2014)
Ross, P.D., Rekharsky, M.V.: Thermodynamics of hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interactions in cyclodextrin complexes. Biophys. J. 71, 2144–2154 (1996)
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research was provided by the Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serio, N., Levine, M. Solvent effects in the extraction and detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from complex oils in complex environments. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 84, 61–70 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0583-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-015-0583-y