Abstract
Introduction
Interventional radiology (IR) plays a vital role in modern medicine, with increasing demand for services, but with a shortage of experienced interventionalists. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of a recently introduced IR curriculum on perception, knowledge, and interest of medical students regarding various aspects of IR.
Methods
In 2014, an anonymous web-based questionnaire was sent to 309 4th year medical students in a single institution within an EU country, both before and after delivery of a 10-h IR teaching curriculum.
Results
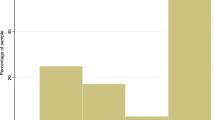
Seventy-six percent (236/309) of the respondents participated in the pre-IR module survey, while 50 % (157/309) responded to the post-IR module survey. While 62 % (147/236) of the respondents reported poor or no knowledge of IR compared to other medical disciplines in the pre-IR module survey, this decreased to 17 % (27/157) in the post-IR module survey. The correct responses regarding knowledge of selected IR procedures improved from 70 to 94 % for venous access, 78 to 99 % for uterine fibroid embolization, 75 to 97 % for GI bleeding embolization, 60 to 92 % for trauma embolization, 71 to 92 % for tumor ablation, and 81 to 94 % for angioplasty and stenting in peripheral arterial disease. With regard to knowledge of IR clinical roles, responses improved from 42 to 59 % for outpatient clinic review of patients and having inpatient beds, 63–76 % for direct patient consultation, and 43–60 % for having regular ward rounds. The number of students who would consider a career in IR increased from 60 to 73 %.
Conclusion
Delivering an undergraduate IR curriculum increased the knowledge and understanding of various aspects of IR and also the general enthusiasm for pursuing this specialty as a future career choice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorfman GS. The 2002 Dr. Charles T. Dotter lecture: revolution, evolution, or extinction—a report of an imaginary conversation among Dotter, Darwin, and a few selected revolutionaries. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(9):869–78.
Adam A. The 2006 Charles T. Dotter lecture: interventional radiology—veni, vidi, vanished? J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17(9):1399–403.
Sunshine JH, Cypel YS, Schepps B. Diagnostic radiologists in 2000: basic characteristics, practices, and issues related to the radiologist shortage. Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(2):291–301.
Leong S, Keeling AN, Lee MJ. A survey of interventional radiology awareness among final-year medical students in a European country. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2009;32(4):623–9.
Ghatan CE, Kuo WT, Hofmann LV, Kothary N. Making the case for early medical student education in interventional radiology: a survey of 2nd-year students in a single US institution. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(4):549–53.
Nissim L, Krupinski E, Hunter T, Taljanovic M. Exposure to, understanding of, and interest in interventional radiology in American medical students. Acad Radiol. 2013;20(4):493–9.
O’Malley L, Athreya S. Awareness and level of knowledge of interventional radiology among medical students at a Canadian institution. Acad Radiol. 2012;19(7):894–901.
(CIRSE) CaIRSoE. Interventional radiology curriculum for medical students 2012. http://www.cirse.org/files/files/Publications/CIRSE_IR_Curriculum_for_Medical_Students.pdf. Accessed 01 Aug 2015.
(BSIR) BSoIR. Defining and developing the interventional radiology workforce: British Society of Interventional Radiology; 2013. www.bsir.org/static/uploads/resources/Work_Force_Development_1_7210413_proofedv9.pdf. Accessed 01 Aug 2015.
(BSIR) BSoIR. Provision of interventional radiology services: British Society of Interventional Radiology; 2013. https://www.rcr.ac.uk/sites/default/files/publication/BFCR(14)12_POIR.pdf.
Levin DC, Abrams HL, Castaneda-Zuniga WR, Fellows KE, Grollman J Jr, Mitchell WA, et al. Lessons from history: Why radiologists lost coronary angiography and what can be done to prevent future similar losses. Invest Radiol. 1994;29(4):480–4.
Commander CW, Pabon-Ramos WM, Isaacson AJ, Yu H, Burke CT, Dixon RG. Assessing medical students’ knowledge of IR at two american medical schools. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(11):1801–7.
Branstetter BF IV, Faix LE, Humphrey AL, Schumann JB. Preclinical medical student training in radiology: the effect of early exposure. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(1):W9–14.
Donnelly LF, Racadio JM, Strife JL. Exposure of first-year medical students to a pediatric radiology research program: is there an influence on career choice? Pediatr Radiol. 2007;37(9):876–8.
Branstetter BF, Humphrey AL, Schumann JB. The long-term impact of preclinical education on medical students’ opinions about radiology. Acad Radiol. 2008;15(10):1331–9.
Singh N, Causey W, Brounts L, Clouse WD, Curry T, Andersen C. Vascular surgery knowledge and exposure obtained during medical school and the potential impact on career decisions. J Vasc Surg. 2010;51(1):252–8.
Malikova M, Doros G, Joglar F, Rybin D, Petros J, Farber A. A third-year surgery clerkship with extensive exposure to vascular surgery improves knowledge about vascular disease and the role of vascular surgeons in its management. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;44:361–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
None.
Informed Consent
None.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaikh, M., Shaygi, B., Asadi, H. et al. The Introduction of an Undergraduate Interventional Radiology (IR) Curriculum: Impact on Medical Student Knowledge and Interest in IR. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 514–521 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1215-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1215-z