Abstract
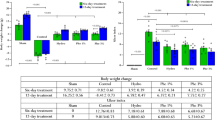
Clinical studies have suggested that treatment with the prostaglandin E1 analog, misoprostol, leads to significant healing of ulcers in patients taking regular nonsteroidal antiinflammatory therapy. This study aimed to investigate mechanisms involved in this healing using a rat model. Gastric ulcers were induced by application of acetic acid using a standard technique. Rats were treated with 200 mg/kg aspirin, 100 µg/kg misoprostol, a combination of both treatments, or methylcellulose vehicle for up to two weeks, starting two days after ulcer induction. Ulcers were assessed by macroscopic measurements of area and by quantitative histological measurements. Aspirin delayed ulcer healing compared with controls, while misoprostol significantly reversed this effect. Quantitative histology revealed that misoprostol cotreatment significantly increased mucosal regeneration compared with aspirin treatment alone. However, misoprostol did not reverse the effects of aspirin on an index of wound contraction. We conclude that treatment with misoprostol significantly reverses the delayed healing effect of aspirin, and this may occur via an effect on epithelial regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaszewski R, Calzada R, Dhar R: Persistence of gastric ulcers caused by plain aspirin or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents in patients treated with a combination of cimetidine, antacids, and enteric-coated aspirin. Dig Dis Sci 34:1361–1364, 1989
Graham DY, Agrawal NM, Roth SH: Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcer with misoprostol: Multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2:1277–1280, 1988
Armstrong CP, Blower AL: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and life threatening complications of peptic ulceration. Gut 28:527–532, 1987
Geczy M, Peltier L, Wolbach R: Naproxen tolerability in the elderly: A summary report. J Rheumatol 14:348–354, 1987
Roth S, Agrawal N, Mahowald M, Montoya H, Robbins D, Miller S, Nutting E, Woods E, Crager M, Nissen C, Swabb E: Misoprostol heals gastroduodenal injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving aspirin. Arch Intern Med 149:775–779, 1989
Tarnawski A, Hollander D, Stachura J, Krause WJ, Eltorai M, Dabros W, Gergely H: Vascular and microvascular changes—key factors in the development of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats. J Clin Gastroenterol 12:S148–157, 1990
Tsuchida T, Tsukamoto Y, Segawa K, Goto H, Hase S: Effects of cimetidine and omeprazole on angiogenesis in granulation tissue of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Digestion 47:8–14, 1990
Helpap B, Hattori T, Gedigk P: Repair of gastric ulcer. A cell kinetic study, Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 392:159–170, 1981
Helander HF: Morphological studies on the margin of gastric corpus wounds in the rat. J Submicrosc Cytol 15:627–643, 1983
Ogihara Y, Fuse Y, Okabe S: Effects of indomethacin and prednisolone on connective tissue at the base on acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats.In Mechanisms of Injury, Protection and Repair in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. A Garner, PE O'Brien (eds). John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1991, pp 455–465
Hirose H, Takeuchi K, Okabe S: Effect of indomethacin on gastric mucosal blood flow around acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats. Gastroenterology 100:1259–1265, 1991
Szabo S, Hollander D: Pathways of gastrointestinal protection and repair: Mechanisms of action of sucralfate. Am J Med 86:23–31, 1989
Wang JY, Yamasaki S, Takeuchi K, Okabe S: Delayed healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers in rats by indomethacin. Gastroenterology 96:393–402, 1989
Levi S, Goodlad RA, Lee CY, Stamp G, Walport MJ, Wright NA, Hodgson HJF: Inhibitory effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on mucosal cell proliferation associated with gastric ulcer healing. Lancet 1:840–843, 1990
Konturek SJ, Stachura J, Radecki T, Drozdowicz D, Brzozowski T: Cytoprotective and ulcer healing properties of prostaglandin E2, colloidal bismuth and sucralfate in rats. Digestion 38:103–113, 1987
Okabe S, Takeuchi K, Honda K, Takagi K: Effects of acetylsalicyclic acid (ASA), ASA plusl-glutamine andl-glutamine on healing of chronic gastric ulcer in the rat. Digestion 14:85–88, 1976
Bauer RF, Bianchi RG, Casler J, Goldstin B: Comparative mucosal protective properties of misoprostol, cimetidine, and sucralfate. Dig Dis Sci 31:81S-85S, 1986
Tabayashi T: Production of chronic ulcer in rats by clamping-cortisone method and histological findings. J Gastroenterol 62:1533–1547, 1965
Umehara S, Ito H, Tabayashi T, Hayashi T, Ishii A, Kawasaki H, Imai K, Hori H: Studies of an experimental chronic gastric ulcer induced by the clamping cortisone method in rats.In Peptic Ulcer. CJ Pfieffer (ed). Munksgaard, Copenhagen, 1971, pp 118–137
Nakumura M, Oda M, Inoue J, Nishizaki Y, Tsuchiya M: Roles of the muscularis mucosae and myofibroblasts in the healing process of acetic acid-induced ulcer. J Clin Gastroenterol 12:S39-S47, 1990
Szelenyi I, Engler H, Herzog P, Postius S, Vergin H, Holtermuller KH: Influence of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory compounds on healing of chronic gastric ulcers in rats. Agents Actions 12:180–182, 1982
Uchida M, Kawano O, Misaki N, Irino O: Healing process of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer and gastric mucosal prostaglandin E generation level in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 50:366–368, 1989
Uchida M, Kawano O, Misaki N, Saitoh K, Irino O: Healing of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer and gastric mucosal prostaglandin I2 level in rats. Dig Dis Sci 35:80–85, 1990
Eastwood GL, Quimby GF: Effect of chronic aspirin ingestion on epithelial proliferation in rat fundus, antrum, and duodenum. Gastroenterology 82:852–856, 1982
Szelenyi I, Postius S, Engler H: Prostaglandin content in the rat gastric mucosa during healing of chronic ulcers induced by aceteic acid. Agents Actions 13:207–209, 1983
Rowe PH, Starlinger MJ, Kasdon E, Marrone G, Silen W: Effect of simulated systemic administration of aspirin, salicylate and indomethacin on amphibian gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 90:559–569, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant from the Alfred Hospital Medical Research Advisory Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penney, A.G., Andrews, F.J. & O'Brien, P.E. Effects of misoprostol on delayed ulcer healing induced by aspirin. Digest Dis Sci 39, 934–939 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087540
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087540