Abstract
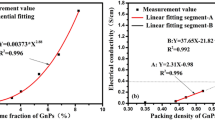
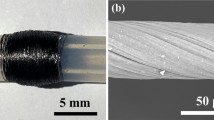
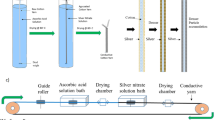
A facile and original method was developed to fabricate flexible conductive yarns using cotton roving and carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The CNTs were assembled to cotton roving and then wrapped around by fibers through twisting during ring spinning. The obtained CNT treated cotton yarns (CNT-CYs) showed great electrical conductivity and durability properties. The CNT-CYs were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and Raman scattering spectroscopy. The electrical conductivity, mechanical property and flexibility of CNT-CYs were investigated. The results show that electrical resistance of roving, twist and linear density of yarn affect the electrical conductivity of CNT-CYs. Combination with CNTs increased the breaking strength of cotton yarns. The electrical resistance of CNT-CYs was relatively stable during stretching and human motions. Moreover, no obvious changes in electrical resistance were found after CNT-CYs were bent 100 times. The CNT-CYs possessed good durability to repeated washing and abrasion.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, De Heer WA (2002) Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297:787–792
Cai G, Xu Z, Yang M, Tang B, Wang X (2017a) Functionalization of cotton fabrics through thermal reduction of graphene oxide. Appl Surf Sci 393:441–448
Cai G, Yang M, Xu Z, Liu J, Tang B, Wang X (2017b) Flexible and wearable strain sensing fabrics. Chem Eng J 325:396–403
Choi GR et al (2016) Strain sensing characteristics of rubbery carbon nanotube composite for flexible sensors. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16:1607–1611
Cooper CA, Young RJ, Halsall M (2001) Investigation into the deformation of carbon nanotubes and their composites through the use of Raman spectroscopy. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 32:401–411
Deng F, Lu W, Zhao H, Zhu Y, Kim B-S, Chou T-W (2011) The properties of dry-spun carbon nanotube fibers and their interfacial shear strength in an epoxy composite. Carbon 49:1752–1757
Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Saito R, Jorio A (2005) Raman spectroscopy of carbon nanotubes. Phys Rep 409:47–99
Egami Y, Suzuki K, Tanaka T, Yasuhara T, Higuchi E, Inoue H (2011) Preparation and characterization of conductive fabrics coated uniformly with polypyrrole nanoparticles. Synth Met 161:219–224
Gao Z, Song N, Zhang Y, Li X (2015) Cotton-textile-enabled, flexible lithium-ion batteries with enhanced capacity and extended lifespan. Nano Lett 15:8194–8203
Gao Z, Bumgardner C, Song N, Zhang Y, Li J, Li X (2016) Cotton-textile-enabled flexible self-sustaining power packs via roll-to-roll fabrication. Nat Commun 7:11586
Guan X, Zheng G, Dai K, Liu C, Yan X, Shen C, Guo Z (2016) Carbon nanotubes-adsorbed electrospun PA66 nanofiber bundles with improved conductivity and robust flexibility. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:14150–14159
Jiang K, Li Q, Fan S (2002) Nanotechnology: spinning continuous carbon nanotube yarns. Nature 419:801
Lee T-W, Lee S-E, Jeong YG (2016) Carbon nanotube/cellulose papers with high performance in electric heating and electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos Sci Technol 131:77–87
Li Y, Samad YA, Liao K (2015) From cotton to wearable pressure sensor. J Mater Chem A 3:2181–2187
Li L, Fan T, Hu R, Liu Y, Lu M (2017a) Surface micro-dissolution process for embedding carbon nanotubes on cotton fabric as a conductive textile. Cellulose 24:1121–1128
Li Y, Li Q, Zhang C, Cai P, Bai N, Xu X (2017b) Intelligent self-healing superhydrophobic modification of cotton fabrics via surface-initiated ARGET ATRP of styrene. Chem Eng J 323:134–142
Liang G, Zhu L, Xu J, Fang D, Bai Z, Xu W (2013) Investigations of poly (pyrrole)-coated cotton fabrics prepared in blends of anionic and cationic surfactants as flexible electrode. Electrochim Acta 103:9–14
Lima MD et al (2011) Biscrolling nanotube sheets and functional guests into yarns. Science 331:51–55
Liu X, Chang H, Li Y, Huck W, Zheng Z (2010) Polyelectrolyte-bridged metal/cotton hierarchical structures for highly durable conductive yarns. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:529–535
Liu C, Cai Z, Zhao Y, Zhao H, Ge F (2016a) Potentiostatically synthesized flexible polypyrrole/multi-wall carbon nanotube/cotton fabric electrodes for supercapacitors. Cellulose 23:637–648
Liu H et al (2016b) Electrically conductive strain sensing polyurethane nanocomposites with synergistic carbon nanotubes and graphene bifillers. Nanoscale 8:12977–12989
Liu Y, Song T, Jia X, Meng L, Mao X (2017) Gold nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotube probe based immunochromatographic assay on cotton thread. Sens Actuators B 251:1112–1118
Lou C-W (2005) Process of complex core spun yarn containing a metal wire. Text Res J 75:466–473
Makowski T, Kowalczyk D, Fortuniak W, Jeziorska D, Brzezinski S, Tracz A (2014) Superhydrophobic properties of cotton woven fabrics with conducting 3D networks of multiwall carbon nanotubes, MWCNTs. Cellulose 21:4659–4670
Osswald S, Havel M, Gogotsi Y (2007) Monitoring oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc 38:728–736. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.1686
Pan H, Li J, Feng Y (2010) Carbon nanotubes for supercapacitor. Nanoscale Res Lett 5:654
Pang Y et al (2016) Flexible, highly sensitive, and wearable pressure and strain sensors with graphene porous network structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:26458–26462
Pu X et al (2016) Wearable self-charging power textile based on flexible yarn supercapacitors and fabric nanogenerators. Adv Mater 28:98–105
Ren J, Wang C, Zhang X, Carey T, Chen K, Yin Y, Torrisi F (2017) Environmentally-friendly conductive cotton fabric as flexible strain sensor based on hot press reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 111:622–630
Soltani P, Johari M (2012) A study on siro-, solo-, compact-, and conventional ring-spun yarns. Part II: yarn strength with relation to physical and structural properties of yarns. J Text Inst 103:921–930
Tang B, Zhang M, Hou X, Li J, Sun L, Wang X (2012) Coloration of cotton fibers with anisotropic silver nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:12807–12813
Thangakameshwaran N, Santhoskumar A (2014) Cotton fabric dipped in carbon nano tube ink for smart textile applications. J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 63:557–562
Thostenson ET, Ren Z, Chou T-W (2001) Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: a review. Compos Sci Technol 61:1899–1912
Tran C, Humphries W, Smith S, Huynh C, Lucas S (2009) Improving the tensile strength of carbon nanotube spun yarns using a modified spinning process. Carbon 47:2662–2670
Wang H et al (2016a) Downsized sheath–core conducting fibers for weavable superelastic wires, biosensors, supercapacitors, and strain sensors. Adv Mater 28:4998–5007
Wang Z et al (2016b) Polyurethane/cotton/carbon nanotubes core-spun yarn as high reliability stretchable strain sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:24837–24843
Wang N, Xu Z, Zhan P, Dai K, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C (2017a) A tunable strain sensor based on a carbon nanotubes/electrospun polyamide 6 conductive nanofibrous network embedded into poly(vinyl alcohol) with self-diagnosis capabilities. J Mater Chem C 5:4408–4418
Wang R et al (2017b) A Bi-sheath fiber sensor for giant tensile and torsional displacements. Adv Funct Mater 27:1702134. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201702134
Wei Y, Chen S, Lin Y, Yuan X, Liu L (2016) Silver nanowires coated on cotton for flexible pressure sensors. J Mater Chem C 4:935–943
Weng W, Chen P, He S, Sun X, Peng H (2016) Smart electronic textiles. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:6140–6169
Xia Z, Xu W (2013) A review of ring staple yarn spinning method development and its trend prediction. J Nat Fibers 10:62–81
Xu P et al (2014) Carbon nanotube fiber based stretchable wire-shaped supercapacitors. Adv Energy Mater 4:1300759
Xu Q, Fan L, Yuan Y, Wei C, Bai Z, Xu J (2016) All-solid-state yarn supercapacitors based on hierarchically structured bacterial cellulose nanofiber-coated cotton yarns. Cellulose 23:3987–3997
Yang L, Li M, Zhang Y, Yi K, Ma J, Liu Y (2014) Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole nanotubes/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composites with superior electrochemical performance. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 25:1047–1052
Ye X, Zhou Q, Jia C, Tang Z, Wan Z, Wu X (2016) A knittable fibriform supercapacitor based on natural cotton thread coated with graphene and carbon nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 206:155–164
Yildiz SK, Mutlu R, Alici G (2016) Fabrication and characterisation of highly stretchable elastomeric strain sensors for prosthetic hand applications. Sens Actuators A 247:514–521
Yu D et al (2014a) Scalable synthesis of hierarchically structured carbon nanotube-graphene fibres for capacitive energy storage. Nat Nanotechnol 9:555–562
Yu Y, Yan C, Zheng Z (2014b) Polymer-assisted metal deposition (PAMD): a full-solution strategy for flexible, stretchable, compressible, and wearable metal conductors. Adv Mater 26:5508–5516
Yu Y, Zhang L, Yildiz O, Deng H, Zhao C, Bradford P, Zhu Y (2017) Investigation of microcombing parameters in enhancing the properties of carbon nanotube yarns. Mater Des 134:181–187
Zahid M, Heredia-Guerrero JA, Athanassiou A, Bayer IS (2017) Robust water repellent treatment for woven cotton fabrics with eco-friendly polymers. Chem Eng J 319:321–332
Zeng W, Shu L, Li Q, Chen S, Wang F, Tao XM (2014) Fiber-based wearable electronics: a review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv Mater 26:5310–5336
Zhang H, Cao J, Wu W, Cao Z, Ma H (2016) Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide on viscose fibers for the fabrication of flexible conductive devices. Cellulose 23:3761–3770
Zhao Z, Yan C, Liu Z, Fu X, Peng L, Hu Y, Zheng Z (2016) Machine-washable textile triboelectric nanogenerators for effective human respiratory monitoring through loom weaving of metallic yarns. Adv Mater 28:10267–10274
Zhong W et al (2016) A nanofiber based artificial electronic skin with high pressure sensitivity and 3D conformability. Nanoscale 8:12105–12112
Zhu L et al (2014) Cotton fabrics coated with lignosulfonate-doped polypyrrole for flexible supercapacitor electrodes. RSC Adv 4:6261–6266
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 51503164 and 51403162), the MoE Innovation Team Project in Biological Fibers Advanced Textile Processing and Clean Production (No. IRT13086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Fu, C., Xia, Z. et al. Conductive and durable CNT-cotton ring spun yarns. Cellulose 25, 4239–4249 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1839-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1839-7