Abstract
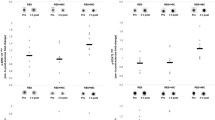
The striated muscle activator of Rho signaling (STARS) protein and members of its downstream signaling pathway, including myocardin-related transcription factor-A (MRTF-A) and SRF, are increased in response to prolonged resistance exercise training but also following a single bout of endurance cycling. The aim of the present study was to measure and compare the regulation of STARS, MRTF-A and SRF mRNA and protein following 10 weeks of endurance training (ET) versus resistance training (RT), as well as before and following a single bout of endurance (EE) versus resistance exercise (RE). Following prolonged training, STARS, MRTF-A and SRF mRNA levels were all increased by similar magnitude, irrespective of training type. In the training-habituated state, STARS mRNA increased following a single-bout RE when measured 2.5 and 5 h post-exercise and had returned to resting level by 22 h following exercise. MRTF-A and SRF mRNA levels were decreased by 2.5, 5, and 22 h following a single bout of RE and EE exercise when compared to their respective basal levels, with no significant difference seen between the groups at any of the time points. No changes in protein levels were observed following the two modes of exercise training or a single bout of exercise. This study demonstrates that the stress signals elicited by ET and RT result in a comparable regulation of members of the STARS pathway. In contrast, a single bout of EE and RE, performed in the trained state, elicit different responses. These observations suggest that in the trained state, the acute regulation of the STARS pathway following EE or RE may be responsible for exercise-specific muscle adaptations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen LB (1995) A maximal cycle exercise protocol to predict maximal oxygen uptake. Scand J Med Sci Sports 5:143–146
Arai A, Spencer JA, Olson EN (2002) STARS, a striated muscle activator of Rho signaling and serum response factor-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 277:24453–24459
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol 23:369–379
Camera DM, Edge J, Short MJ, Hawley JA, Coffey VG (2010) Early time course of Akt phosphorylation after endurance and resistance exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1843–1852
Cartoni R, Leger B, Hock MB, Praz M, Crettenand A, Pich S, Ziltener JL, Luthi F, Deriaz O, Zorzano A, Gobelet C, Kralli A, Russell AP (2005) Mitofusins 1/2 and ERRalpha expression are increased in human skeletal muscle after physical exercise. J Physiol 567:349–358
Charvet C, Houbron C, Parlakian A, Giordani J, Lahoute C, Bertrand A, Sotiropoulos A, Renou L, Schmitt A, Melki J, Li Z, Daegelen D, Tuil D (2006) New role for serum response factor in postnatal skeletal muscle growth and regeneration via the interleukin 4 and insulin-like growth factor 1 pathways. Mol Cell Biol 26:6664–6674
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Finck BN, Kelly DP (2006) PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest 116:615–622
Kuwahara K, Barrientos T, Pipes GCT, Li S, Olson EN (2005) Muscle-specific signaling mechanism that links actin dynamics to serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol 25:3173–3181
Kuwahara K, Pipes GC, McAnally J, Richardson JA, Hill JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2007) Modulation of adverse cardiac remodeling by STARS, a mediator of MEF2 signaling and SRF activity. J Clin Invest 117:1324–1334
Lamon S, Wallace MA, Leger B, Russell AP (2009) Regulation of STARS and its downstream targets suggest a novel pathway involved in human skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. J Physiol 587:1795–1803
Leger B, Cartoni R, Praz M, Lamon S, Deriaz O, Crettenand A, Gobelet C, Rohmer P, Konzelmann M, Luthi F, Russell AP (2006) Akt signalling through GSK-3beta, mTOR and Foxo1 is involved in human skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. J Physiol 576:923–933
MacNeil LG, Melov S, Hubbard AE, Baker SK, Tarnopolsky MA (2010) Eccentric exercise activates novel transcriptional regulation of hypertrophic signaling pathways not affected by hormone changes. PLoS One 5:e10695
Mahadeva H, Brooks G, Lodwick D, Chong NW, Samani NJ (2002) ms1, a novel stress-responsive, muscle-specific gene that is up-regulated in the early stages of pressure overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy. FEBS Lett 521:100–104
Miano JM, Long X, Fujiwara K (2007) Serum response factor: master regulator of the actin cytoskeleton and contractile apparatus. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C70–81
Moore ML, Wang GL, Belaguli NS, Schwartz RJ, McMillin JB (2001) GATA-4 and serum response factor regulate transcription of the muscle-specific carnitine palmitoyltransferase I beta in rat heart. J Biol Chem 276:1026–1033
Olson EN, Nordheim A (2010) Linking actin dynamics and gene transcription to drive cellular motile functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 11:353–365
Peng YB, Guan HP, Fan B, Zhao SH, Xu XW, Li K, Zhu MJ, Yerle M, Liu B (2008) Molecular characterization and expression pattern of the porcine STARS, a striated muscle-specific expressed gene. Biochem Genet 46:644–651
Pollanen E, Fey V, Tormakangas T, Ronkainen PH, Taaffe DR, Takala T, Koskinen S, Cheng S, Puolakka J, Kujala UM, Suominen H, Sipila S, Kovanen V (2010) Power training and postmenopausal hormone therapy affect transcriptional control of specific co-regulated gene clusters in skeletal muscle. Age 32:347–363
Rivera VM, Miranti CK, Misra RP, Ginty DD, Chen RH, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1993) A growth factor-induced kinase phosphorylates the serum response factor at a site that regulates its DNA-binding activity. Mol Cell Biol 13:6260–6273
Rose AJ, Frosig C, Kiens B, Wojtaszewski JF, Richter EA (2007) Effect of endurance exercise training on Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II expression and signalling in skeletal muscle of humans. J Physiol 583:785–795
Russell AP (2010) Molecular regulation of skeletal muscle mass. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:378–384
Schreiber SN, Emter R, Hock MB, Knutti D, Cardenas J, Podvinec M, Oakeley EJ, Kralli A (2004) The estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) functions in PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha)-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6472–6477
Sipila S, Taaffe DR, Cheng S, Puolakka J, Toivanen J, Suominen H (2001) Effects of hormone replacement therapy and high-impact physical exercise on skeletal muscle in post-menopausal women: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Clin Sci (Lond) 101:147–157
Troidl K, Ruding I, Cai WJ, Mucke Y, Grossekettler L, Piotrowska I, Apfelbeck H, Schierling W, Volger OL, Horrevoets AJ, Grote K, Schmitz-Rixen T, Schaper W, Troidl C (2009) Actin-binding rho activating protein (Abra) is essential for fluid shear stress-induced arteriogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:2093–2101
Vissing K, Brink M, Lonbro S, Sorensen H, Overgaard K, Danborg K, Mortensen J, Elstrom O, Rosenhoj N, Ringgaard S, Andersen JL, Aagaard P (2008) Muscle adaptations to plyometric vs. resistance training in untrained young men. J Strength Cond Res 22:1799–1810
Vissing K, McGee SL, Farup J, Kjolhede T, Vendelbo MH, Jessen N (2011) Differentiated mTOR but not AMPK signaling after strength vs endurance exercise in training-accustomed individuals. Scand J Med Sci Sports (in press)
Vissing K, McGee SL, Roepstorff C, Schjerling P, Hargreaves M, Kiens B (2008) Effect of sex differences on human MEF2 regulation during endurance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:E408–415
Wallace MA, Hock MB, Hazen BC, Kralli A, Snow RJ, Russell AP (2011) Striated muscle activator of Rho signalling (STARS) is a PGC-1alpha/oestrogen-related receptor-alpha target gene and is upregulated in human skeletal muscle after endurance exercise. J Physiol 589:2027–2039
Yan Z, Lira VA, Greene NP (2012) Exercise training-induced regulation of mitochondrial quality. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 40:159–164
Acknowledgments
Séverine Lamon was supported by an Alfred Deakin postdoctoral fellowship from Deakin University. Kristian Vissing was supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
Conflict of interest
We state that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamon, S., Wallace, M.A., Stefanetti, R.J. et al. Regulation of the STARS signaling pathway in response to endurance and resistance exercise and training. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 1317–1325 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1265-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1265-5