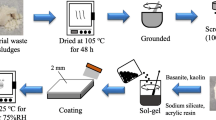
Abstract
It has been found that the preparation of green silica based on agricultural crops preserves environmental sustainability. In this study, rice husk silica (RHS) ash was prepared by burning rice husk (RH) at different temperatures (400 and 1200 °C). Both types of green RHS ash additives were blended with polysulfone dope, after which membranes were fabricated via phase inversion. The RHS ash that was synthesised at 400 °C (RHS400) had an amorphous structure with strong hydrophilic properties, while the composite membrane containing 3 wt% of RHS400 (A3 membrane) achieved the optimum properties of a dense top, an extended sub-layer of continuous smaller finger-like pores and a bottom layer of macrovoids. A satisfactory mean surface roughness, average pore size (1.90 ± 9.50 × 10−2 µm), porosity (40.66 ± 2.03%) and tensile strength (3.27 ± 0.16 MPa) were also obtained. The contact angle (52.5° ± 3.6°) further proved that this membrane was hydrophilic. The elemental and thermal analyses confirmed the presence of Si and O, which correlated with the 12% residual that was contributed by the silica inside the membrane. The optimum properties of the A3 membrane were an increased PWF (154.04 ± 7.70 L m−2 h−1) with the highest rejection of HA (96.00 ± 4.80%) and a fouling mitigation with the lowest internal resistance (6.79 ± 0.34 × 1012 m−1).
Graphic abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sapawe N, Osman NS, Zakaria MZ, Fikry SASSM, Aris MAM (2018) Synthesis of green silica from agricultural waste by sol–gel method. Mater Today: Proc 5(10):21861–21866
Costa JAS, Paranhos CM (2018) Systematic evaluation of amorphous silica production from rice husk ashes. J Clean Prod 192:688–697
Hubadillah SK, Othman MHD, Harun Z, Ismail A, Rahman MA, Jaafar J (2017) A novel green ceramic hollow fiber membrane (CHFM) derived from rice husk ash as combined adsorbent-separator for efficient heavy metals removal. Ceram Int 43(5):4716–4720
Prasara-A J, Gheewala SH (2017) Sustainable utilization of rice husk ash from power plants: A review. J Clean Prod 167:1020–1028
Suryana R, Iriani Y, Nurosyid F, Fasquelle D (2018) Characteristics of silica rice husk ash from Mojogedang Karanganyar Indonesia. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing, p 012008
Krishnadevi K, Selvaraj V (2017) Development of cyclophosphazene and rice husk ash incorporated epoxy composites for high performance applications. Polym Bull 74(5):1791–1815
Sheykh MJ, Tarmian A, Doosthoseini K (2017) Wear resistance and friction coefficient of nano-SiO2 and ash-filled HDPE/lignocellulosic fiber composites. Polym Bull 74(11):4537–4547
You P, Kamarudin S, Masdar M (2019) Improved performance of sulfonated polyimide composite membranes with rice husk ash as a bio-filler for application in direct methanol fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(3):1857–1866
Pode R (2016) Potential applications of rice husk ash waste from rice husk biomass power plant. Renew Sust Energy Rev 53:1468–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.09.051
Msinjili NS, Schmidt W, Rogge A, Kühne H-C (2017) Performance of rice husk ash blended cementitious systems with added superplasticizers. Cem Concr Comp 83:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2017.07.014
Alshatwi AA, Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS (2015) Biocompatibility assessment of rice husk-derived biogenic silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C-Biomim Supramol Syst 47:8–16
Hubadillah SK, Othman MHD, Ismail AF, Rahman MA, Jaafar J, Iwamoto Y, Honda S, Dzahir MIHM, Yusop MZM (2018) Fabrication of low cost, green silica based ceramic hollow fibre membrane prepared from waste rice husk for water filtration application. Ceram Int 44(9):10498–10509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.067
Jamalludin MR, Harun Z, Hubadillah SK, Basri H, Ismail AF, Othman MHD, Shohur MF, Yunos MZ (2016) Antifouling polysulfone membranes blended with green SiO2 from rice husk ash (RHA) for humic acid separation. Chem Eng Res Des 114:268–279
Kang S-H, Hong S-G, Moon J (2019) The use of rice husk ash as reactive filler in ultra-high performance concrete. Cem Concr Res 115:389–400
Van Tuan N, Ye G, Van Breugel K, Copuroglu O (2011) Hydration and microstructure of ultra high performance concrete incorporating rice husk ash. Cem Concr Res 41(11):1104–1111
Xu W, Lo YT, Ouyang D, Memon SA, Xing F, Wang W, Yuan X (2015) Effect of rice husk ash fineness on porosity and hydration reaction of blended cement paste. Constr Build Mater 89:90–101
Hamid MAA, Chung YT, Rohani R, Junaidi MUM (2019) Miscible-blend polysulfone/polyimide membrane for hydrogen purification from palm oil mill effluent fermentation. Sep Purif Technol 209:598–607
Xu Z, Liao J, Tang H, Li N (2018) Antifouling polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes with pendent sulfonamide groups. J Membr Sci 548:481–489
Kim J-j, Kim K, Choi Y-S, Kang H, Kim DM, Lee J-C (2018) Polysulfone based ultrafiltration membranes with dopamine and nisin moieties showing antifouling and antimicrobial properties. Sep Purif Technol 202:9–20
Zambare RS, Dhopte KB, Patwardhan AV, Nemade PR (2017) Polyamine functionalized graphene oxide polysulfone mixed matrix membranes with improved hydrophilicity and anti-fouling properties. Desalination 403:24–35
Alias SS, Harun Z, Shohur MF (2019) Effect of monovalent and divalent ions in non-solvent coagulation bath-induced phase inversion on the characterization of a porous polysulfone membrane. Polym Bull 76:1–23
Dickhout JM, Moreno J, Biesheuvel P, Boels L, Lammertink RG, de Vos WM (2017) Produced water treatment by membranes: a review from a colloidal perspective. J Colloid Interface Sci 487:523–534
Maurya S, Parashuram K, Singh P, Ray P, Reddy A (2012) Preparation of polysulfone–polyamide thin film composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes and their performance in the treatment of aqueous dye solutions. Desalination 304:11–19
Sharma N, Purkait M (2017) Impact of synthesized amino alcohol plasticizer on the morphology and hydrophilicity of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. J Membr Sci 522:202–215
Song H, Kim C (2013) Fabrication and properties of ultrafiltration membranes composed of polysulfone and poly (1-vinylpyrrolidone) grafted silica nanoparticles. J Membr Sci 444:318–326
Galiano F, Briceño K, Marino T, Molino A, Christensen KV, Figoli A (2018) Advances in biopolymer-based membrane preparation and applications. J Membr Sci 564:562–586
Ochoa NA, Masuelli M, Marchese J (2003) Effect of hydrophilicity on fouling of an emulsified oil wastewater with PVDF/PMMA membranes. J Membr Sci 226(1):203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2003.09.004
Alias SS, Harun Z, Azhar FH, Yusof KN, Jamalludin MR, Hubadillah SK, Basri SN, Al-Harthi MA (2019) Enhancing the performance of a hybrid porous polysulfone membrane impregnated with green Ag/AgO additives derived from the Parkia speciosa. Vacuum 163:301–311
Ahmad RAR, Harun Z, Othman MHD, Basri H, Yunos MZ, Ahmad A, Akhair SHM, Rashid AQA, Azhar FH, Alias SS (2019) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by using fruits extracts of Ananas comosus and its antibacterial activity. Malays J Fundam Appl Sci 15(2):268–273
Yang Y, Zhang H, Wang P, Zheng Q, Li J (2007) The influence of nano-sized TiO2 fillers on the morphologies and properties of PSF UF membrane. J Membr Sci 288(1):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.11.019
Ahmad AL, Majid MA, Ooi BS (2011) Functionalized PSf/SiO2 nanocomposite membrane for oil-in-water emulsion separation. Desalination 268(1):266–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.017
Genne I, Kuypers S, Leysen R (1996) Effect of the addition of ZrO2 to polysulfone based UF membranes. J Membr Sci 113(2):343–350
Cong H, Radosz M, Towler BF, Shen Y (2007) Polymer-inorganic nanocomposite membranes for gas separation. Sep Purif Technol 55(3):281–291
Ai X, Hu X (2004) Study on organic-inorganic hybrid membranes. Prog Chem 16(4):654–659
Ma Y, Shi F, Zhao W, Wu M, Zhang J, Ma J, Gao C (2012) Preparation and characterization of PSf/clay nanocomposite membranes with LiCl as a pore forming additive. Desalination 303:39–47
Jamalludin MR, Harun Z, Hubadillah SK, Basri H, Ismail AF, Othman MHD, Shohur MF, Yunos MZ (2016) Antifouling polysulfone membranes blended with green SiO2 from rice husk ash (RHA) for humic acid separation. Chem Eng Res Des 114:268–279
Soltani N, Bahrami A, Pech-Canul MI, González LA (2015) Review on the physicochemical treatments of rice husk for production of advanced materials. Chem Eng J 264:899–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.056
Almandoz M, Pagliero C, Ochoa N, Marchese J (2015) Composite ceramic membranes from natural aluminosilicates for microfiltration applications. Ceram Int 41(4):5621–5633
Yusof KN, Alias SS, Harun Z, Basri H, Azhar FH (2018) Parkia speciosa as reduction agent in green synthesis silver nanoparticles. Chem Sel 3(31):8881–8885. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201801846
Hu H, Xin JH, Hu H, Chan A, He L (2013) Glutaraldehyde–chitosan and poly (vinyl alcohol) blends, and fluorescence of their nano-silica composite films. Carbohydr Polym 91(1):305–313
Nassibeh M, Nazanin F, Mirabdullah SS, Shabadra R, Gargh S (2015) Synthesis and Chracterization of Folic Acid conjugated ZnO/Silica Core-shell as Cancer Therapeutic and Imaging Agent. Res J Biotechnol 10(3):25–29
Allahbakhsh A, Khodabadi FN, Hosseini FS, Haghighi AH (2017) 3-Aminopropyl-triethoxysilane-functionalized rice husk and rice husk ash reinforced polyamide 6/graphene oxide sustainable nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 94:417–430
Yu L-Y, Xu Z-L, Shen H-M, Yang H (2009) Preparation and characterization of PVDF–SiO2 composite hollow fiber UF membrane by sol–gel method. J Membr Sci 337(1–2):257–265
Deng Z, Nicolas C-H, Guo Y, Giroir-Fendler A, Pera-Titus M (2010) Synthesis and characterization of nanocomposite B-MFI-alumina hollow fibre membranes and application to xylene isomer separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 133(1–3):18–26
Wongchitphimon S, Wang R, Jiraratananon R (2011) Surface modification of polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF–HFP) hollow fiber membrane for membrane gas absorption. J Membr Sci 381(1–2):183–191
Zhu W, Jiang H, Zhang H, Jia S, Liu Y (2018) Effect of TiO2 and CaF2 on the crystallization behavior of Y2O3–Al2O3–SiO2 glass ceramics. Ceram Int 44:6653–6658
Ahmaruzzaman M, Gupta VK (2011) Rice Husk and Its Ash as Low-Cost Adsorbents in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(24):13589–13613. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201477c
Kim I-C, Lee K-H (2004) Effect of poly (ethylene glycol) 200 on the formation of a polyetherimide asymmetric membrane and its performance in aqueous solvent mixture permeation. J Membr Sci 230(1–2):183–188
Khayet M, Matsuura T (2011) Formation of flat sheet phase inversion MD membranes. In: Souhaimi MK, Matsuura T (eds) Membrane distillation: principles and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 41–58
Sadrzadeh M, Bhattacharjee S (2013) Rational design of phase inversion membranes by tailoring thermodynamics and kinetics of casting solution using polymer additives. J Membr Sci 441:31–44
Razali NF, Mohammad AW, Hilal N, Leo CP, Alam J (2013) Optimisation of polyethersulfone/polyaniline blended membranes using response surface methodology approach. Desalination 311:182–191
Yan L, Li YS, Xiang CB, Xianda S (2006) Effect of nano-sized Al2O3-particle addition on PVDF ultrafiltration membrane performance. J Membr Sci 276(1–2):162–167
Alias SS, Harun Z, Latif ISA (2018) Characterization and performance of porous photocatalytic ceramic membranes coated with TiO2 via different dip-coating routes. J Mater Sci 53(16):11534–11552
Ravishankar H, Roddick F, Navaratna D, Jegatheesan V (2018) Preparation, characterisation and critical flux determination of graphene oxide blended polysulfone (PSf) membranes in an MBR system. J Environ Manag 213:168–179
Vatanpour V, Madaeni SS, Rajabi L, Zinadini S, Derakhshan AA (2012) Boehmite nanoparticles as a new nanofiller for preparation of antifouling mixed matrix membranes. J Membr Sci 401:132–143
Xu Z, Zhang J, Shan M, Li Y, Li B, Niu J, Zhou B, Qian X (2014) Organosilane-functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced antifouling and mechanical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 458:1–13
Zhang Y, Jin Z, Shan X, Sunarso J, Cui P (2011) Preparation and characterization of phosphorylated Zr-doped hybrid silica/PSF composite membrane. J Hazard Mater 186(1):390–395
Zhang Y, Liu P (2015) Polysulfone (PSF) composite membrane with micro-reaction locations (MRLs) made by doping sulfated TiO2 deposited on SiO2 nanotubes (STSNs) for cleaning wastewater. J Membr Sci 493:275–284
Krathumkhet N, Vongjitpimol K, Chuesutham T, Changkhamchom S, Phasuksom K, Sirivat A, Wattanakul K (2018) Preparation of sulfonated zeolite ZSM-5/sulfonated polysulfone composite membranes as PEM for direct methanol fuel cell application. Solid State Ion 319:278–284
Liang Z-M, Yin J, Xu H-J (2003) Polyimide/montmorillonite nanocomposites based on thermally stable, rigid-rod aromatic amine modifiers. Polymer 44(5):1391–1399
Noda I, Dowrey AE, Haynes JL, Marcott C (2007) Group frequency assignments for major infrared bands observed in common synthetic polymers. In: Mark JE (ed) Physical properties of polymers handbook. Springer, New York, pp 395–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-69002-5_22
Sezer UA, Ozturk K, Aru B, Demirel GY, Sezer S (2018) A design achieved by coaxial electrospinning of polysulfone and sulfonated polysulfone as a core-shell structure to optimize mechanical strength and hemocompatibility. Surf Interfaces 10:176–187
Mulder J (2012) Basic principles of membrane technology. Springer, Dordrecht
Huang J, Zhang K, Wang K, Xie Z, Ladewig B, Wang H (2012) Fabrication of polyethersulfone-mesoporous silica nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes with antifouling properties. J Membr Sci 423:362–370
Cho J, Amy G, Pellegrino J (2000) Membrane filtration of natural organic matter: factors and mechanisms affecting rejection and flux decline with charged ultrafiltration (UF) membrane. J Membr Sci 164(1):89–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(99)00176-3
Azat S, Korobeinyk A, Moustakas K, Inglezakis V (2019) Sustainable production of pure silica from rice husk waste in Kazakhstan. J Clean Prod 217:352–359
Liu F, Ma B-R, Zhou D, Xiang Y-h, Xue L-x (2014) Breaking through tradeoff of Polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by zeolite 4A. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 186:113–120
Momeni S, Pakizeh M (2013) Preparation, characterization and gas permeation study of PSf/MgO nanocomposite membrane. Braz J Chem Eng 30(3):589–597
Raabe J, de Souza Fonseca A, Bufalino L, Ribeiro C, Martins MA, Marconcini JM, Tonoli GHD (2014) Evaluation of reaction factors for deposition of silica (SiO2) nanoparticles on cellulose fibers. Carbohydr Polym 114:424–431
Arsuaga JM, Sotto A, del Rosario G, Martínez A, Molina S, Teli SB, de Abajo J (2013) Influence of the type, size, and distribution of metal oxide particles on the properties of nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 428:131–141
Yunos MZ, Harun Z, Basri H, Ismail AF (2012) Effects of water as non-solvent additive on performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. In: Advanced materials research. Trans Tech Publications, Zurich, pp 46–50
Zhang Z, An Q, Liu T, Zhou Y, Qian J, Gao C (2011) Fabrication of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes of a density gradient cross section with good anti-pressure stability and relatively high water flux. Desalination 269(1–3):239–248
Zangeneh H, Zinatizadeh A, Habibi M, Akia M, Isa MH (2015) Photocatalytic oxidation of organic dyes and pollutants in wastewater using different modified titanium dioxides: A comparative review. J Ind Eng Chem 26:1–36
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Centre (AMMC), Institute Integrated Engineering, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, under the Post Doc Grant (D005), Transdisciplinary Research Grant Scheme (TRGS Vot T001) and Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alias, S.S., Harun, Z., Manoh, N. et al. Effects of temperature on rice husk silica ash additive for fouling mitigation by polysulfone–RHS ash mixed-matrix composite membranes. Polym. Bull. 77, 4043–4075 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02950-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02950-5