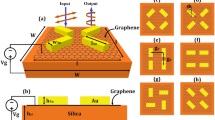
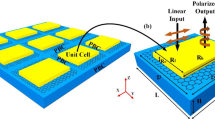
Abstract
We theoretically demonstrate that an electrically tunable polarizer can be obtained using a periodic array of graphene ribbons supported on a dielectric film on top of a thick piece of metal. The polarizing mechanism originates from anisotropic absorption of the graphene ribbons. The results of fullwave numerical simulations reveal that absorption of 0.0075 for one polarization and 0.9986 for another polarization can be obtained at normal incidence in the THz range. For circular incidence polarization, the corresponding polarizing extinction ratio increases to 65 dB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Lajunen, J. Turunen, J. Tervo, Design of polarization gratings for broadband illumination. Opt. Express 13, 3055–3067 (2005)
R. Magnusson, M. Shokooh-Saremi, E.G. Johnson, Guided-mode resonant wave plates. Opt. Lett. 35, 2472–2474 (2010)
D.R. Smith, J.B. Pendry, M.C.K. Wiltshire, Metamaterials and negative refractive index. Science 305, 788–792 (2004)
S. Linden, C. Enkrich, M. Wegener, J. Zhou, T. Koschny, C.M. Soukoulis, Magnetic response of metamaterials at 100 terahertz. Science 306, 1351–1353 (2004)
W.L. Barnes, A. Dereux, T.W. Ebbesen, Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003)
H. Jiaming, Y. Yu, R. Lixin, J. Tao, K.J. Au, C.T. Chan, Z. Lei, Manipulating electromagnetic wave polarizations by anisotropic metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 063908 (2007)
A.V. Rogacheva, V.A. Fedotov, A.S. Schwanecke, N.I. Zheludev, Giant gyrotropy due to electromagnetic-field coupling in a bilayered chiral structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 177401 (2006)
E. Plum, X.X. Liu, V.A. Fedotov, Y. Chen, D.P. Tsai, N.I. Zheludev, Metamaterials: optical activity without chirality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 113902 (2009)
Z.H. Zhu, H. Liu, S.M. Wang, W.M. Ye, X.D. Yuan, S.N. Zhu, Double-resonance nanolaser based on coupled slit-hole resonator structures. Opt. Lett. 35, 754–756 (2010)
R. Gordon, A.G. Brolo, A. McKinnon, A. Rajora, B. Leathem, K.L. Kavanagh, Strong polarization in the optical transmission through elliptical nanohole arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 037401 (2004)
Z.H. Zhu, C.C. Guo, K. Liu, W.M. Ye, X.D. Yuan, B. Yang, T. Ma, Metallic nanofilm half-wave plate based on magnetic plasmon resonance. Opt. Lett. 37, 698–700 (2012)
A. Drezet, C. Genet, T.W. Ebbesen, Miniature plasmonic wave plates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 043902 (2008)
M. Freitag, T. Low, F. Xia, P. Avouris, Photoconductivity of biased grapheme. Nat. Photonics 7, 53–59 (2013)
M. Freitag, T. Low, W. Zhu, H. Yan, F. Xia, P. Avouris, Photocurrent in graphene harnessed by tunable intrinsic plasmons. Nat. Commun. 4, 1951 (2013)
M. Liu, X. Yin, E. Ulin-Avila, B. Geng, T. Zentgraf, L. Ju, F. Wang, X. Zhang, A graphene-based broadband optical modulator. Nature 474, 64–67 (2011)
B. Sensale-Rodriguez, T. Fang, R. Yan, M.M. Kelly, D. Jena, L. Liu, H. (Grace) Xing, Unique prospects for graphene-based terahertz modulators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 113104 (2011)
B. Sensale-Rodriguez, R. Yan, M. Kelly, Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions. Nat. Commun. 3, 780–787 (2012)
S.H. Lee, M. Choi, T–.T. Kim, S. Lee, M. Liu, X. Yin, H.K. Choi, S.S. Lee, C.-G. Choi, S.-Y. Choi, X. Zhang, B. Min, Switching terahertz waves with gate-controlled active graphene metamaterials. Nat. Mat. 11, 936–941 (2012)
A. Andryieuski, A. Lavrinenko, D. Chigrin, Graphene hyperlens for terahertz radiation. Phys. Rev. B 86, 121108(R) (2012)
H. Yan, X. Li, B. Chandra, G. Tulevski, Y. Wu, M. Freitag, W. Zhu, P. Avouris, F. Xia, Tunable infrared plasmonic devices using graphene/insulator stacks. Nat. Nanotech. 7, 330–334 (2012)
A. Fallahi, J. Perruisseau-Carrier, Design of tunable biperiodic graphene metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. B 86, 195408 (2012)
S. Thongrattanasiri, F. Koppens, F. Garc′ıa de Abajo, Complete optical absorption in periodically patterned graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 047401 (2012)
A. Andryieuski, A.V. Lavrinenko, Graphene metamaterials based tunable terahertz absorber: effective surface conductivity approach. Opt. Express 21, 9144–9155 (2013)
R. Alaee, M. Farhat, C. Rockstuhl, F. Lederer, A perfect absorber made of a graphene micro-ribbon metamaterial. Opt. Express 20, 28017–28024 (2012)
B. Sensale-Rodriguez, R. Yan, S. Rafique, M. Zhu, W. Li, X. Liang, D. Gundlach, V. Protasenko, M.M. Kelly, D. Jena, L. Liu, H.G. Xing, Extraordinary control of terahertz beam reflectance in graphene electroabsorption modulators. Nano Lett. 12, 4518–4522 (2012)
A. Nikitin, F. Guinea, F. Garcia-Vidal, L. Martin-Moreno, Surface plasmon enhanced absorption and suppressed transmission in periodic arrays of graphene ribbons. Phys. Rev. B 85, 081405 (2012)
A.Y. Nikitin, F. Guinea, L. Martin-Moreno, Resonant plasmonic effects in periodic graphene antidot arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 151119 (2012)
Q. Bao, H. Zhang, B. Wang, Z. Ni, C.H. Lim, Y. Wang, D.Y. Tang, K.P. Loh, Broadband graphene polarizer. Nat. Photonics 5, 411–415 (2011)
A. Vakil, N. Engheta, Transformation optics using graphene. Science 332(6035), 1291–1294 (2011)
N.K. Emani, T.-F. Chung, X. Ni, A.V. Kildishev, Y.P. Chen, A. Boltasseva, Electrically tunable damping of plasmonic resonances with graphene. Nano Lett. 12, 5202–5206 (2012)
L.A. Falkovsky, S.S. Pershoguba, Optical far-infrared properties of a graphene monolayer and multilayer. Phys. Rev. B 76, 153410 (2007)
T. Søndergaard, J. Beermann, A. Boltasseva, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, Slow plasmon resonant-nanostrip antennas: analysis and demonstration. Phys. Rev. B 77, 011520 (2008)
Z.H. Zhu, Z.H. Han, S.I. Bozhevolnyi, Wide bandwidth polarization-independent optical band-stop filter based on plasmonic nanoantennas. Appl. Phys. A 110, 71–75 (2013)
A.N. Grigorenko, M. Polini, K.S. Novoselov, Graphene plasmonics. Nat. Photonics 6, 749–758 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Key Program for Basic Research of China (No. 2012CB933501), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61177051 and 61205087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z.H., Guo, C.C., Liu, K. et al. Electrically tunable polarizer based on anisotropic absorption of graphene ribbons. Appl. Phys. A 114, 1017–1021 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8269-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8269-7