Abstract
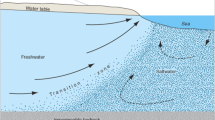
Time-lapse resistivity measurements and groundwater geochemistry were used to study salinity effect on groundwater aquifer at the ex-promontory-land of Carey Island in Malaysia. Resistivity was measured by ABEM Terrameter SAS4000 and ES10-64 electrode selector. Relationship between earth resistivity and total dissolved solids (TDS) was derived, and with resistivity images, used to identify water types: fresh (ρ e > 6.5 Ω m), brackish (3 Ω m < ρ e < 6.5 Ω m), or saline (ρ e < 3 Ω m). Long-term monitoring of the studied area’s groundwater quality via measurements of its time-lapse resistivity showed salinity changes in the island’s groundwater aquifers not conforming to seawater-freshwater hydraulic gradient. In some aquifers far from the coast, saline water was dominant, while in some others, freshwater 30 m thick showed groundwater potential. Land transformation is believed to have changed the island’s hydrogeology, which receives saltwater pressure all the time, limiting freshwater recharge to the groundwater system. The time-lapse resistivity measurements showed active salinity changes at resistivity-image bottom moving up the image for two seasons’ (wet and dry) conditions. The salinity changes are believed to have been caused by incremental tide passing through highly porous material in the active-salinity-change area. The study’s results were used to plan a strategy for sustainable groundwater exploration of the island.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABEM (2009). Instruction manual Terrameter SAS 4000 and SAS 1000. ABEM printed matter 93109 (pp. 1–136). Available from: http://www.abem.se/software.php.
Abdul Nassir, S. S., Loke, M. H., Lee, C. Y., & Nawawi, M. N. M. (2000). Salt-water intrusion mapping by geoelectrical imaging surveys. Geophysical Prospecting, 48(4), 647–661. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2478.2000.00209.x. Available from: http://web.ebscohost.com/ehost/pdf?vid=3&hid=113&sid=f505c08d-d330-4dc5-99bo-df1909144ee2%40sessionmgr109. Accessed 4 January 2009.
Adepelumi, A., Ako, B. D., Ajayi, T. R., Afolabi, O., & Omotoso, E. J. (2009). Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environmental Geology, 56(5), 927–933. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1194-3. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/ekj1477561052r10/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 8 January 2009.
APHA (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association. ISBN 0-87553-047-8.
Awni, T. B. (2006). Use of electrical resistivity methods for detecting subsurface fresh and saline water and delineating their interfacial configuration: a case study of the eastern Dead Sea coastal aquifers, Jordan. Hydrogeology Journal, 14, 1277–1283. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0034-3. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/95613003427232r6/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 28 December 2008.
Baba, M. F. (1997). Geology quaternary at Teluk Datuk area, state of Selangor (Sheet 101). Geology Quaternary Report, Department of Mineral and Geoscience Malaysia, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment Malaysia. Malaysia Government.
Barker, R. & Moore, J. (1998). The application of time-lapse electrical tomography in groundwater studies. The Leading Edge, 17, 1454–1458. Available from: http://segdl.org/getpdf/servlet/GetPDFServlet?filetype=pdf&id=LEEDFF00001700001454000001&idtype=cvips. Accessed 13 April 2010.
Benkabbour, B., Toto, E. A. & Fakir, Y. (2004). Using DC resistivity method to characterize the geometry and the salinity of the Plioquaternary consolidated coastal aquifer of the Mamora plain, Morocco. Environmental Geology, 45(4), 518–526. doi:10.1007/s00254-003-0906-y. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/3ejfg3cn4t89r141/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 4 January 2009.
BS (British Standard) 1377 (1990). Part 2: Method of test for soils for civil engineering purposes (pp. 1–68). London: British Standard Institution. ISBN: 0580178676.
Cartwright, K., & McComas, M. R. (1968). Geophysical surveys in the vicinity of sanitary landfills in northeastern Illinois. Ground Water, 5, 23–30. Available from: http://info.ngwa.org/GWOL/pdf/682578001.PDF.
Cassiani, G., Bruno, V., Villa, A., Nicoletta Fusi, N., & Binley, A. M. (2006). A saline trace test monitored via time-lapse surface electrical resistivity tomography. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 59, 244–259. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2005.10.007. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6VFC-4JOWRC5-1-8&_cdi=6007&_user=15079. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Dahlin, T., & Loke, M. H. (1998). Resolution of 2D Wenner resistivity imaging as assessed by numerical modelling. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 38(4), 237–249. PII:50926-9851(97)00030-X. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6VFC-35x5299-8-1&-cdi=60078_user=15079. Accessed 8 January 2009.
Dey, A., & Morrison, H. F. (1979). Resistivity modelling for arbitrarily shaped two-dimensional structures. Geophysical Prospecting, 27(1), 106–136. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1979.tb00961.x. Available from: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/user/ID=119598599&Act=21388code=4726&Page=/cgi-bin/fulltext/11. Accessed 8 January 2009.
Di Sipio, E., Galgaro, A., & Zuppi, G. M. (2006). New geophysical knowledge of groundwater systems in Venice estuarine environment. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 66, 6–12. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2005.07.015. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WDV-4H6PKWO-1-H&cdi=67768_user=15079. Accessed 6 January 2010.
DSMM (2009). Tide tables 2009 Malaysia (pp. 52–72). Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia.
DSMM (2010). Tide tables 2010 Malaysia (pp. 55–72). Department of Survey and Mapping Malaysia.
Ebraheem, A. M., Hamburger, M. W., Bayless, E. R., & Krothe, N. C. (1990). A study of acid mine drainage using earth resistivity measurements. Ground Water, 28(3), 361–368. Available from http://info.ngwa.org/GWOL/pdf/901550570.PDF. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Ebraheem, A. M., Senosy, M. M., & Dahab, K. A. (1997). Geoelectrical and hydrogeochemical studies for delineating groundwater contamination due to saltwater intrusion in the northern part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Ground Water, 35(2), 216–222. Available from http://info.ngwa.org/GWOL/pdf/971262673.PDF. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Fetter, C. W. (2001). Applied hydrogeology (4th ed., p. 598). New Jersey: Prentice Hall. ISBN: 0131226878.
Golden Hope Plantation Berhad (2006). Carey Island; a golden heritage; reliving history, preserving legacy, golden hope plantation Berhad (pp 1–16). ISBN 967-969-547-6.
Hamzah, U., Yaacup, R., Samsudin, A. R., & Ayub, M. S. (2006). Electrical imaging of the groundwater aquifer at Banting, Selangor, Malaysia. Environmental Geology, 49(8), 1156–1162. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0160-6. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/r8q5880065u3857/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 4 January 2009.
Ismail, R. (2008). Construction and exploration of deep wells at Carey Island and Kg Kelanang, Kuala Langat District, Banting Selangor. National Groundwater Resources Study under Subproject groundwater resources for State of Selangor. Report done by KS Global Sdn Bhd with collaboration Multical Card (M) Sdn Bhd under instruction the Department of Mineral and Geoscience Selangor State, Malaysia.
JICA MDGM (2002). The study on the sustainable groundwater resources and environmental management for the Langat Basin in Malaysia (Vol. 3). Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and Mineral and Geoscience Department Malaysia (MDGM) Report.
Kemna, A., Vanderborght, J., Kulessa, B. & Harry Vereecken, H. (2002). Imaging and characterisation of subsurface solute transport using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and equivalent transport models. Journal of Hydrology, 3–4(267), 125–146. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6V6C-46NYFK8-2-44&-cdi=5811&_user=1507. PII: S0 02 2-1694 (02) 00145-2. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Loke, M. H., & Barker, R. D. (1996). Rapid least squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosection using a quasi-Newton method. Geophysical Prospecting, 44(3), 131–152. GPPRAR44(1)1-178(1996). ISSN 0016-8025.
Loke, M. H., Acworth, I., & Dahlin, T. (2003). A comparison of smooth and blocky inversion methods in 2D electrical imaging surveys. Exploration Geophysics, 34(3), 182–187. (Available online at www.geoelectrical.com/downloads.php and email to mhloke@tm.net.my).
Loke, M. H. (1999). Time lapse resistivity imaging inversion. In Proceedings of the 5 th meeting of the EEGS European section, Em1. Available online at www.geoelectrical.com/timeabs.pdf.
Loke, M. H. (2010a). Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D electrical imaging surveys (pp. 1–145). Available online at www.geoelectrical.com/downloads.php.
Loke, M. H. (2010b). RES2DINV ver. 3.59 for Windows XP/Vista/7 for rapid 2-D resistivity and IP inversion using the least squares method (pp 1–148). Available online at www.geoelectrical.com/downloads.php.
Maillet, G. M., Rizzo, E., Revil, A., & Vella, C. (2005). High resolution electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) in a transition zone environment: application for detailed internal architecture and infilling processes study of a Rhone River paleo-channel. Marine Geophysical Researches, 26, 317–328. doi:10.1007/s11001-005-3726-5. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content1y1x7m7247q5x40p6/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Ngah, D. S. (1988). Groundwater investigation for determination of suitability using hand-pump at rural area of Kuala Langat District, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Report No. GPH1/1988. Department of Mineral and Geosciences Malaysia, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Ogilvy, R. D., Meldrum, P. I., Kuras, O., Wilkinson, P. B., Chambers, J. E., Sen, M., et al. (2009). Automated monitoring of coastal aquifers with electrical resistivity tomography. Near Surface Geophysics, 7(5–6), 367–375. doi:10.3997/1873-0604.2009027. (Available online at http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/8645/).
Oldenborger, G. A., Knoll, M. D., Routh, P. S., & LaBrecque, D. J. (2007). Time-lapse ERT monitoring of an injection/withdrawal experiment in a shallow unconfined aquifer. Geophysics, 72, 177–188. doi: 10.1190/1.2734365. http://www.eos.ubc.ca/~goldenbo/geop0313.pdf. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Olofsson, B., & Lundmark, A. (2009). Monitoring the impact of de-icing salt on roadside soils with time-lapse resistivity measurements. Environmental Geology, 57, 217–229. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1302-4. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/j00744004jqn8062/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Pujari, P. R., & Soni, A. K. (2008). Sea water intrusion studies near Kovaya limestone mine, Saurashtra coast, India. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 154(1–4), 93–109. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0380-9. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/5w365533728128x2/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Samsudin, A. R., Haryono, A., Hamzah, U., & Rafek, A. G. (2008). Salinity mapping of coastal groundwater aquifers using hydrogeochemical and geophysical methods: A case study from north Kelantan, Malaysia. Environmental Geology, 55(8), 1737–1743. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1124-9. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/6865279tg71287u5/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 3 January 2009.
Sherif, M., El Mahmoudi, A., Garamoon, H., Kacimov, A., Akram, S., Ebraheem, A., et al. (2006). Geoelectrical and hydrogeochemical studies for delineating seawater intrusion in the Outlet of Wadi Ham, UAE. Environmental Geology, 49(4), 536–551. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0081-4. Available from: http://www.spingerlink.com/content/7w07144t21663226/fulltext.pdf. Accessed 4 January 2009.
Suntharalingam, T., & Teoh, L. H. (1985). Quaternary geology of the coastal plains of Taiping. Quaternary Geology Report. Geological Survey Malaysia. Ministry of Primary Industries Malaysia.
Suratman, S., & Awang, N. (1998). Recent groundwater studies in the Klang Valley, Selangor Malaysia (Vol. 24, p. 315). Warta Geologi Geological Society of Malaysia.
Tahir, H., & Abdul Hamid, I. (2003). The study of groundwater resource at Teluk Gong, Pelabuhan Kelang, Selangor Darul Ehsan. Report No. JMG.SWP (HG) 03/2003. Department of Mineral and Geosciences Malaysia, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
Wilson, S. R., Ingham, M., & McConchie, J. A. (2006). The applicability of earth resistivity methods for saline interface definition. Journal of Hydrology, 316, 301–312. doi:10.1016lj.jhydrol.2005.05.004. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?-ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6V6C-4GFCR6N-4-R&_cdi=5811&_user=15079. Accessed 6 January 2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tajul Baharuddin, M.F., Taib, S., Hashim, R. et al. Time-lapse resistivity investigation of salinity changes at an ex-promontory land: a case study of Carey Island, Selangor, Malaysia. Environ Monit Assess 180, 345–369 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1792-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1792-x