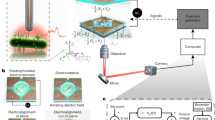
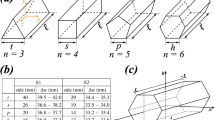
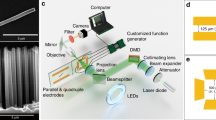
Abstract
The motion control of individual nanowires is essential for effective nanowire manipulation strategies. In this paper, we demonstrate a simple and general method to dynamically control the motion of a chemically untreated nanowire in a quadrupole electrode structure. The motion of single nanowires was determined by positive dielectrophoresis and orientational torque, which were induced by optionally exerting ac signals onto specific electrodes for regulating the electric field distribution in real time. A silver nanowire was guided to transform postures and transport directionally in a working regime of about 115 μm × 115 μm. The selected nanowire was then transported to a region of weak gradients and forced to rotate at the designated location subsequently. The behavior of the nanowires, including their posture, cornering time, linear displacement and location-designated rotation, was dynamically monitored and regulated. A simple analytical model was developed to derive the driving forces and torques on the nanowire.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal R, Ladavac K, Roichman Y, Yu GH, Lieber CM, Grier DG (2005) Manipulation and assembly of nanowires with holographic optical traps. Opt Express 13(22):8906–8912
Boote JJ, Evans SD (2005) Dielectrophoretic manipulation and electrical characterization of gold nanowires. Nanotechnology 16(9):1500–1505
Cui Y, Wei QQ, Park HK, Lieber CM (2001) Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 293(5533):1289–1292
Dong LF, Bush J, Chirayos V, Solanki R, Jiao J, Ono Y, Conley JF, Ulrich BD (2005) Dielectrophoretically controlled fabrication of single-crystal nickel silicide nanowire interconnects. Nano Lett 5(10):2112–2115
Edwards B, Mayer TS, Bhiladvala RB (2006) Synchronous electrorotation of nanowires in fluid. Nano Lett 6(4):626–632
Evoy S, DiLello N, Deshpande V, Narayanan A, Liu H, Riegelman M, Martin BR, Hailer B, Bradley JC, Weiss W, Mayer TS, Gogotsi Y, Bau HH, Mallouk TE, Raman S (2004) Dielectrophoretic assembly and integration of nanowire devices with functional CMOS operating circuitry. Microelectron Eng 75(1):31–42
Fan DL, Zhu FQ, Cammarata RC, Chien CL (2004) Manipulation of nanowires in suspension by ac electric fields. Appl Phys Lett 85(18):4175–4177
Fan DL, Zhu FQ, Cammarata RC, Chien CL (2005) Controllable high-speed rotation of nanowires. Phys Rev Lett 94(24):247208
Fan DL, Cammarata RC, Chien CL (2008a) Precision transport and assembling of nanowires in suspension by electric fields. Appl Phys Lett 92(9):093115
Fan ZY, Ho JC, Jacobson ZA, Yerushalmi R, Alley RL, Razavi H, Javey A (2008b) Wafer-scale assembly of highly ordered semiconductor nanowire arrays by contact printing. Nano Lett 8(1):20–25
Fan DL, Yin ZZ, Cheong R, Zhu FQ, Cammarata RC, Chien CL, Levchenko A (2010) Subcellular-resolution delivery of a cytokine through precisely manipulated nanowires. Nat Nanotechnol 5(7):545–551
Freer EM, Grachev O, Duan XF, Martin S, Stumbo DP (2010) High-yield self-limiting single-nanowire assembly with dielectrophoresis. Nat Nanotechnol 5(7):525–530
Hangarter CM, Myung NV (2005) Magnetic alignment of nanowires. Chem Mater 17(6):1320–1324
Jamshidi A (2009) Optoelectronic manipulation, assembly, and patterning of nanoparticles. University of California, Berkeley
Jamshidi A, Pauzauskie PJ, Schuck PJ, Ohta AT, Chiou PY, Chou J, Yang PD, Wu MC (2008) Dynamic manipulation and separation of individual semiconducting and metallic nanowires. Nat Photonics 2(2):85–89
Jones TB (1995) Electromechanics of particles. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Keshoju K, Xing H, Sun L (2007) Magnetic field driven nanowire rotation in suspension. Appl Phys Lett 91(12):123114
Law M, Greene LE, Johnson JC, Saykally R, Yang PD (2005) Nanowire dye-sensitized solar cells. Nat Mater 4(6):455–459
Lee SH, Lee HJ, Ino K, Shiku H, Yao T, Matsue T (2009) Microfluid-assisted dielectrophoretic alignment and device characterization of single ZnO wires. J Phys Chem C 113(45):19376–19381
Liu YL, Chung JH, Liu WK, Ruoff RS (2006) Dielectrophoretic assembly of nanowires. J Phys Chem B 110(29):14098–14106
Marczak M, Hourlier D, Melin T, Adamowicz L, Diesinger H (2010) Frequency dependent rotation and translation of nanowires in liquid environment. Appl Phys Lett 96(23):233502
Molhave K, Wich T, Kortschack A, Boggild P (2006) Pick-and-place nanomanipulation using microfabricated grippers. Nanotechnology 17(10):2434–2441
Morgan H, Green NG (2002) AC electrokinetics:colloids and nanoparticles. Research Studies Press, Philadelphia
Pauzauskie PJ, Radenovic A, Trepagnier E, Shroff H, Yang PD, Liphardt J (2006) Optical trapping and integration of semiconductor nanowire assemblies in water. Nat Mater 5(2):97–101
Pevzner A, Engel Y, Elnathan R, Ducobni T, Ben-Ishai M, Reddy K, Shpaisman N, Tsukernik A, Oksman M, Patolsky F (2010) Knocking down highly-ordered large-scale nanowire arrays. Nano Lett 10(4):1202–1208
Raychaudhuri S, Dayeh SA, Wang DL, Yu ET (2009) Precise semiconductor nanowire placement through dielectrophoresis. Nano Lett 9(6):2260–2266
Sherman FS (1990) Viscous Flow. Mcgraw Hill, New York
Smith PA, Nordquist CD, Jackson TN, Mayer TS, Martin BR, Mbindyo J, Mallouk TE (2000) Electric-field assisted assembly and alignment of metallic nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 77(9):1399
Sosnowchik BD, Chang J, Lin LW (2010) Pick, break, and placement of one-dimensional nanostructures for direct assembly and integration. Appl Phys Lett 96(15):153101
Tao A, Kim F, Hess C, Goldberger J, He RR, Sun YG, Xia YN, Yang PD (2003) Langmuir–Blodgett silver nanowire monolayers for molecular sensing using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett 3(9):1229–1233
Wang ZL, Song JH (2006) Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 312(5771):242–246
Wiley B, Sun YG, Mayers B, Xia YN (2005) Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: the case of silver. Chem Eur J 11(2):454–463
Xia YN, Yang PD, Sun YG, Wu YY, Mayers B, Gates B, Yin YD, Kim F, Yan YQ (2003) One-dimensional nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv Mater 15(5):353–389
Xie P, Xiong QH, Fang Y, Qing Q, Lieber CM (2012) Local electrical potential detection of DNA by nanowire-nanopore sensors. Nat Nanotechnol 7(2):119–125
Xu F, Durham JW, Wiley BJ, Zhu Y (2011) Strain-release assembly of nanowires on stretchable substrates. ACS Nano 5(2):1556–1563
Yan Z, Jureller JE, Sweet J, Guffey MJ, Pelton M, Scherer NF (2012) Three-dimensional optical trapping and manipulation of single silver nanowires. Nano Lett 12(10):5155–5161
Zhang L, Petit T, Lu Y, Kratochvil BE, Peyer KE, Pei R, Lou J, Nelson BJ (2010) Controlled propulsion and cargo transport of rotating nickel nanowires near a patterned solid surface. ACS Nano 4(10):6228–6234
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91023024), National 973 Program of China (2011CB707601), The National Natural Science Foundation of China (51145009), New Century Elitist Program by Ministry of Education of China (NCET-07-0180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 914 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MPG 4038 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MPG 5664 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Xiang, N., Quan, Y. et al. Directed transport and location-designated rotation of nanowires using ac electric fields. Microfluid Nanofluid 16, 237–246 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1203-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1203-z