Abstract
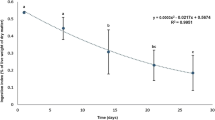
This paper presents the first data on ammonia excretion by fed and starved juvenile common tench. The aim of the study was to determine the amount of ammonia excretion by juvenile common tench Tinca tinca (L.), fed with a commercial feed under intensive rearing conditions. Rearing was conducted for a period of 4 weeks at a water temperature of 27 °C. On the test day, the amounts of ammonia excreted by starved fish (over 12 h: control group) and fish fed with a morning feed dose (3 % of biomass: experimental group) were determined at 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11 h after feeding. Ammonia excretion measurements were taken in 7-day intervals. Despite the increased growth rate in successive weeks of experiment, the amount of ammonia excreted by the fish was always at a similar level within the control (maximum 0.26 mg g−1) and the experimental group (maximum 0.39 mg g−1). This paper presents for the first time reliable amount of ammonia excreted by fed and starved juvenile common tench. The obtained results may also increase the effectiveness of intensive rearing procedures (taking into account stocking density and feeding regime) and allow to design the most effective biofiltration capacity of recirculating aquaculture systems for the commercial production of this species.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avnimelech Y (1999) Carbon/nitrogen ratio as a control element in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 176:227–235
Barak Y, van Rijn J (2000) Biological phosphate removal in a prototype recirculating aquaculture treatment system. Aquacult Eng 22:121–136
Celada JD, Aguilera A, Carral JM, Saez-Royuela M, Melendre PM (2008) Rearing tench (Tinca tinca L.) larvae on live feed (Artemia) and on two transition schedules from live to dry diets. J Appl Ichthyol 24:595–600
Celada JD, Aguilera A, Garcia V, Carral JM, Saez-Royuela M, Gonzalez R, Gonzalez A (2009) Rearing juvenile tench (Tinca tinca L.) under controlled conditions using Artemia nauplii as supplement to a dry diet. Aquacult Int 17:565–570
Crab R, Avnimelech Y, Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Verstraete W (2007) Nitrogen removal techniques in aquaculture for a sustainable production. Aquaculture 270:1–14
Dolomatov SI, Shekk PV, Żukow W, Kryukova MI (2011) Features of nitrogen metabolism in fishes. Rev Fish Biol Fish 21:733–737
Domurat J (1976) Fizjologia trawienia niektórych ryb słodkowodnych. ART, Olsztyn
Gela D, Flajshans M, Kocour M, Rodina M, Linhart O (2006) Tench (Tinca tinca) broodstock management in breeding station under conditions of pond culture, a review. Aquacult Int 14:195–203
Gomułka P, Żarski D, Kucharczyk D, Kupren K, Krejszeff S, Targońska K (2011) Acute ammonia toxicity during early ontogeny of chub, Leuciscus cephalus (Cyprinidae). Aquat Living Resour 24:211–217
Green BW, Boyd CE (1995) Chemical budgets for organically fertilized ponds in the dry tropics. J World Aquac Soc 26:284–296
Hargrove LL, Westerman PW, Losordo TM (1996) Nitrification in three-stage and single-stage floating bead biofilters in a laboratory-scale recirculating aquaculture system. Aquacult Eng 15:67–80
Horvath L, Szabo T, Burke J (1997) Hatchery testing of GnRH analogue-containing pellets on ovulation in four cyprinid species. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 44:221–226
Jobling M (1994) Fish bioenergetics. Chapman and Hall, London
Kamler E, Myszkowsky L, Kaminński R, Korwin-Kossakowski M, Wolnicki J (2006) Does overfeeding affect tench Tinca tinca (L.) juveniles? Aquacult Int 14:99–111
Krejszeff S, Żarski D, Kucharczyk D, Kupren K, Targońska K, Mamcarz A (2010) An experimental device for egg incubation and fish larvae rearing under laboratory conditions. Pol J Nat Sci 25:190–199
Kujawa R, Kucharczyk D, Mamcarz A (2010) The effect of tannin concentration and egg unsticking time on the hatching success of tench Tinca tinca (L.) larvae. Rev Fish Biol Fish 20:339–343
Kujawa R, Kucharczyk D, Mamcarz A, Żarski D, Targońska K (2011) Artificial spawning of common tench Tinca tinca (Linnaeus, 1758), obtained from wild and domestic stocks. Aquacult Int 19:513–521
Lazur AM, Britt DC (1997) Pond recirculating production systems. SRAC Publication No 455, University of Florida, 8 pp
Lazzari R, Baldisserotto B (2008) Nitrogen and phosphorus waste in fish farming. B Inst Pesca, São Paulo 34(4):591–600
LeGrow SM, Beamish FWH (1986) Influence of dietary protein and lipid on apparent heat increment of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43:19–25
Linhart O, Gela D, Flajshans M, Rodina M (2003) Proteolytic enzyme treatment: an improved method for elimination of egg stickiness in tench, Tinca tinca L., in aquaculture. J Appl Ichthyol 19:134–137
Mamcarz A, Targońska K, Kucharczyk D, Kujawa R, Żarski D (2011) Effect of live and dry food on rearing of tench (Tinca tinca L.) larvae under controlled conditions. Ital J Anim Sci 10:42–45
Myszkowski L, Kamiński R, Wolnicki J (2003) Response of juvenile tench Tinca tinca (L.) to the anaesthetic 2-phenoxyethanol. J Appl Ichthyol 19:142–145
Oliva-Teles A, Pereira JP, Gouveia A, Gomes E (1998) Utilisation of diets supplemented with microbial phytase by seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquat Living Resour 11:255–259
Ostaszewska T, Korwin-Kosakowski M, Wolnicki J (2006) Morphological changes of digestive structures in starved tench Tinca tinca (L.) juveniles. Aquacult Int 14:113–126
Quirós M, Alvarino JMR (2000) Growth and survival of tench larvae fed under different feeding strategies. J Appl Ichthyol 16:32–35
Quirós M, Nicodemus N, Alonso M, Bartolome M, Ecija JL, Alvarino JMR (2003) Survival and changes in growth of juvenile tench (Tinca tinca L.) fed on defined diets commonly used to culture non-cyprinid species. J Appl Ichthyol 19:149–151
Read P, Fernandes T (2003) Management of environmental impacts of marine aquaculture in Europe. Aquaculture 226:139–163
Rennert B, Kohlmann K, Hack H (2003) A performance test with five different strains of tench (Tinca tinca L.) under controlled warm water conditions. J Appl Ichthyol 19:161–164
Ridha MT, Cruz EM (2001) Effect of biofilter media on water quality and biological performance of the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus L. reared in a simple recirculating system. Aquacult Eng 24:157–166
Steffens W (1995) The tench (Tinca tinca L.), a neglected pond fish species. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 42:161–180
Valbuena-Villarreal RD, Vásquez-Torres W (2011) Body weight is inversely associated with ammonia excretion in red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Rev Colomb de Cienc Pecu 24:191–200
van Rijn J (1996) The potential for integrated biological treatment systems in recirculating fish culture. Rev Aquac 139:181–201
Wolnicki J (2005) Intensywny podchów wczesnych stadiów ryb karpiowatych w warunkach kontrolowanych. Arch Pol Fish 13:5–87
Wolnicki J, Górny W (1995) Suitability of two commercial dry diets for intensive rearing of larval tench (Tinca tinca L.) under controlled conditions. Aquaculture 129:256–258
Wolnicki J, Korwin-Kossakowski M (1993) Survival and growth of larval and juvenile tench, Tinca tinca L., fed different diets under controlled conditions. Aquac Fish Manag 24:707–713
Wolnicki J, Myszkowski L, Kaminski R (2003) Effect of supplementation of a dry feed with natural food on growth, condition and size distribution of juvenile tench Tinca tinca (L.). J Appl Ichthyol 19:157–160
Wolnicki J, Myszkowski L, Korwin-Kossakowski M, Stawny A (2006) Effects of different diets on juvenile tench, Tinca tinca (L.) reared under controlled conditions. Aquacult Int 14:89–98
Zakęś Z, Demska-Zakęś K, Karczewski P, Karpinński A (2001) Selected metabolic aspects of pikeperch, Stizostedion lucioperca (L.) reared in a water recirculation system. Arch Pol Fish 9:25–37
Zakęś Z, Demska-Zakęś K, Kata K (2003) Rates of oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of juvenile Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis L. Aquacult Int 11:277–288
Zakęś Z, Demska-Zakęś K, Jarocki P, Stawecki K (2005) The effect of feeding on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of juvenile tench Tinca tinca (L.) reared in a water recirculating system. Aquacult Int 14:127–140
Zakęś Z, Szczepkowski M, Demska-Zakęś K, Jesiołowski M (2007) Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion by juvenile pike, Esox lucius L. Arch Pol Fish 15:79–92
Żarski D, Kucharczyk D, Targońska K, Chyła B, Dobrołowicz A (2008) Dynamics of changes in nitrogen and phosphorus compounds during intensive culture of ide Leuciscus idus (L.) in a recirculating system. Arch Pol Fish 16:459–467
Żarski D, Kucharczyk D, Targońska K, Krejszeff S, Czarkowski T, Babiarz E, Nowosielska DB (2010) Dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus in closed and semi-closed recirculating aquaculture systems during the intensive culture of goldfish, Carassius auratus auratus (L.), juveniles. Arch Pol Fish 18:187–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowosad, J., Żarski, D., Biłas, M. et al. Dynamics of ammonia excretion in juvenile common tench, Tinca tinca (L.), during intensive rearing under controlled conditions. Aquacult Int 21, 629–637 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-012-9596-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-012-9596-3