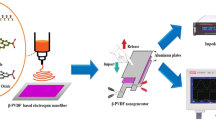
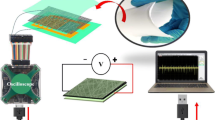
Abstract
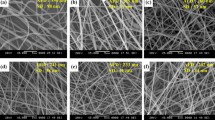
For the first time, a nanocomposite of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/cellulose nanocrystal (PVDF/CNC) is developed as a piezoelectric energy harvester. This is implemented through electrospinning of PVDF solutions containing different levels of CNC loading, i.e., 0, 1, 3 and 5 % with respect to PVDF weight. Analytical techniques including DSC, FTIR and WAXD are conducted to monitor the polymorphism evolution within electrospun nanocomposites as the CNC content is varied. The results imply that CNCs at the optimum concentration (3 and 5 %) can effectively nucleate β crystalline phases. The nucleation of α crystalline phases is also prevented when CNCs are present within the structure of PVDF electrospun fibers. These changes in polymorphism give PVDF/CNC nanocomposites enhanced piezoelectric characteristics compared to pure PVDF nanofibers. We have demonstrated that the developed nanocomposites can charge a 33-μF capacitor over 6 V and light up a commercial LED for more than 30 s. It is envisaged that the PVDF/CNC nanocomposites provide the opportunity for the development of efficient electrical generators as self-powering devices to charge portable electronics.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolhasani MM (2015) Effects of dynamic vulcanization on the kinetics of isothermal crystallization in a miscible polymeric blend. New J Chem 39:6130–6140
Abolhasani MM, Naebe M, Guo Q (2014a) A new approach for mechanisms of ferroelectric crystalline phase formation in PVDF nanocomposites. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:10679–10687
Abolhasani MM, Naebe M, Jalali-Arani A, Guo Q (2014b) Crystalline structures and α → β and γ polymorphs transformation induced by nanoclay in PVDF-based nanocomposite. NANO 9:1450065
Abolhasani MM, Zarejousheghani F, Cheng Z, Naebe M (2015a) A facile method to enhance ferroelectric properties in PVDF nanocomposites. RSC Adv 5:22471–22479
Abolhasani MM, Ashjari M, Azimi S, Fashandi H (2015b) Investigation of an abnormal α polymorph formation in miscible PVDF nanocomposite blend using kinetics of crystallization. Macromol Chem Phys 217:543–553
Abolhasani MM, Azimi S, Fashandi H (2015c) Enhanced ferroelectric properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers by adjusting processing parameters. RSC Adv 5:61277–61283
Abolhasani MM, Fashandi H, Naebe M (2016) Crystalline polymorph transition in poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF)/acrylic rubber (ACM)/clay partially miscible hybrid. Polym Bull 73:65–73
Ahn Y, Lim JY, Hong SM, Lee J, Ha J, Choi HJ et al (2013) Enhanced piezoelectric properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites due to high β-phase formation in poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Phys Chem C 117:11791–11799
Baniasadi M, Huang J, Xu Z, Moreno S, Yang X, Chang J et al (2015) High-performance coils and yarns of polymeric piezoelectric nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:5358–5366
Baniasadi M, Xu Z, Hong S, Naraghi M, Minary-Jolandan M (2016) Thermo-electromechanical behavior of piezoelectric nanofibers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:2540–2551
Baqeri M, Abolhasani MM, Mozdianfard MR, Guo Q, Oroumei A, Naebe M (2015) Influence of processing conditions on polymorphic behavior, crystallinity, and morphology of electrospun poly(vInylidene fluoride) nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci 132:1–10
Cao X, Dong H, Li CM (2007) New nanocomposite materials reinforced with flax cellulose nanocrystals in waterborne polyurethane. Biomacromolecules 8:899–904
Cao Y, Zavaterri P, Youngblood J, Moon R, Weiss J (2015) The influence of cellulose nanocrystal additions on the performance of cement paste. Cem Concr Compos 56:73–83
Cha SN, Seo J-S, Kim SM, Kim HJ, Park YJ, Kim S-W et al (2010) Sound-driven piezoelectric nanowire-based nanogenerators. Adv Mater 22:4726–4730
Cha S, Kim SM, Kim H, Ku J, Sohn JI, Park YJ et al (2011) Porous PVDF as effective sonic wave driven nanogenerators. Nano Lett 11:5142–5147
Chang C, Tran VH, Wang J, Fuh Y-K, Lin L (2010) Direct-write piezoelectric polymeric nanogenerator with high energy conversion efficiency. Nano Lett 10:726–731
Chang J, Dommer M, Chang C, Lin L (2012) Piezoelectric nanofibers for energy scavenging applications. Nano Energy 1:356–371
Chen D, Zhang JXJ (2015) Microporous polyvinylidene fluoride film with dense surface enables efficient piezoelectric conversion. Appl Phys Lett 106:193901
Chen X, Xu S, Yao N, Shi Y (2010) 1.6 V nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting using PZT nanofibers. Nano Lett 10:2133–2137
Choi D, Choi M-Y, Choi WM, Shin H-J, Park H-K, Seo J-S et al (2010) Fully rollable transparent nanogenerators based on graphene electrodes. Adv Mater 22:2187–2192
Ding Y, Duan Y, Huang Y (2015) Electrohydrodynamically printed, flexible energy harvester using in situ poled piezoelectric nanofibers. Energy Technol 3:351–358
El Achaby M, Arrakhiz FZ, Vaudreuil S, Essassi EM, Qaiss A (2012) Piezoelectric β-polymorph formation and properties enhancement in graphene oxide—PVDF nanocomposite films. Appl Surf Sci 258:7668–7677
Fashandi H, Yegane A, Abolhasani MM (2015) Interplay of liquid-liquid and solid-liquid phase separation mechanisms in porosity and polymorphism evolution within poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers. Fibers Polym 16:326–344
French AD (2013) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Gheibi A, Bagherzadeh R, Merati AA, Latifi M (2014) Electrical power generation from piezoelectric electrospun nanofibers membranes: electrospinning parameters optimization and effect of membranes thickness on output electrical voltage. J Polym Res 21:1–14
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110:3479–3500
Hadimani RL, Bayramol DV, Sion N, Shah T, Limin Q, Shaoxin S et al (2013) Continuous production of piezoelectric PVDF fibre for e-textile applications. Smart Mater Struct 22:075017
Henrique MA, Flauzino Neto WP, Silvério HA, Martins DF, Gurgel LVA, Barud HdS et al (2015) Kinetic study of the thermal decomposition of cellulose nanocrystals with different polymorphs, cellulose I and II, extracted from different sources and using different types of acids. Ind Crops Prod 76:128–140
Huan S, Bai L, Liu G, Cheng W, Han G (2015) Electrospun nanofibrous composites of polystyrene and cellulose nanocrystals: manufacture and characterization. RSC Adv 5:50756–50766
Jin E, Guo J, Yang F, Zhu Y, Song J, Jin Y et al (2016) On the polymorphic and morphological changes of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC-I) upon mercerization and conversion to CNC-II. Carbohydr Polym 143:327–335
Lalia BS, Samad YA, Hashaikeh R (2012) Nanocrystalline cellulose-reinforced composite mats for lithium-ion batteries: electrochemical and thermomechanical performance. J Solid State Electrochem 17:575–581
Lee M, Chen C-Y, Wang S, Cha SN, Park YJ, Kim JM et al (2012) A hybrid piezoelectric structure for wearable nanogenerators. Adv Mater 24:1759–1764
Lee J-H, Lee KY, Kumar B, Tien NT, Lee N-E, Kim S-W (2013) Highly sensitive stretchable transparent piezoelectric nanogenerators. Energy Environ Sci 6:169–175
Lin Y-F, Song J, Ding Y, Lu S-Y, Wang ZL (2008) Alternating the output of a CdS nanowire nanogenerator by a white-light-stimulated optoelectronic effect. Adv Mater 20:3127–3130
Liu Y-L, Li Y, Xu J-T, Fan Z-Q (2010) Cooperative effect of electrospinning and nanoclay on formation of polar crystalline phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:1759–1768
Liu Z, Pan C, Lin L, Lai H (2013) Piezoelectric properties of PVDF/MWCNT nanofiber using near-field electrospinning. Sens Actuators A 193:13–24
Lu P, Hsieh Y-L (2010) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr Polym 82:329–336
Lu M-Y, Song J, Lu M-P, Lee C-Y, Chen L-J, Wang ZL (2009) ZnO–ZnS heterojunction and ZnS nanowire arrays for electricity generation. ACS Nano 3:357–362
Ma W, Zhang J, Wang X, Wang S (2007) Effect of PMMA on crystallization behavior and hydrophilicity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blend prepared in semi-dilute solutions. Appl Surf Sci 253:8377–8388
Mandal D, Yoon S, Kim KJ (2011) Origin of piezoelectricity in an electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) nanofiber web-based nanogenerator and nano-pressure sensor. Macromol Rapid Commun 32:831–837
Mandal D, Henkel K, Schmeißer D (2014) Improved performance of a polymer nanogenerator based on silver nanoparticles doped electrospun P (VDF–HFP) nanofibers. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:10403–10407
Mao Y, Zhao P, McConohy G, Yang H, Tong Y, Wang X (2014) Sponge-like piezoelectric polymer films for scalable and integratable nanogenerators and self-powered electronic systems. Adv Energy Mater 4:1–7
Martins P, Lopes AC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2014) Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog Polym Sci 39:683–706
Nakagawa K, Ishida Y (1973) Annealing effects in poly(vinylidene fluoride) as revealed by specific volume measurements, differential scanning calorimetry, and electron microscopy. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed 11:2153–2171
Peresin MS, Habibi Y, Zoppe JO, Pawlak JJ, Rojas OJ (2010) Nanofiber composites of polyvinyl alcohol and cellulose nanocrystals: manufacture and characterization. Biomacromolecules 11:674–681
Persano L, Dagdeviren C, Su Y, Zhang Y, Girardo S, Pisignano D et al (2013) High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene). Nat Commun 4:1633
Pörhönen J, Rajala S, Lehtimäki S, Tuukkanen S (2014) Flexible piezoelectric energy harvesting circuit with printable supercapacitor and diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Dev 61:3303–3308
Pu J, Yan X, Jiang Y, Chang C, Lin L (2010) Piezoelectric actuation of direct-write electrospun fibers. Sens Actuators A 164:131–136
Pu X, Li L, Song H, Du C, Zhao Z, Jiang C et al (2015) A self-charging power unit by integration of a textile triboelectric nanogenerator and a flexible lithium-ion battery for wearable electronics. Adv Mater 27:2472–2478
Rajala S, Siponkoski T, Sarlin E, Mettänen M, Vuoriluoto M, Pammo A et al (2016) Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:15607–15614
Seminara L, Capurro M, Cirillo P, Cannata G, Valle M (2011) Electromechanical characterization of piezoelectric PVDF polymer films for tactile sensors in robotics applications. Sens Actuators A 169:49–58
Shi Q, Zhou C, Yue Y, Guo W, Wu Y, Wu Q (2012) Mechanical properties and in vitro degradation of electrospun bio-nanocomposite mats from PLA and cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 90:301–308
Shin S-H, Kim Y-H, Lee MH, Jung J-Y, Nah J (2014) Hemispherically aggregated BaTiO3 nanoparticle composite thin film for high-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 8:2766–2773
Shiyou X, Yong S, Sang-Gook K (2006) Fabrication and mechanical property of nano piezoelectric fibres. Nanotechnology 17:4497
Soin N, Shah TH, Anand SC, Geng J, Pornwannachai W, Mandal P et al (2014) Novel “3-D spacer” all fibre piezoelectric textiles for energy harvesting applications. Energy Environ Sci 7:1670–1679
Sun LL, Li B, Zhang ZG, Zhong WH (2010) Achieving very high fraction of β-crystal PVDF and PVDF/CNF composites and their effect on AC conductivity and microstructure through a stretching process. Eur Polym J 46:2112–2119
Wang ZL, Song J (2006) Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312:242–246
Wang X, Song J, Zhang F, He C, Hu Z, Wang Z (2010) Electricity generation based on one-dimensional group-III nitride nanomaterials. Adv Mater 22:2155–2158
Xie Y, Wang S, Lin L, Jing Q, Lin Z-H, Niu S et al (2013) Rotary triboelectric nanogenerator based on a hybridized mechanism for harvesting wind energy. ACS Nano 7:7119–7125
Xie Y, Wang S, Niu S, Lin L, Jing Q, Yang J et al (2014) Grating-structured freestanding triboelectric-layer nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical energy at 85% total conversion efficiency. Adv Mater 26:6599–6607
Yee WA, Kotaki M, Liu Y, Lu X (2007) Morphology, polymorphism behavior and molecular orientation of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Polymer 48:512–521
Yee WA, Nguyen AC, Lee PS, Kotaki M, Liu Y, Tan BT et al (2008) Stress-induced structural changes in electrospun polyvinylidene difluoride nanofibers collected using a modified rotating disk. Polymer 49:4196–4203
Yu L, Cebe P (2009) Crystal polymorphism in electrospun composite nanofibers of poly(vinylidene fluoride) with nanoclay. Polymer 50:2133–2141
Zeng W, Tao X-M, Chen S, Shang S, Chan HLW, Choy SH (2013) Highly durable all-fiber nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting. Energy Environ Sci 6:2631–2638
Zhang Z, Wu Q, Song K, Lei T, Wu Y (2015) Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/cellulose nanocrystals composites: rheological, hydrophilicity, thermal and mechanical properties. Cellulose 22:2431–2441
Zhou C, Chu R, Wu R, Wu Q (2011) Electrospun polyethylene oxide/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous mats with homogeneous and heterogeneous microstructures. Biomacromolecules 12:2617–2625
Zhu G, Su Y, Bai P, Chen J, Jing Q, Yang W et al (2014) Harvesting water wave energy by asymmetric screening of electrostatic charges on a nanostructured hydrophobic thin-film surface. ACS Nano 8:6031–6037
Zimmermann T, Pöhler E, Geiger T (2004) Cellulose fibrils for polymer reinforcement. Adv Eng Mater 6:754–761
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 2844 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fashandi, H., Abolhasani, M.M., Sandoghdar, P. et al. Morphological changes towards enhancing piezoelectric properties of PVDF electrical generators using cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 23, 3625–3637 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1070-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1070-3