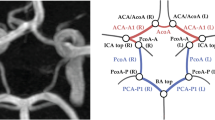
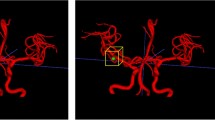
Abstract
Automatically labeling intracranial arteries (ICA) with their anatomical names is beneficial for feature extraction and detailed analysis of intracranial vascular structures. There are significant variations in the ICA due to natural and pathological causes, making it challenging for automated labeling. However, the existing public dataset for evaluation of anatomical labeling is limited. We construct a comprehensive dataset with 729 Magnetic Resonance Angiography scans and propose a Graph Neural Network (GNN) method to label arteries by classifying types of nodes and edges in an attributed relational graph. In addition, a hierarchical refinement framework is developed for further improving the GNN outputs to incorporate structural and relational knowledge about the ICA. Our method achieved a node labeling accuracy of 97.5%, and 63.8% of scans were correctly labeled for all Circle of Willis nodes, on a testing set of 105 scans with both healthy and diseased subjects. This is a significant improvement over available state-of-the-art methods. Automatic artery labeling is promising to minimize manual effort in characterizing the complicated ICA networks and provides valuable information for the identification of geometric risk factors of vascular disease. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/clatfd/GNN-ART-LABEL.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kayembe, K.N., Sasahara, M., Hazama, F.: Cerebral aneurysms and variations in the circle of Willis. Stroke 15, 846–850 (1984)
Alpers, B.J., Berry, R.G., Paddison, R.M.: Anatomical studies of the circle of willis in normal brain. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry. 81, 409–418 (1959)
Chen, L., et al.: Quantitative intracranial vasculature assessment to detect dementia using the intra-Cranial Artery Feature Extraction (iCafe) technique. In: Proc. Annu. Meet. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. Palais des congrès Montréal, Montréal, QC, Canada May, pp. 11–16 (2019)
Alpers, B.J., Berry, R.G.: Circle of willis in cerebral vascular disorders. Anat. Struct. Arch. Neurol. 8, 398–402 (1963)
Ustabaşıoğlu, F.E.: Magnetic resonance angiographic evaluation of anatomic variations of the circle of willis. Med. J. Haydarpaşa Numune Training Res. Hosp. 59, 291–295 (2018)
Bullitt, E., et al.: Vessel tortuosity and brain tumor malignancy: a blinded study. Acad. Radiol. 12, 1232–1240 (2005)
Takemura, A., Suzuki, M., Harauchi, H., Okumura, Y.: Automatic anatomical labeling method of cerebral arteries in MR-angiography data set. Japanese J. Med. Phys. 26, 187–198 (2006)
Dunås, T., Wåhlin, A., Ambarki, K., Zarrinkoob, L., Malm, J., Eklund, A.: A stereotactic probabilistic atlas for the major cerebral arteries. Neuroinformatics 15(1), 101–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9320-y
Dunås, T., et al.: Automatic labeling of cerebral arteries in magnetic resonance angiography. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys., Biol. Med. 29(1), 39–47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-015-0512-5
Bilgel, M., Roy, S., Carass, A., Nyquist, P.A., Prince, J.L.: Automated anatomical labeling of the cerebral arteries using belief propagation. Med. Imaging 2013 Image Process. 8669, 866918 (2013)
Bogunović, H., Pozo, J.M., Cárdenes, R., Frangi, A.F.: Automatic identification of internal carotid artery from 3DRA images. In: 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, pp. 5343–5346. IEEE (2010)
Bogunović, H., Pozo, J.M., Cárdenes, R., Frangi, A.F.: Anatomical labeling of the anterior circulation of the circle of willis using maximum a posteriori classification. In: Fichtinger, G., Martel, A., Peters, T. (eds.) MICCAI 2011. LNCS, vol. 6893, pp. 330–337. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23626-6_41
Bogunović, H., Pozo, J.M., Cardenes, R., Roman, L.S., Frangi, A.F.: Anatomical labeling of the circle of willis using maximum a posteriori probability estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 32, 1587–1599 (2013)
Robben, D., et al.: Simultaneous segmentation and anatomical labeling of the cerebral vasculature. Med. Image Anal. 32, 201–215 (2016)
Zhou, J., et al.: Graph neural networks: a review of methods and applications, pp. 1–22 (2018)
Battaglia, P.W., et al.: Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and graph networks. arXiv: 1806.01261, pp. 1–40 (2018)
Zhai, Z., et al.: Linking convolutional neural networks with graph convolutional networks: application in pulmonary artery-vein separation. In: Zhang, D., Zhou, L., Jie, B., Liu, M. (eds.) GLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11849, pp. 36–43. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35817-4_5
Wolterink, J.M., Leiner, T., Išgum, I.: Graph convolutional networks for coronary artery segmentation in cardiac CT angiography. In: Zhang, D., Zhou, L., Jie, B., Liu, M. (eds.) GLMI 2019. LNCS, vol. 11849, pp. 62–69. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35817-4_8
Chen, L., et al.: Development of a quantitative intracranial vascular features extraction tool on 3D MRA using semiautomated open-curve active contour vessel tracing. Magn. Reson. Med. 79, 3229–3238 (2018)
Chen, L., et al.: Quantification of morphometry and intensity features of intracranial arteries from 3D TOF MRA using the intracranial artery feature extraction (iCafe): a reproducibility study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 57, 293–302 (2018)
Gilmer, J., Schoenholz, S.S., Riley, P.F., Vinyals, O., Dahl, G.E.: Neural message passing for quantum chemistry. arXiv:1704.01212v2, (2017)
Pinto, A., Alves, V., Silva, C.A.: Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35, 1240–1251 (2016)
Chen, L., et al.: Quantitative assessment of the intracranial vasculature in an older adult population using iCafe (intraCranial Artery Feature Extraction). Neurobiol. Aging 79, 59–65 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Health under grant R01-NS092207. We are grateful for the collaborators who provided the datasets for this study, including the CROP and BRAVE investigators, and researchers from the University of Arizona, USA, Beijing Anzhen hospital, China, and Tsinghua University, China and the public data from The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (distributed by the MIDAS Data Server at Kitware Inc.). We acknowledge NIVIDIA for providing the GPU used for training the neural network model.
Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/clatfd/GNN-ART-LABEL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chen, L., Hatsukami, T., Hwang, JN., Yuan, C. (2020). Automated Intracranial Artery Labeling Using a Graph Neural Network and Hierarchical Refinement. In: Martel, A.L., et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2020. MICCAI 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12266. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59725-2_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-59724-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-59725-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)