Abstract
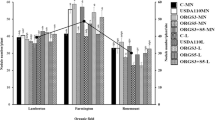
Low effectiveness of native strains remains a limitation to soybean productivity in sub-Saharan Africa; while in other countries commercial inoculants are produced that provide effective strains that stimulate N fixation and growth. An experiment was set up to evaluate the response of a dual purpose promiscuous soybean variety (TGx1740-2F) and a non-promiscuous variety (Nyala) to commercial rhizobium inoculants in soils from central and coastal Kenya. Highest nodulation was observed in some of the treatments with commercial inoculants applied with nodule weights of 4.5 and 1.0 g plant−1 for TGx1740-2F and Nyala, respectively. Average biomass yields of TGx1740-2F (16 g plant−1) were twice as large as of Nyala (7.5 g plant−1) at the podding stage. Nitrogen fixation was higher in TGx1740-2F than in Nyala, and positively affected by a number of commercial inoculants with more than 50% N derived from the atmosphere. Nodule occupancy was 100% on both soybean varieties, indicating that the commercial strains were extremely infective in both of the tested soils. These results showed that commercial strains can be used to inoculate promiscuous soybean and enhance N fixation and yield.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abaidoo RC, Keyser HH, Singleton PW, Dashiell KE, Sanginga N (2007) Population size, distribution and symbiotic characteristics of indigenous Bradyrhizobium spp. that nodulate TGx soybean genotypes in Africa. Appl Soil Ecol 35:57–67
Food and Agricultural Organisation (2006) World reference base for soil resources, a framework for international classification, correlation and communication. 2nd Edition. Rome, Italy
Alves RBJ, Boddey MR, Urquiaga S (2003) The success of BNF in soybean in Brazil. Plant Soil 252:1–9
Barcellos GF, Batista JSS, Menna P, Hungria M (2009) Genetic differences between Bradyrhizobium japonicum variant strains contrasting in N2-fixation efficiency revealed by representational difference analysis. Arch Microbiol 191:113–122
Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE (2005) Bacteria/plant growth-promotion. In: Hillel D (ed) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment, vol. 1. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 103–115
Bizarro MJ, Giongo A, Vargas KL, Roesch LFW, Gano KA, de Sá ELS, Passaglia LMP, Selbac PA (2011) Genetic variability of soybean bradyrhizobia populations under different soil managements. Biol Fert Soils 47:357–362
Boddey RM, Peoples MB, Palmer B, Dart PJ (2000) Use of the 15 N natural abundance technique to quantify biological nitrogen fixation by woody perennials. Nutr Cycl Agroecosy 57:235–270
Bremer E, Van Kessel C, Nelson L, Rennie RJ, Rennie DA (1990) Selection of Rhizobium leguminosarum strains for lentil (Lens culinaris) under growth room and field conditions. Plant Soil 121:47–56
Carsky RJ, Abaidoo R, Dashiel KE, Sanginga N (1997) Effect of soybean on subsequent maize grain yield in Guinea Savannah of West Africa. Afr Crop Sci J 5(416):31–39
Ferreira MC, Hungria MH (2002) Recovery of soybean inoculant strains from uncropped soils in Brazil. Field Crops Res 79:139–152
Galli-Terasawa LV, Glienke-Blanco C, Hungria M (2003) Diversity of soybean rhizobial population adapted to a Cerrados soil. World J Microb Biotechnol 19:933–939
Giller KE (2001) Nitrogen fixation in tropical cropping systems, 2nd edn. CABI, Wallingford, p 423
Guimarães AP, de Morais RF, Urquiaga S, Boddey RM, Alves BJR (2008) Bradyrhizobium strain and the 15 N natural Abundance quantification of biological N2 fixation in soybean. Sci Agric (Piracicaba, Braz) 65:516–524
Herridge DF, Peoples MB, Boddey RM (2008) Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311:1–18
Herrmann L, Atieno OM, Okalebo J, Lesueur D (2010) Molecular identification of the strains in commercial products for improving agriculture in Africa. Poster presented at the 13th international symposium on microbial ecology. 22nd–27th August 2010. Seattle, USA
Houngnandan PR, Yemadje GH, Oikeh SO, Djidohokpin CF, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O (2008) Improved estimation of biological nitrogen fixation of soybean cultivars (Glycine max L. Merrill) using 15 N natural abundance technique. Biol Fert Soils 45:175–183
Hungria M, Lı’gia MO, Chueire MM, Megı’as M, Lamrabet Y, Probanza A, Guttierrez-Mañero FJ, Campo RJ (2006a) Genetic diversity of indigenous tropical fast-growing rhizobia isolated from soybean nodules. Plant Soil 288:343–356
Hungria M, Campo RJ, Mendes IC, Graham PH (2006b) Contribution of biological nitrogen fixation to the nitrogen nutrition of grain crops in the tropics: the success of soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) in South America. In: Singh RP, Shankar N, Jaiwal PK (eds) Nitrogen nutrition in plant productivity. Studium, Houston, pp 43–93
Hymowitz T (1970) On the domestication of the soybean. Econ Bot 24:408–421
Krasova-Wade T, Ndoye I, Braconnier S, Sarr B, de Lajuide P, Neyra M (2003) Diversity of indigenous bradyrhizobia associated with three cowpea cultivars (Vigna unguiculata L.) (Walp) grown under limited and favourable water conditions in Senegal (West Africa). Afr J Biotechnol 2:13–22
Kueneman EA, Root WR, Dashiell KE, Hohenberg J (1984) Breeding soybean for the tropics capable of nodulating effectively with indigenous Rhizobium spp. Plant Soil 82:387–396
Lata SAK, Tilak KVBR (2000) Biofertilizers to augment soil fertility and crop production. In: Krishna KR (ed) Soil fertility and crop production. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 279–312
Lynch JM (1990) Beneficial interactions between microorganisms and roots. Biotech Adv 8:335–346
Mariotti A, Pierre D, Vedy JC, Brukert S, Guillemot J (1980) The abundance of natural 15 N in the organic matter of soils along an altitudinal gradient (Chablais, Haute Savoie, France). Catena 7:293–300
Matiru VN, Dakora FD (2004) Potential use of rhizobial bacteria as promoters of plant growth for increased yield in landraces of African cereal crops. Afr J Biotechnol 3:1–7
Melchiorre M, de Luca MJ, Anta GG, Suarez P, Lopez C, Lascano R, Racca RW (2011) Evaluation of bradyrhizobia strains isolated from field-grown soybean plants in Argentina as improved inoculants. Biol Fert Soils 47:81–89
Morse WJ (1950) History of soybean production. In: Markley KL (ed) Soybeans and soybean products. Interscience Publ. Inc., New York, pp 3–59
Mpepereki S, Javaheri F, Davis P, Giller KE (2000) Soybeans and sustainable agriculture: promiscuous soybeans in southern Africa. Field Crops Res 65:137–149
Musiyima K, Mpepereki S, Giller KE (2005) Symbiotic effectiveness and host ranges of indigenous nodulating promiscuous soybean varieties in Zimbabwean soils. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1169–1176
Navarro E, Simonet P, Normand P, Bardin R (1992) Characterization of natural population of Nitrobacter spp using PCR-RFLP analysis of ribosomal intergenic spacer. Arch Microbiol 157:107–115
Okereke GU, Eaglesham ARJ (1993) Nodulation and nitrogen fixation by 79 promiscuous soybean genotypes in soil in eastern Nigeria. Agro Afrique 2:113–122
Peoples MB, Brockwel J, Herridge DF, Rochester IJ, Alves BRJ, Urquiaga S, Boddey RM, Dakora FD, Bhattarai S, Maskey SL, Sampet C, Rerkasem B, Khans DF, Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Jensen BS (2009) The contributions of nitrogen-fixing crop legumes to the productivity of agricultural systems. Symbiosis 48:1–17
Perret X, Staehelin C, Spaink HP (2000) Molecular basis of symbiotic promiscuity. Microbiol Mol Biol R 64:180–201
Ponsonet C, Nesme X (1994) Identification of agrobacterium strains by PCR-RFLP analysis of pTi and chromosomal regions. Arch Microbiol 16:300–309
Rouvier C, Prin Y, Reddel P, Normand P, Simonet P (1996) Genetic diversity among Frankia strains nodulating members of the family Casuarinaceae in Australia revealed by PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis with crushed root nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:979–985
Salvagiotti F, Cassman KG, Specht JE, Walters DT, Weiss A, Dobermann (2008) Nitrogen uptake, fixation and response to fertilizer N in soybean: a review. Field Crops Res 108:1–13
Sanginga N, Abaidoo RC, Dashiell K, Carsky RJ, Okogun JA (1996) Persistence and effectiveness of rhizobia nodulating promiscuous soybeans in moist savanna zones of Nigeria. Appl Soil Ecol 3:215–224
Sanginga N, Dashiell K, Okogun JA, Thottappilly G (1997) Nitrogen fixation and N contribution by promiscuous nodulating soybeans in the southern Guinea savanna of Nigeria. Plant Soil 195:257–266
Sanginga N, Thottappilly G, Dashiell KE (2000) Effectiveness of rhizobia nodulating recent promiscuous soybean selections in the moist savannah of Nigeria. Soil Biol Biochem 32:215–224
Sanginga N, Dashiell K, Diels J, Vanlauwe B, Lyasse O, Carsky RJ, Tarawali S, Asafo-Adjei B, Menkir A, Schulz S, Singh BB, Chikoye D, Keatinge D, Rodomiro O (2003) Sustainable resource management coupled to resilient germplasm to provide new intensive cereal–grain legume–livestock systems in the dry savanna. Agr Ecosyst Environ 100:305–314
SAS Institute Inc (2006) SAS user’s guide: statistics. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Saxena AK, Shende R, Grover M (2006) Interactions among beneficial microorganisms. In: Mukerirji KG, Manoharachary C, Singh J (eds) Microbial activity in the rhizosphere. Springer, Berlin, pp 121–132
Shearer GB, Kohl DH (1986) N2-fixation in field settings: estimations based on natural 15 N abundance. Austr J Plant Physiol 13:699–756
Shearer G, Kohl DH, Chien SH (1978) The 15 N abundance in a wide variety of soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:899–902
Sprent JI (2001) Nodulation in legumes. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Tewari K, Minagawa R, Suganuma T, Fujikake H, Ohtake N, Sueyoshi K, Takahashi Y, Ohyama T, Tsuchida T (2003) Effect of deep placement of slow release nitrogen fertilizers and inoculation of bradyrhizobia on the first cropping of soybean in the field dressed with mountain soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 74:183–189
Thiao M, Neyra M, Isidore E, Sylla S, Lesueur D (2004) Diversity and effectiveness of rhizobium from Gliricidia sepium native to Reunion Island, Kenya and New Caledonia. World J Microb Biot 20:703–709
Walley FL, Clayton GW, Miller PR, Carr PM, Lafond GP (2007) Nitrogen economy of pulse production in the northern great plains. Agron J 99:1710–1718
Wasike VW, Lesueur D, Wachira FN, Mungai NW, Mumera LM, Sanginga N, Mburu HN, Mugadi D, Wango P, Vanlauwe B (2009) Genetic diversity of indigenous Bradyrhizobium nodulating promiscuous soybean [Glycine max (L) Merr.] varieties in Kenya: impact of phosphorus and lime fertilization in two contrasting sites. Plant Soil 322:151–163
Weaver RW, Frederick LR (1974) A new technique for most probable-number counts of rhizobia. Plant Soil 36:219–222
Willems A (2006) The taxonomy of rhizobia: an overview. Plant Soil 287:3–14
Xavier IJ, Holloway G, Leggett M (2004) Development of rhizobial inoculant formulations. Online. Crop Management doi:10.1094/CM-2004-0301-06-RV
Yusuf AA, Abaidoo RC, Iwuafor ENO, Olufajo OO (2008) Genotype effects of cowpea and soybean on nodulation, N2 fixation and N balance in the Northern Guinea savannah of Nigeria. Agron J 7:258–264
Zengeni R, Giller KE (2007) Effectiveness of indigenous soybean rhizobial isolates to fix nitrogen under field conditions of Zimbabwe. Symbiosis 43:129–135
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation through the Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility Institute of CIAT (TSBF-CIAT) project on commercial microbial products. We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of Edwin Mutegi, Phillip Malala, Harrison Mburu, Elias Mwangi, Ruth Mukhongo, and Samuel Mathu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thuita, M., Pypers, P., Herrmann, L. et al. Commercial rhizobial inoculants significantly enhance growth and nitrogen fixation of a promiscuous soybean variety in Kenyan soils. Biol Fertil Soils 48, 87–96 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0611-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0611-z